Specific protein–DNA interactions underlie binding
As we have seen, transcription factors with specific DNA-
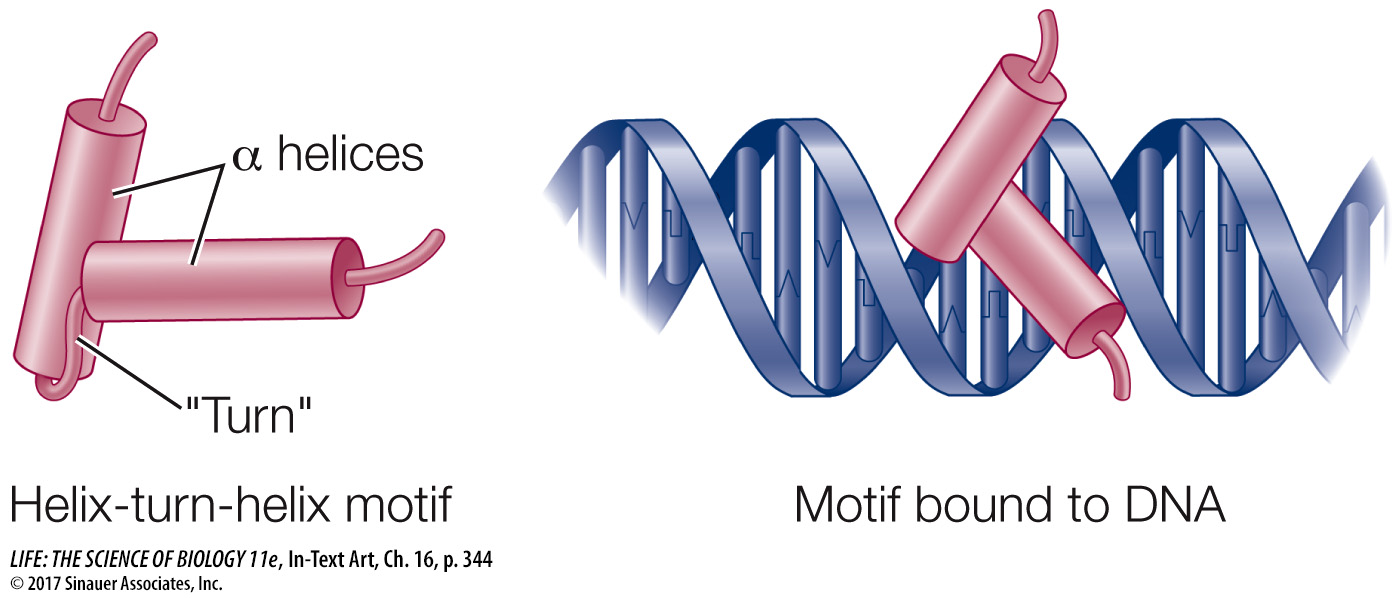
*connect the concepts The structure and chemistry of DNA are key to its recognition by proteins. How the shapes and chemical structures of proteins allow them to bind noncovalently to other molecules is covered in Key Concept 3.2.
How does a protein recognize a sequence in DNA? As you learned in Key Concept 3.2, the complementary bases in DNA not only form hydrogen bonds with each other, but also can form additional hydrogen bonds with proteins, particularly at points exposed in the major and minor grooves. In this way, an intact DNA double helix can be recognized by a protein motif whose structure:
fits into the major or minor groove;
has amino acids that can project into the interior of the double helix; and
has amino acids that can form hydrogen bonds with the interior bases.