Apply What You’ve Learned
Review
46.1
Specific areas within the five lobes of the cerebral cortex have sensory, motor, and associative functions.
46.3
Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive functions.
46.3
Language functions are lateralized (typically within the left cerebral hemisphere). Language ability involves parts of the occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes.
Original Paper: Chee, M. W. L., L. Y. M. Chuah, V. Venkatraman, W. Y. Chan, P. Philip and D. F. Dinges. 2006. Functional imaging of working memory following normal sleep and after 24 and 35 h of sleep deprivation: Correlations of fronto-
Insufficient sleep has negative consequences. There are the physiological ones: lack of energy, difficulty staying awake, and even high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke. And what about cognitive abilities—
In one test (referred to as the LTR test), subjects looked at a picture of four capital letters for 0.5 seconds. Three seconds later they were shown a lowercase letter for 1.5 seconds and were to press a button if the lowercase letter matched one of the capital letters they had just seen.
The second test (referred to as the PLUS test) required more cognitive processing than the LTR test. In the PLUS test, subjects looked at a picture of two capital letters for 0.5 seconds. Three seconds later they were shown a lowercase letter for 1.5 seconds and were to press a button if this was the next letter, in alphabetical sequence, after either of the two capital letters.
The effect of sleep deprivation on working memory was measured by the accuracy of responses of sleep-
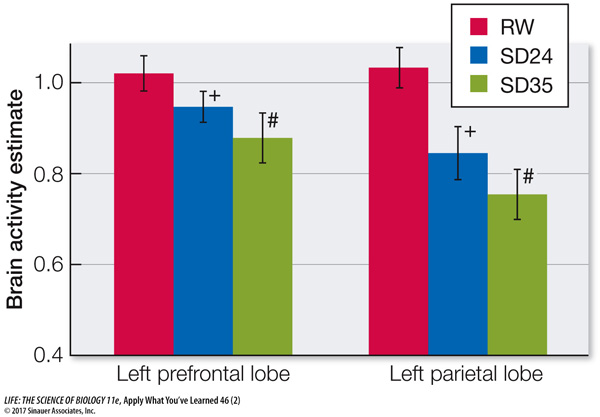
Using MRI, the researchers measured activation of different brain regions during the testing. Two areas with the most significant differences between RW and SD subjects are shown in the graph. Plus signs (+) indicate significant differences between RW and SD24 subjects; hashtags (#) indicate significant differences between RW and SD35 subjects.
| Accuracy (%) | RW | SD24 | SD35 | Reaction time (ms) |
RW | SD24 | SD35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTR | 95.2 | 86.5* | 85.0* | LTR | 745 | 792* | 769 |
| PLUS | 95.0 | 86.6* | 84.3* | PLUS | 698 | 747* | 746* |
Questions
1.
Based on the data in the table, justify the conclusion that sleep deprivation impairs working memory.
The subjects who were well rested gave correct answers to working-
2.
One interpretation of the reaction-
Compared with well-
3.
Based on the information in the text, explain why the areas of the cerebral cortex shown in the graph were more affected by sleep deprivation than most other areas of the cerebral cortex examined in this study.
The left side of the cerebral cortex is responsible for processing and understanding language. Since the tests involved letter recognition and sequencing, this is likely to be the area most activated by the tests.
4.
After looking at the MRI data, the researchers concluded that sleep deprivation has a stronger effect on the parietal lobe than on the frontal lobe. How do the data support that conclusion? What statistical comparison would you use to test this conclusion?
Sleep deprivation caused a 20-
Go to LaunchPad for the eBook, LearningCurve, animations, activities, flashcards, and additional resources and assignments.