Four Models of Bonding
|
MODEL 1: IONIC Properties of ionic substances: Dissolve in water Conduct electricity when dissolved Tend to be brittle solids Made of metal and nonmetal atoms combined 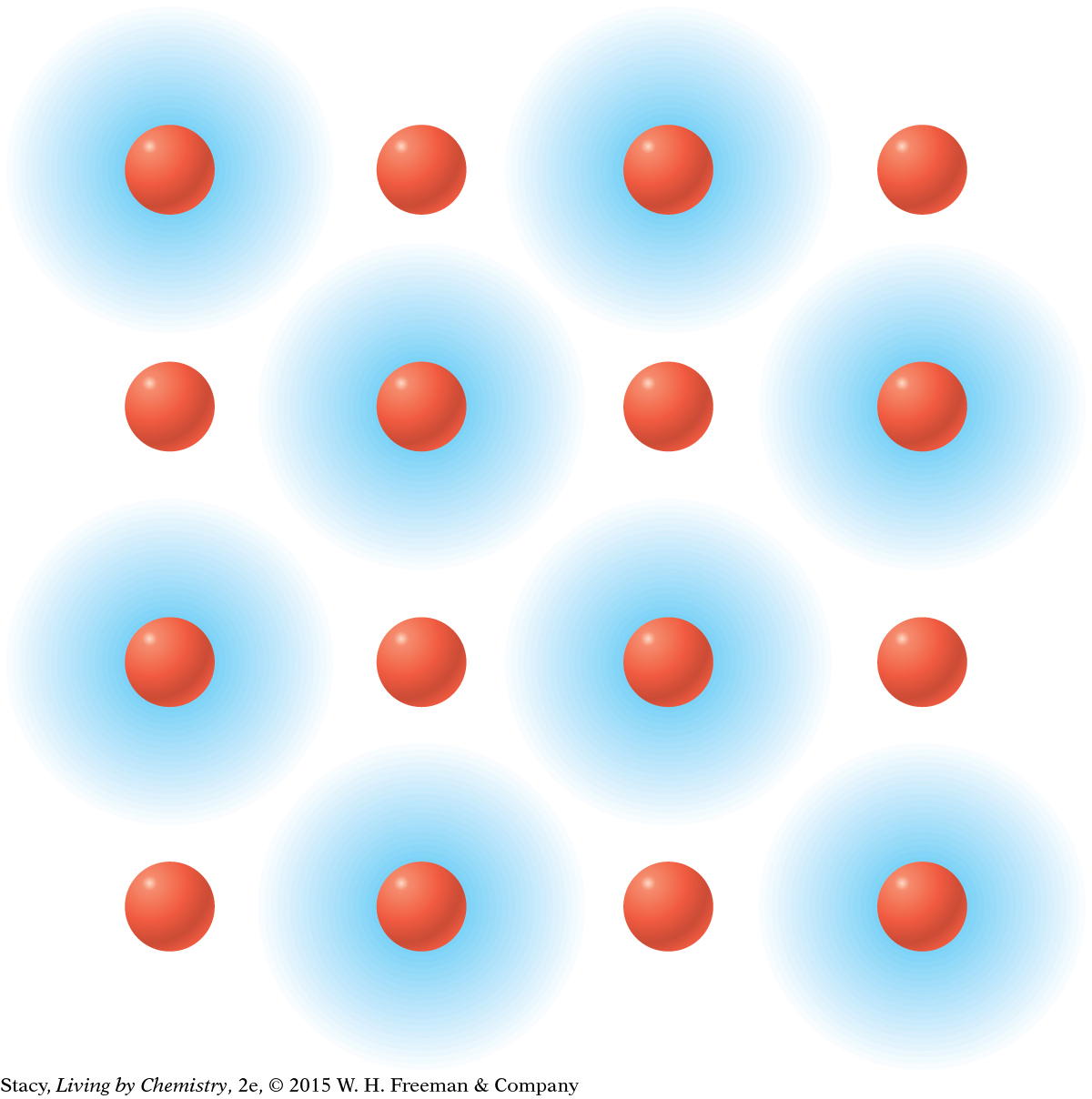
In ionic bonding, the valence electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Metal atoms transfer their valence electrons to nonmetal atoms. |
