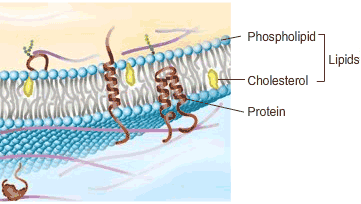
The plasma membrane of a cell is often described as a fluid mosaic. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer that is essentially a flowing film of lipids in which a variety of proteins “float.” Adequate membrane fluidity is important for many membrane functions.
The fluidity of cell membranes is affected by several factors, two of which are particularly important: temperature and the lipid composition of the membrane. Colder temperatures decrease membrane fluidity, while higher temperatures increase it. Some organisms are able to change the lipid composition of their membranes when they get cold to keep their membranes adequately fluid.
Several changes in lipid composition can alter membrane fluidity. Membrane fluidity increases when the membrane contains less cholesterol (an important component of animal membranes), or more short-chain fatty acids, or more unsaturated fatty acids. In contrast, membranes become less fluid when they contain more cholesterol, more long-chain fatty acids, or more saturated fatty acids.
Click the Next button to explore how temperature affects lipid bilayer composition.