Chapter 22. Speciation Simulation
Speciation Simulation
Question 1 of 4
Activity 22.1 Quiz
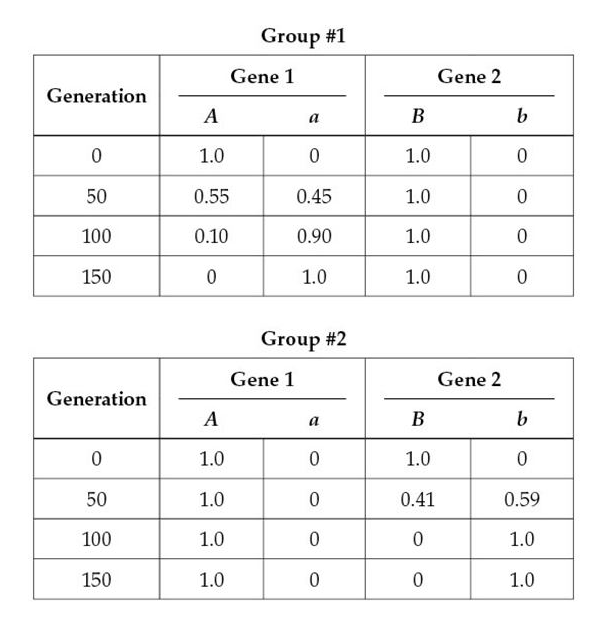
What did the simulation demonstrate about the rate at which geographically isolated subsets of a population become reproductively incompatible?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Correct. See Key Concept 22.2 Speciation Is a Natural Consequence of Population Subdivision
Incorrect. See Key Concept 22.2 Speciation Is a Natural Consequence of Population Subdivision
Activity results are being submitted...