Chapter 7
RECAP 7.1
Autocrine signaling would be important for a cell to maintain a specialized role. For example, a cell might receive a signal to specialize and form a tissue of many cells. The first cell would self-
stimulate to grow and divide to form the tissue in response to self- signaling. Hormones are delivered to target-
cell receptors through the circulatory system. In animals, this is blood; in plants, it is the vascular system. Specificity for signal response occurs because only certain cells make the receptor for a given signal.
RECAP 7.2
The dissociation constant is the ratio of the rate constant for dissociation of a ligand and its receptor to the rate constant for binding. The higher the KD, the less likely it is that a signal will bind to its receptor, and the less likely it is that a cell will respond to a signal at particular concentrations of ligand and receptor.
The chemical nature of receptor–
ligand bonding is shape and the presence of noncovalent interactions, such as hydrophobic and ionic interactions. This provides specificity. Specificity is important to ensure an appropriate biological response to each signal. Cytoplasmic receptors lack nonpolar regions that allow insertion into the cell membrane. Their exteriors are polar, so they can interact with water in the cytoplasm. While membrane receptors stay in the membrane, cytoplasmic receptors may be translocated to the nucleus after binding to their ligand.
RECAP 7.3
Amplification occurs because each activated ras molecule catalyzes the phosphorylation, and therefore activation, of many molecules of Raf, each of which in turn activates many molecules of MEK, etc. The general principle is one enzyme → many molecules of its substrate.
Different cells can have different target molecules to which cAMP binds, and these targets can have different activities and functions. Binding of cAMP changes the structure of its target (e.g., tertiary structure of a protein).
Regulation of cascades occurs in three ways: by differing concentration of a second messenger (e.g., NO is a gas that breaks down readily), by differences in concentration of a single component of the pathway, and by enzymes that change target molecules (e.g., phosphatases that remove phosphate groups on proteins in a cascade).
RECAP 7.4
Oxytocin is involved with both G protein–
coupled and ion channel responses. It binds to a G protein– coupled receptor (see Figure 7.7), resulting in signal transduction through the IL3–DAG pathway, which releases Ca2+ into the cytoplasm via ion channels. In the brain, the effect of Ca2+ is to indirectly stimulate nerve cell activity by the opening of ion channels for Na+. Ion channel opening is a rapid response to signaling. Enzyme modification is also a relatively rapid response mechanism. Changes in gene expression involve many steps, so cell signaling via transcription factors is slower.
RECAP 7.5
Characteristics of direct communication by cell junctions: The size of signal molecules is limited by the size of openings between cells. It is not specific. It is fast. There can be cytoplasmic connection between cells.
Characteristics of receptor-
mediated communication: The signal molecules can be larger. It is specific. It is slower. There is no direct cytoplasmic connection.The advantage of direct communication over chemical signaling is that direct communication enables a rapid, coordinated response of many cells.
From single-
celled Chlamydomonas evolved larger and larger groups of cells with communicating junctions (Gonium, Pandorina, Eudorina). Even larger groups had some differentiation (Pleodorina and Volvox). Experiments might involve applying a solution containing the antibody to the upper part of the Hydra body. The antibody would block diffusion of the signal molecule from the apex to the upper body and—
if the hypothesis is correct— would allow a bud to form in the upper body. A sham experiment, in which the solution without antibody is applied, would be a control. In this case, a bud would not form in the upper body.
WORK WITH THE DATA, P. 143
There was a higher level of trust in the donors who received oxytocin than in those who did not. The difference was about 15 percent. A t-test could be used to assess the difference for statistical significance.
There was no difference in investment between oxytocin-
treated and untreated people when they were told exactly how much to invest. This indicates that oxytocin does not just induce people to take a greater risk, but when considered with the results of the first experiment, oxytocin increases risk when there is a social interaction between people involving trust.
FIGURE QUESTIONS
Figure 7.3 As with the binding of enzyme to substrate, the binding of caffeine and adenosine is noncovalent. Both substances bind to a specific site on the receptor by their shape and by interactions, including hydrophobic interactions (the rings).
Figure 7.10 Raf activity is an early event in the protein kinase cascade that stimulates cell division in kidney cancer. Blockage of raf prevents phosphorylation of MEK, and all the subsequent steps in the protein kinase cascade. Cell division is reduced and the tumor shrinks.
Figure 7.17 Direct communication between cells allows them to rapidly share signals, which travel from one cell to another in a group. This can result in common activities for a group of cells, which is important for tissues.
APPLY WHAT YOU’VE LEARNED
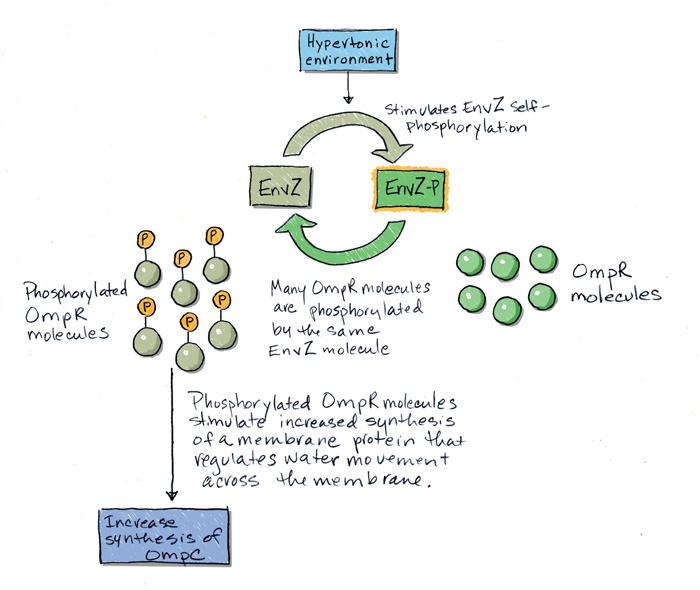
The figure shows that different amounts of the membrane protein OmpC are produced and inserted into the membrane, depending on environmental solute concentration.
The membrane protein EnvZ is a protein kinase that phosphorylates itself and then phosphorylates OmpR in the cytoplasm. This sequential phosphorylation could explain how signal transduction occurs in this signal pathway.
EnvZ + ATP → EnvZ-
P + ADP EnvZ-
P + OmpR → EnvZ + OmpR- P The numbers of molecules of EnvZ are much smaller than the numbers of molecules of OmpR in the cytoplasm, suggesting that a smaller number of the membrane proteins act to stimulate a larger number of cytoplasmic proteins that carry the signal to the next point in the signal transduction pathway.