recap
24.1 recap
Fossils in sedimentary rock strata enabled geologists to determine the relative ages of organisms, but absolute dating was not possible until the discovery of radioactivity. Geologists divide the history of life into eons, eras, and periods, based on assemblages of fossil organisms found in successive layers of rocks.
learning outcomes
You should be able to:
Design and interpret a geological map indicating the ages of exposed rocks.
Suggest appropriate methods for dating fossils and rocks.
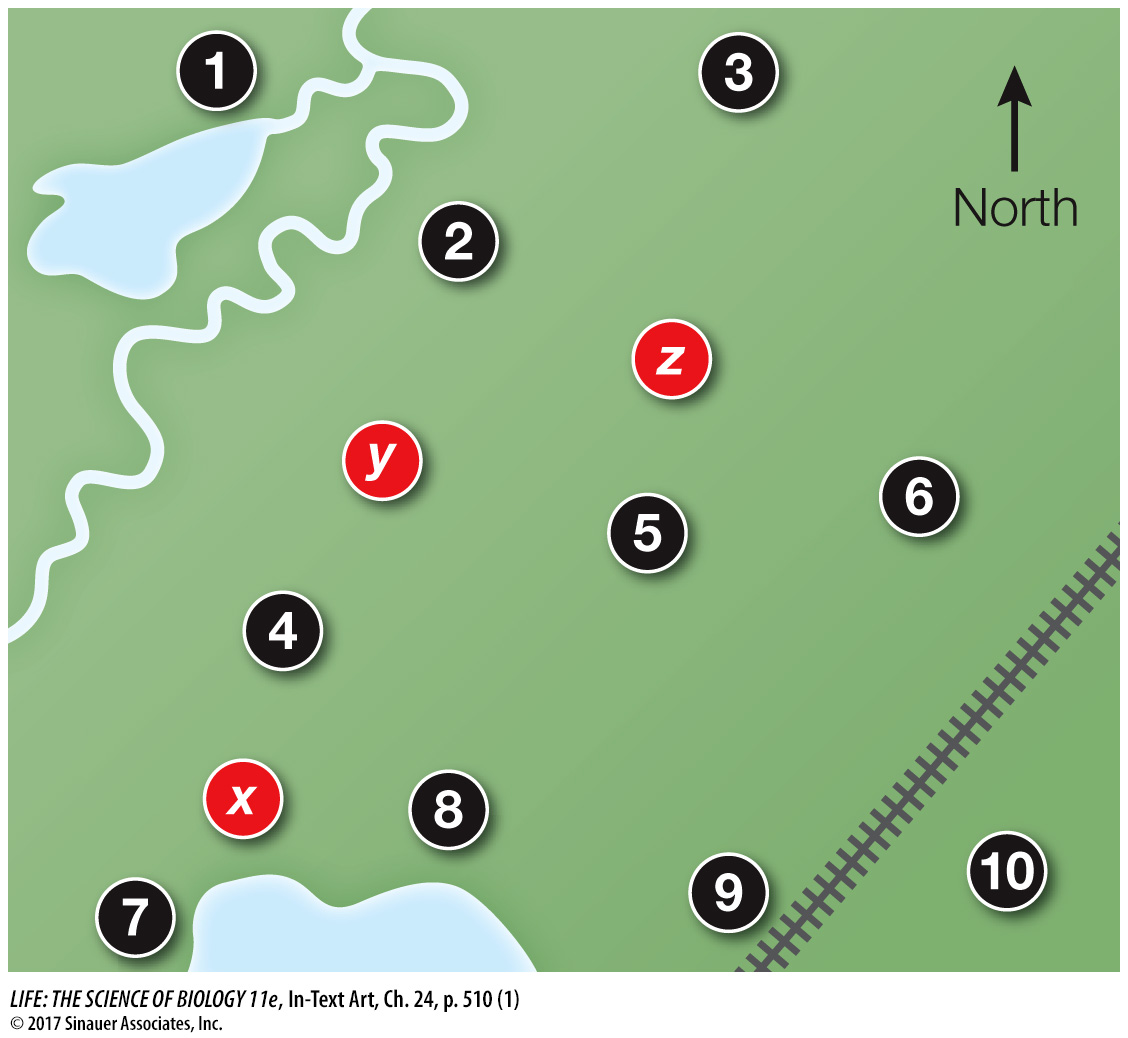
Imagine you have been asked to produce a geological map of volcanic rocks formed between 400 and 600 million years ago. You collect samples from ten sites, as indicated below, and determine the ratio of 206Pb to 238U for each site. Use the data below to answer the following questions.
| Site | 206Pb/238U ratio | Estimated age (mya) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.076 | 474 |
| 2 | 0.077 | 479 |
| 3 | 0.069 | 431 |
| 4 | 0.081 | 505 |
| 5 | 0.076 | 474 |
| 6 | 0.070 | 435 |
| 7 | 0.089 | 550 |
| 8 | 0.080 | 500 |
| 9 | 0.079 | 495 |
| 10 | 0.077 | 479 |
1.
Assign each site to a geological period based on the information in this table and in Table 24.1.
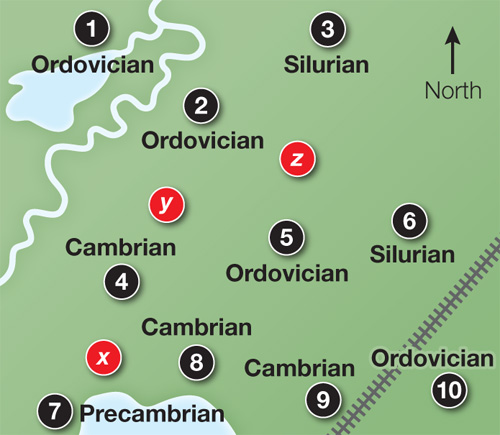
2.
Mark rough boundaries between the sites using the estimated ages and geological periods of the samples.
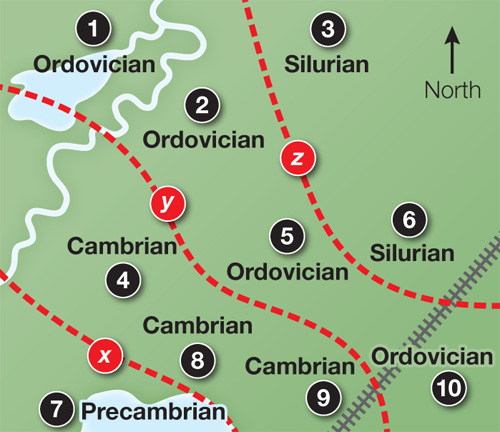
3.
If you wanted to refine the boundary between the Ordovician and Silurian periods on your map, which sampling site would you add to your analysis: x, y, or z?
Site z falls near the predicted border between the Ordovician and Silurian periods on the map shown in the answer to Question 2. Therefore it would be the best site to examine to refine the border between these two periods.
As geologists began to develop accurate ways to measure the age of Earth, they began to understand that Earth is far older than anyone had previously understood. During its 4.5-