MODEL 2: MOLECULAR COVALENT Properties of molecular covalent substances: Some dissolve in water, some do not Do not conduct electricity Some are liquids or gases Made entirely of nonmetal atoms 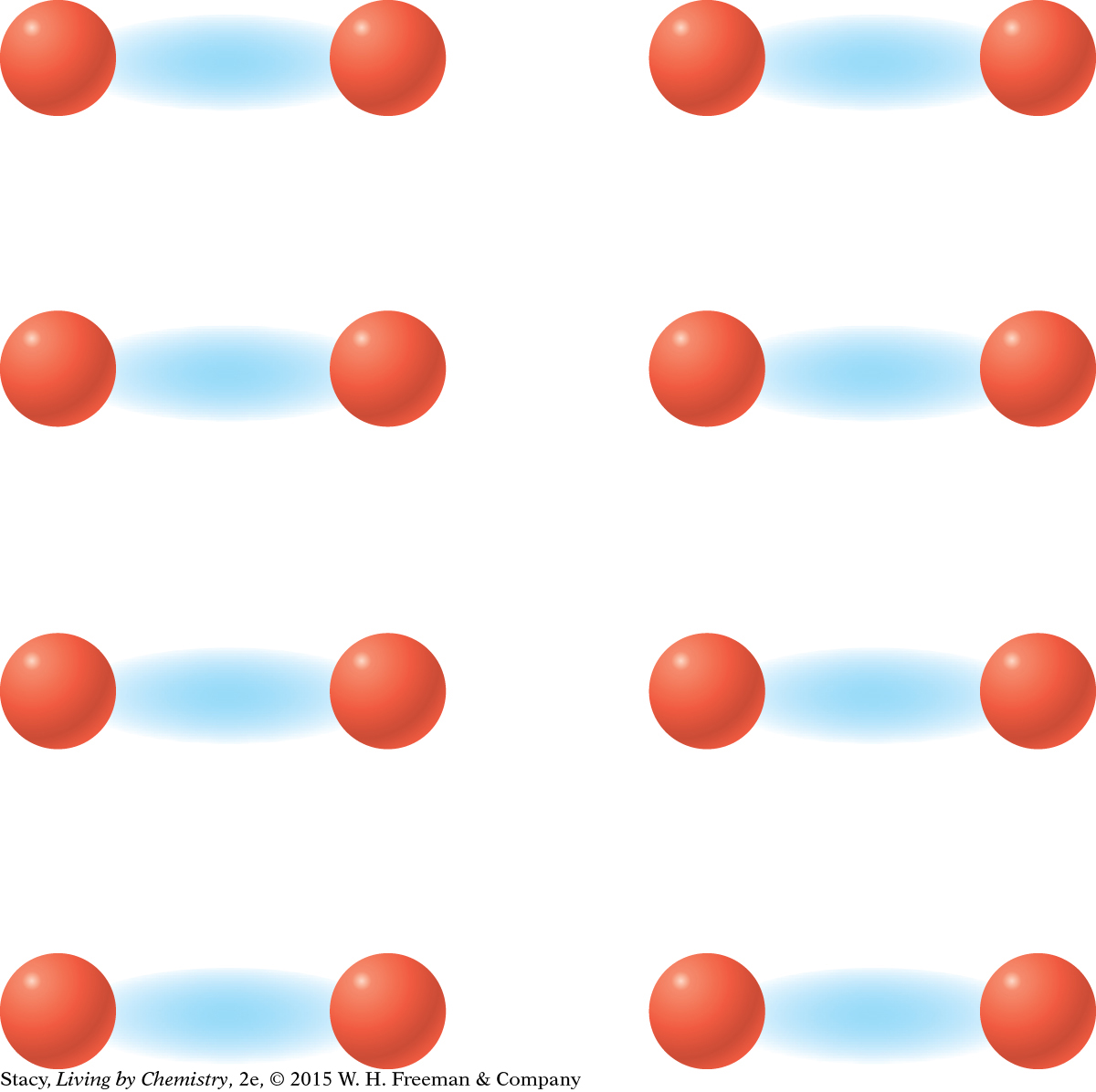
In molecular covalent bonding, the valence electrons are shared between pairs or groups of atoms. This creates small stable units, called molecules, within the substance. |
|
MODEL 3: METALLIC Properties of metallic substances: Do not dissolve in water Conduct electricity Bendable, malleable solids Made entirely of metal atoms 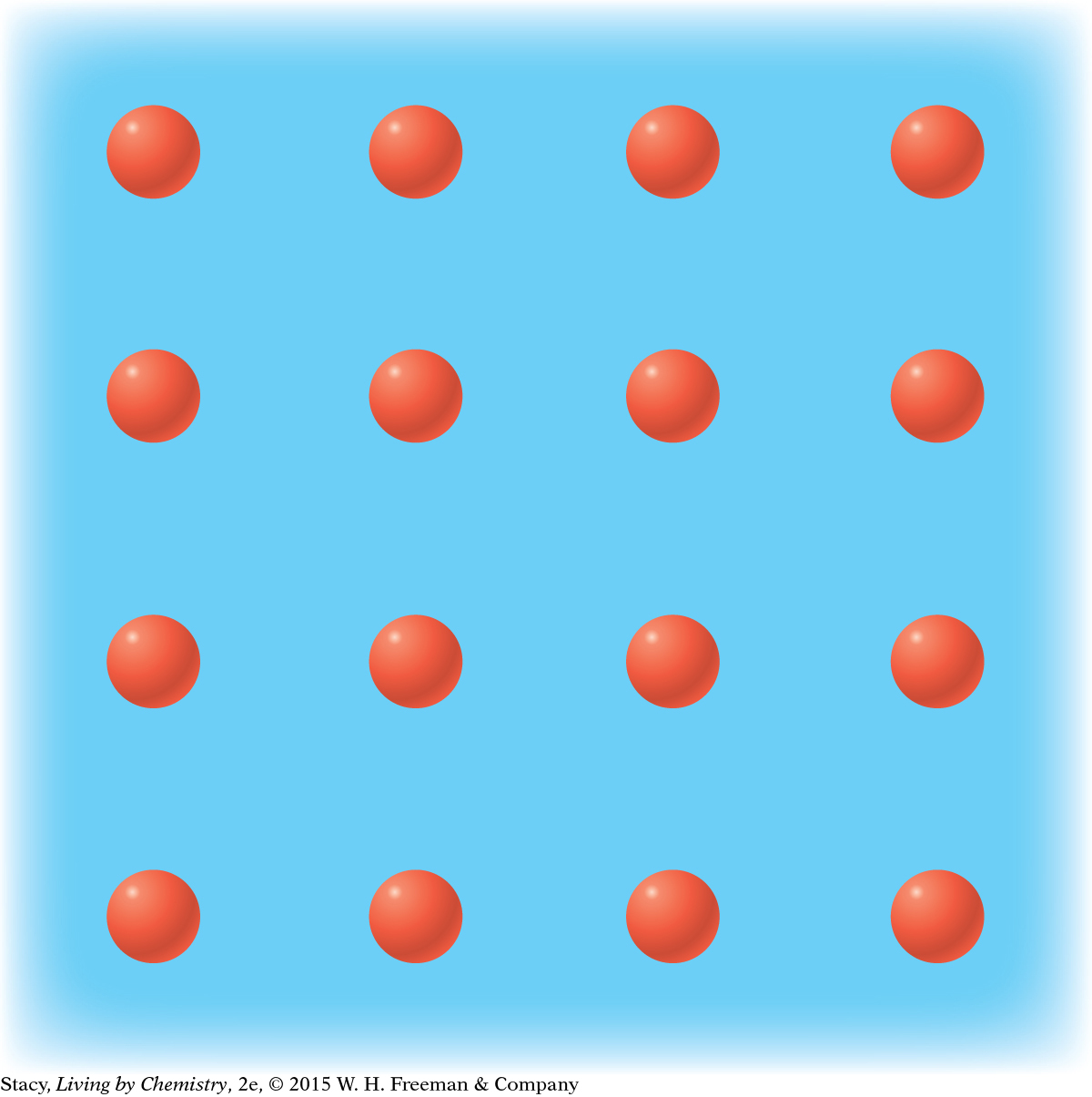
In metallic bonding, the valence electrons are free to move about the substance. |
MODEL 4: NETWORK COVALENT Properties of network covalent substances: Do not dissolve in water Do not conduct electricity Extremely hard solids Made entirely of nonmetal atoms 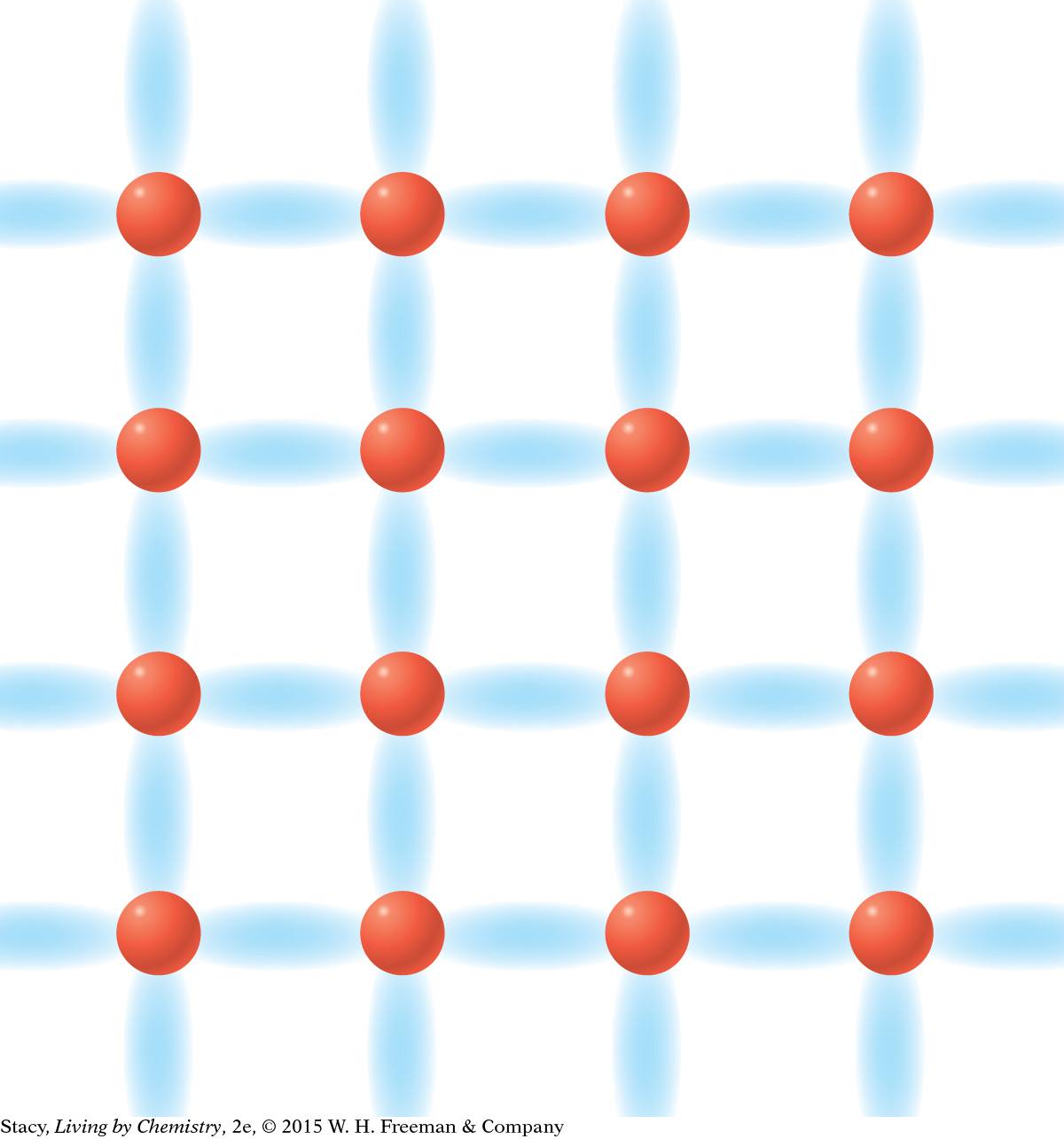
Network covalent bonding is similar to molecular covalent bonding, but the valence electrons are shared throughout the entire substance. |