recap
23.3 recap
Lateral gene transfer can result in the transfer of genetic functions between distantly related species. Gene duplication can lead to the evolution of new functions. Some highly repeated genes undergo concerted evolution, which maintains uniform functionality.
learning outcomes
You should be able to:
Describe how genes can move among different lineages, especially among bacteria, via lateral gene transfer.
Use a phylogenetic tree of a gene family to infer gene duplications across the history of a group of species.
Describe how a duplicated gene provides opportunities for the evolution of new functions.
Diagram and distinguish the two primary processes that produce concerted evolution.
1.
What are some of the potential advantages of lateral gene transfer to the organisms that gain new genes by this mechanism?
New genes can add new functions. For example, lateral transfer of a gene that confers antibiotic resistance would provide a huge advantage to bacteria that are subjected to antibiotics.
2.
Consider the following tree of a gene family sampled from the complete genomes of humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas. All members of the gene family are included in the tree. How many gene duplications and losses are likely to have occurred in the history of this gene family? Diagram their locations on the tree.
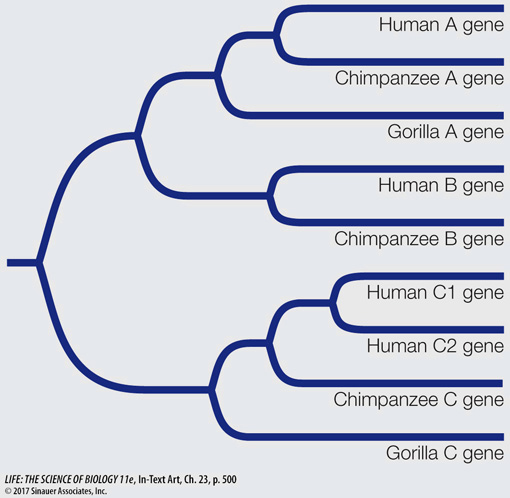
The tree indicates that three gene duplication events and one gene loss occurred. In the tree below, the three gene duplication events are marked in blue, and the gene loss is marked in red. Gene duplication event 1 marked the duplication between gene C and the ancestor of genes A and B. Gene duplication event 2 resulted in genes A and B. Gene duplication event 3 happened in the ancestor of humans and resulted in human genes C1 and C2. Finally, there was a loss of gene B in gorillas (event 4 on the tree). 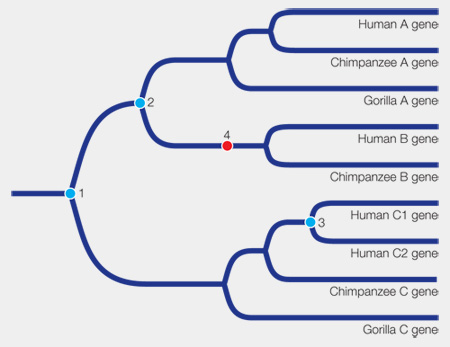
3.
Why is gene duplication considered important for longterm evolutionary change?
Gene duplication provides the raw material for much of evolution. A duplicated gene is free to diverge from its ancestral function, since the original copy of the gene can continue to provide the original function.
4.
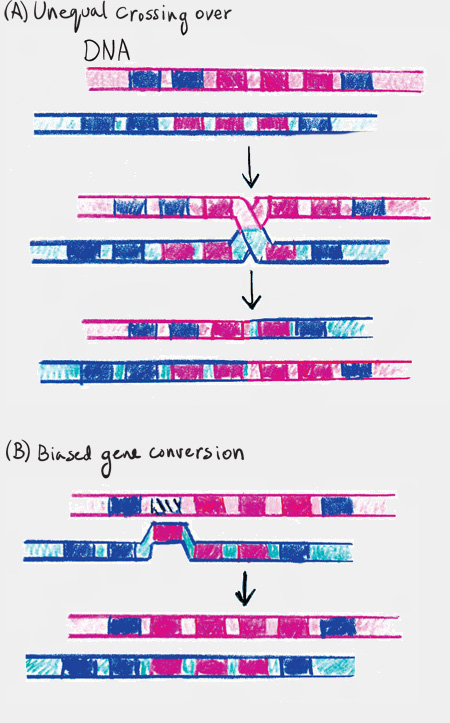
Describe the pattern of concerted evolution among highly repeated genes, and diagram the processes that lead to concerted evolution.
Concerted evolution refers to highly repeated gene families where all the copies evolve together so that all the copies maintain a high degree of similarity. Two processes can produce concerted evolution: unequal crossing over and biased gene conversion. The two processes differ as follows: