In the glycolysis pathway, glucose is partially oxidized
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm and involves ten enzyme-
To help you understand the process without getting into extensive detail, we will focus on two consecutive reactions in this pathway (Steps 6 and 7 in Figure 9.5).
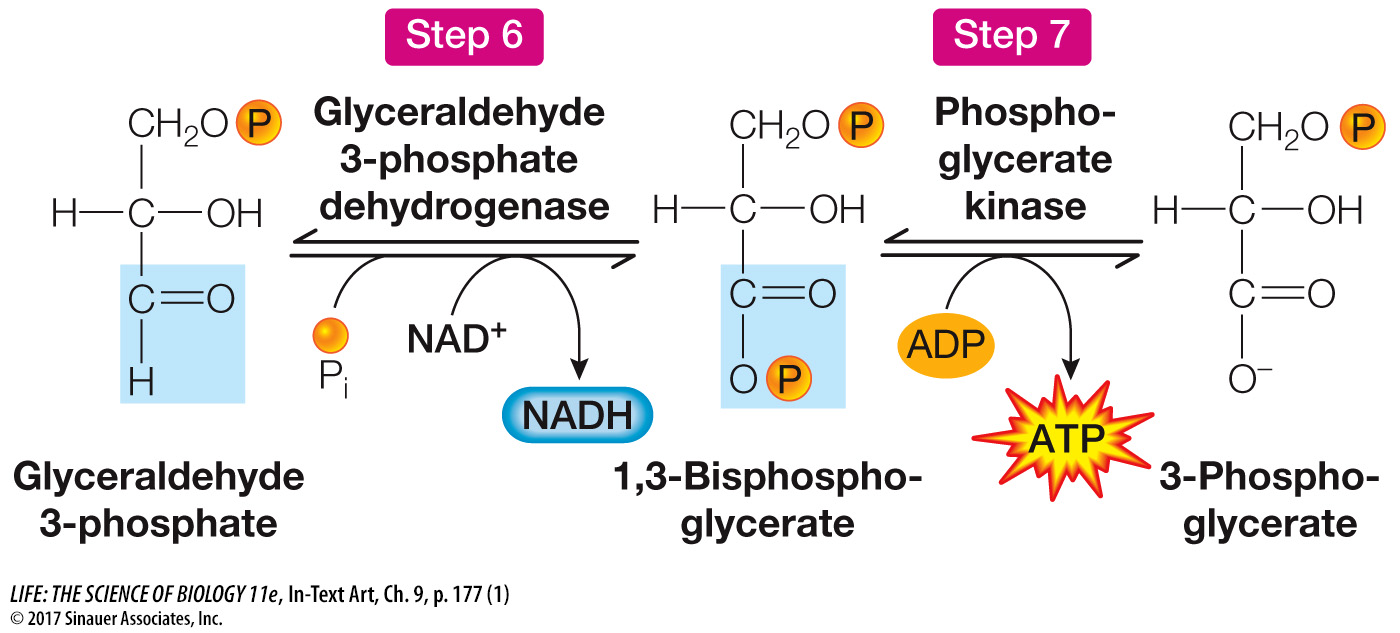
Steps 6 and 7 are examples of two types of reactions that occur repeatedly in glycolysis and in many other metabolic pathways:
Oxidation–
reduction : The first reaction is exergonic—more than 50 kcal/mol of energy are released in the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate. (Look at the bottom carbon atom, where an H is replaced by an O.) The energy is trapped via the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. Substrate-
level phosphorylation : The second reaction in this series is also exergonic, but in this case less energy is released, sufficient to transfer a phosphate directly from the substrate to ADP, forming ATP.
The end product of glycolysis, pyruvate, is somewhat more oxidized than glucose. In the presence of O2, further oxidation can occur. In prokaryotes these subsequent reactions take place in the cytoplasm, but in eukaryotes they take place in the mitochondrial matrix.
To summarize:
The initial steps of glycolysis use the energy of hydrolysis of two ATP molecules per glucose molecule.
The remaining steps produce four ATP molecules per glucose molecule, so the net production of ATP is two molecules.
Glycolysis produces two molecules of NADH.
If O2 is present, glycolysis is followed by the three stages of cellular respiration: pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the respiratory chain/ATP synthesis.