Parthenogenesis is the development of unfertilized eggs
Not all eggs must be fertilized to develop. A common mode of asexual reproduction in arthropods (including aphids) is the development of offspring from unfertilized eggs. This phenomenon, called parthenogenesis, also occurs in some species of fish, amphibians, and reptiles. Most species that reproduce parthenogenetically also engage in sexual reproduction or at least sexual behavior at other times. In some species, parthenogenesis is part of the mechanism that determines sex. In honeybees (as well as in most ants and wasps), males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, whereas females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid.
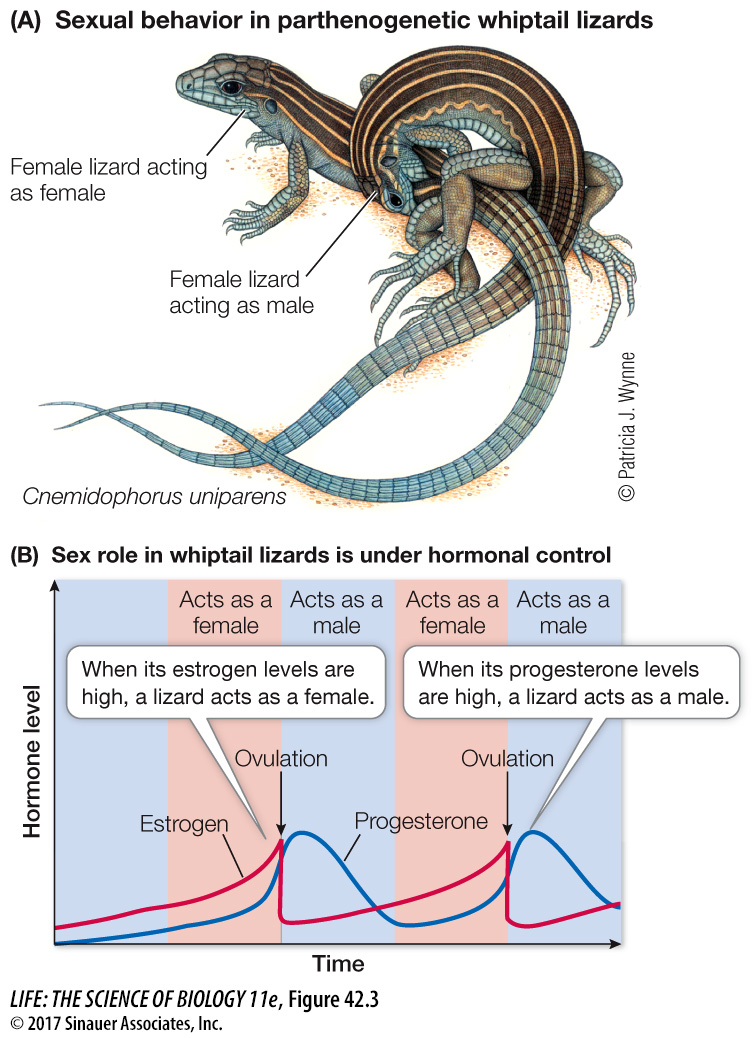
Parthenogenetic reproduction in some species requires sexual behavior even though sperm are not involved and eggs are not fertilized. David Crews and his students at the University of Texas extensively investigated one such case, that of parthenogenetic reproduction in a species of whiptail lizard. There are no males of this species. Females can act as males, engaging in all aspects of courtship display and mating, although no sperm are produced or transferred (Figure 42.3). Whether a specific female acts as a female or as a male depends on cyclical hormonal states. When estrogen levels are high, she acts as a female. When her progesterone levels peak, she acts as a male. The stimulation resulting from the sexual activity triggers the release of eggs from the ovaries of the acting female.
Q: What selective advantages could accrue to a bisexual species becoming unisexual? What disadvantages?
The selective advantage that could accrue to a bisexual species that becomes unisexual is that each member of the population could produce offspring. A disadvantage would be loss of genetic diversity.