Chapter 20. Genetic Drift Simulation
Genetic Drift Simulation
Question 1 of 4
Activity 20.3 Quiz
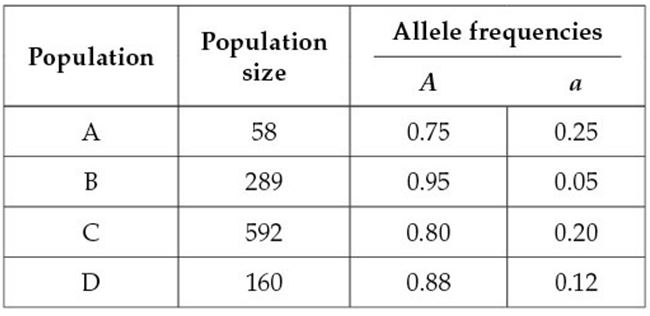
Which statement can be made about genetic drift?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Correct. See Key Concept 20.2 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Result in Evolution
Incorrect. See Key Concept 20.2 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Result in Evolution
Activity results are being submitted...