Water and ions pass to the xylem by way of the apoplast and symplast
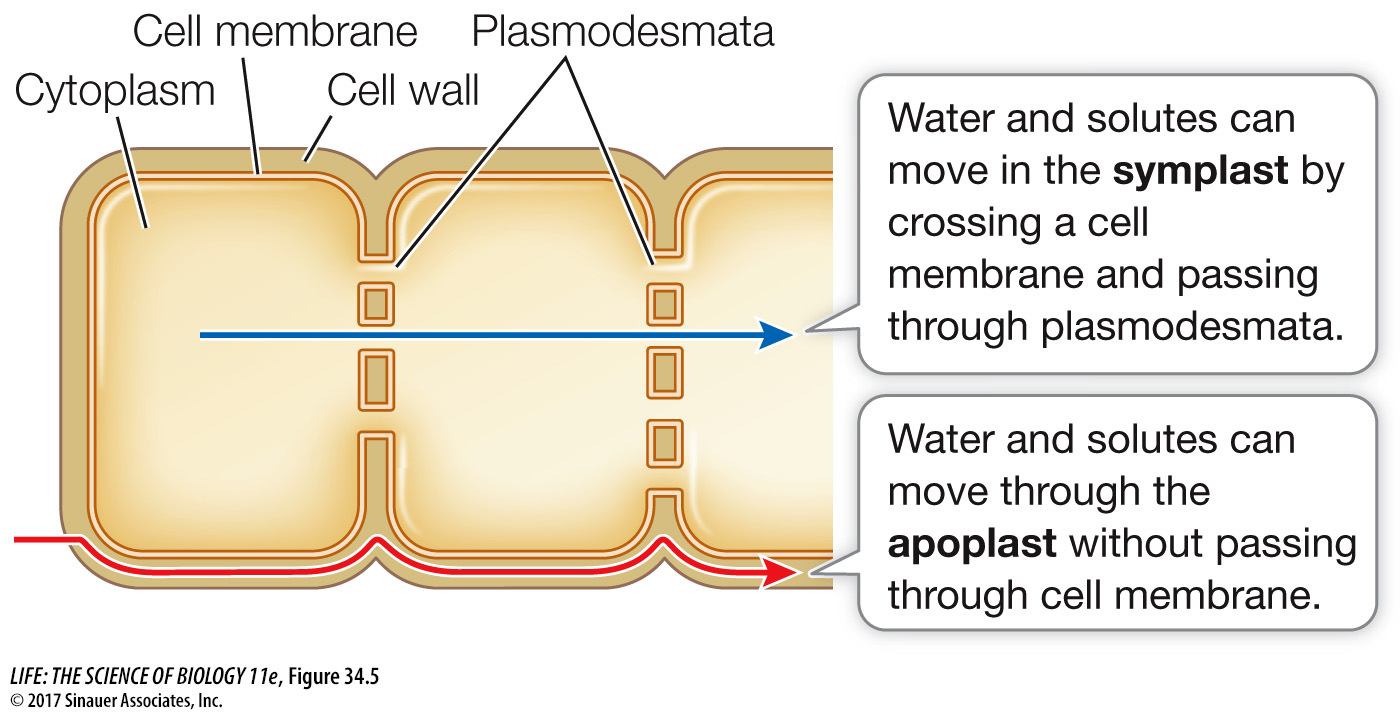
The journey from the soil through the roots to the xylem occurs primarily by one of two pathways, either separately or simultaneously: the fast lane (called the apoplast) and the slow(er) lane (called the symplast) (Figure 34.5):
The apoplast (Greek apo, “away from”; plast, “living material”) consists of the cell walls, which lie outside the cell membranes, and the intercellular spaces (spaces between cells) that are common in many plant tissues. Typically, the apoplast occupies 5–
20 percent of plant tissues by volume. The apoplast is a continuous meshwork through which water and dissolved substances can flow without ever having to cross a membrane. Movement of materials through the apoplast is thus unregulated and rapid. The symplast (Greek sym, “together with”) is the continuous cytoplasm of the living cells, which are connected by plasmodesmata (see Figure 7.16). Secretory cells such as those in flowers that make nectar have a lot of plasmodesmata. So do cells in the root tip, where the selectively permeable cell membranes of the root cells control access to the symplast. Movement of water and dissolved substances into the symplast is tightly regulated.
Q: What type of animal cell junction is best compared with the Casparian strip? See Figure 6.7.
Tight junction.
