Protonephridia of flatworms excrete water and conserve salts
Many free-
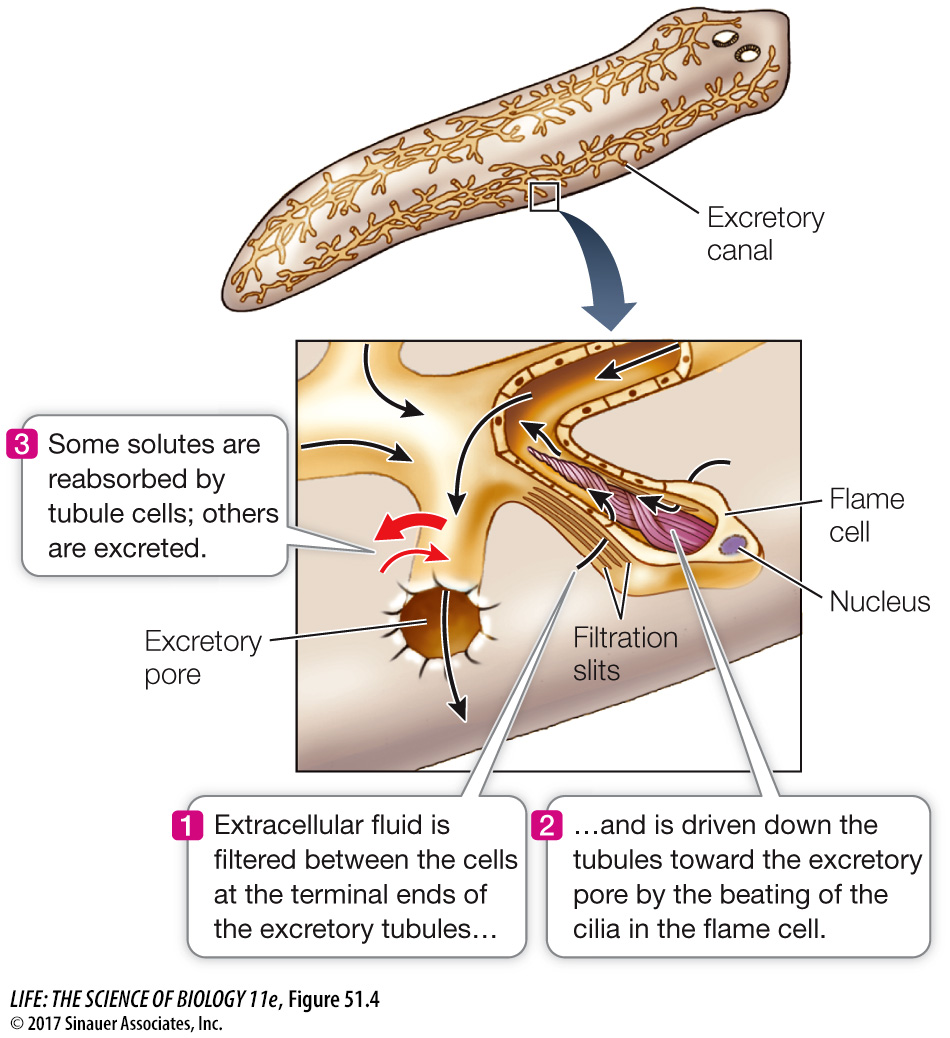
Q: Do you expect the fluid coming out of the excretory pore to be hypertonic or hypotonic to the flatworm’s interstitial fluid?
For the freshwater planarian, the excretory product would be hypotonic to the interstitial fluid because the animal has to be excreting excess water that is entering its body by osmosis.
Extracellular fluid enters the tubules by filtration. The beating of the cilia causes a slight negative pressure in the tubule, and movements of the animal create positive pressure in the extracellular fluid. This pressure difference causes extracellular fluid to be filtered through tiny spaces between tubule cells. The filtrate flows toward the animal’s excretory pore, and along the way the cells of the tubules modify the composition of the fluid by reabsorption and secretion of specific ions and molecules. Because more ions are reabsorbed than are secreted, the urine that leaves the flatworm’s body is less concentrated than the extracellular fluid. Thus the protonephridium conserves ions and excretes water and wastes.