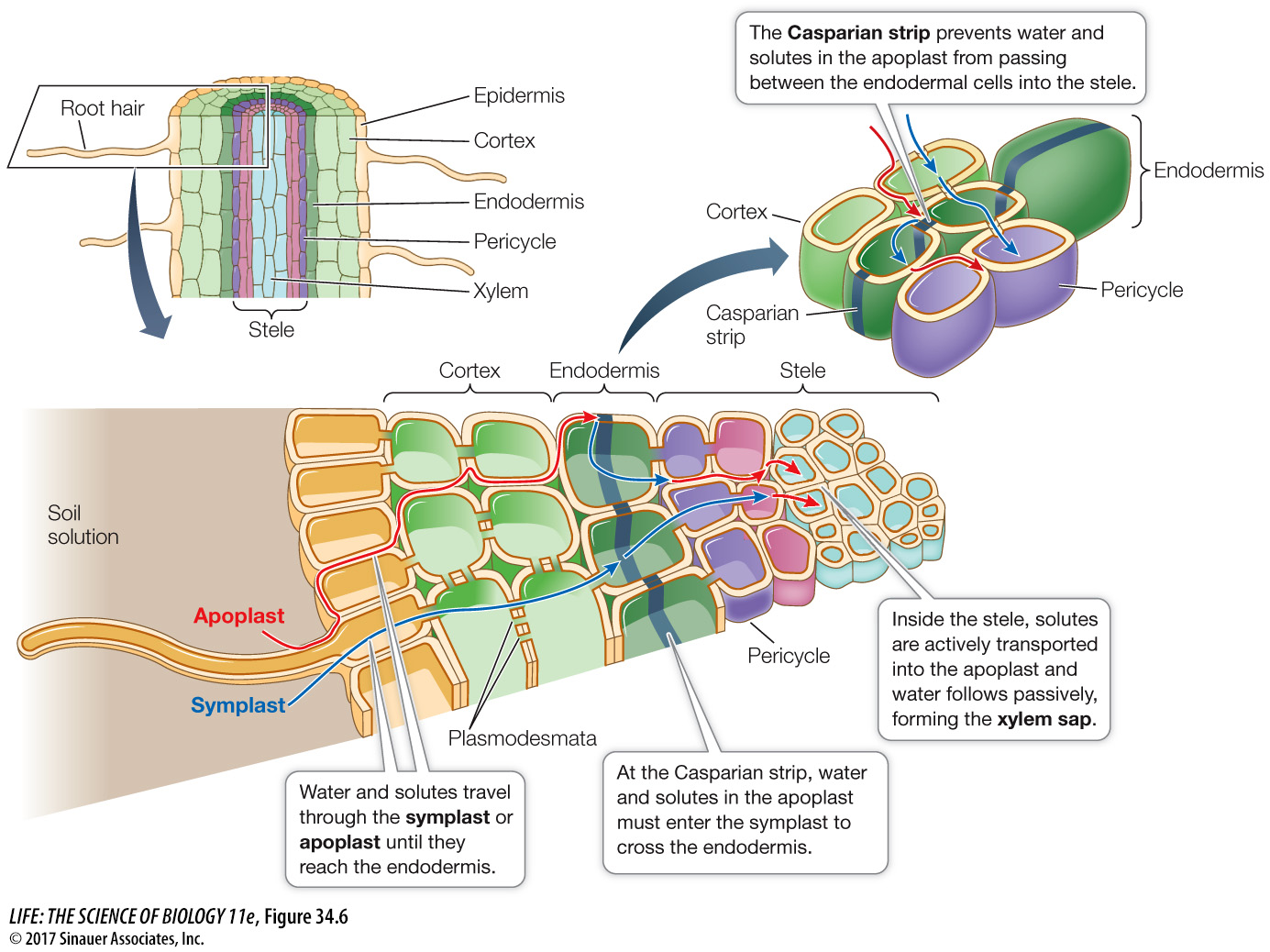
Water and minerals that pass from the soil solution through the apoplast can travel as far as the endodermis, the innermost layer of the root cortex (Figure 34.6; see Key Concept 33.3). The endodermis is distinguished from the rest of the ground tissue by the presence of the Casparian strip. This waxy, suberin-
Activity 34.2 Apoplast and Symplast of the Root
Once they have passed the endodermal barrier, water and minerals remain in the symplast until they reach parenchyma cells in the pericycle or xylem. These cells then actively export mineral ions into the apoplast of the stele. As the concentrations of mineral ions in the apoplast increase, its water potential becomes more negative. Consequently, water moves out of the cells and into the apoplast by osmosis. In other words, ions are transported actively, and water follows passively. The end result of transport is that water and minerals end up in the xylem, where they constitute the xylem sap. Table 34.1 shows the composition of xylem sap.
| Substance | Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|---|
| Ions, minerals (g/L) | 0.2– |
1– |
| Amino acids (g/L) | 0.1– |
5– |
| Sugars (g/L) | 0 | 100– |
| Solute potential, ΨS (MPa) | –0.02 to –0.2 | –0.6 to –3 |