MODEL 1: IONIC Properties of ionic substances: Dissolve in water Conduct electricity when dissolved Tend to be brittle solids Made of metal and nonmetal atoms combined 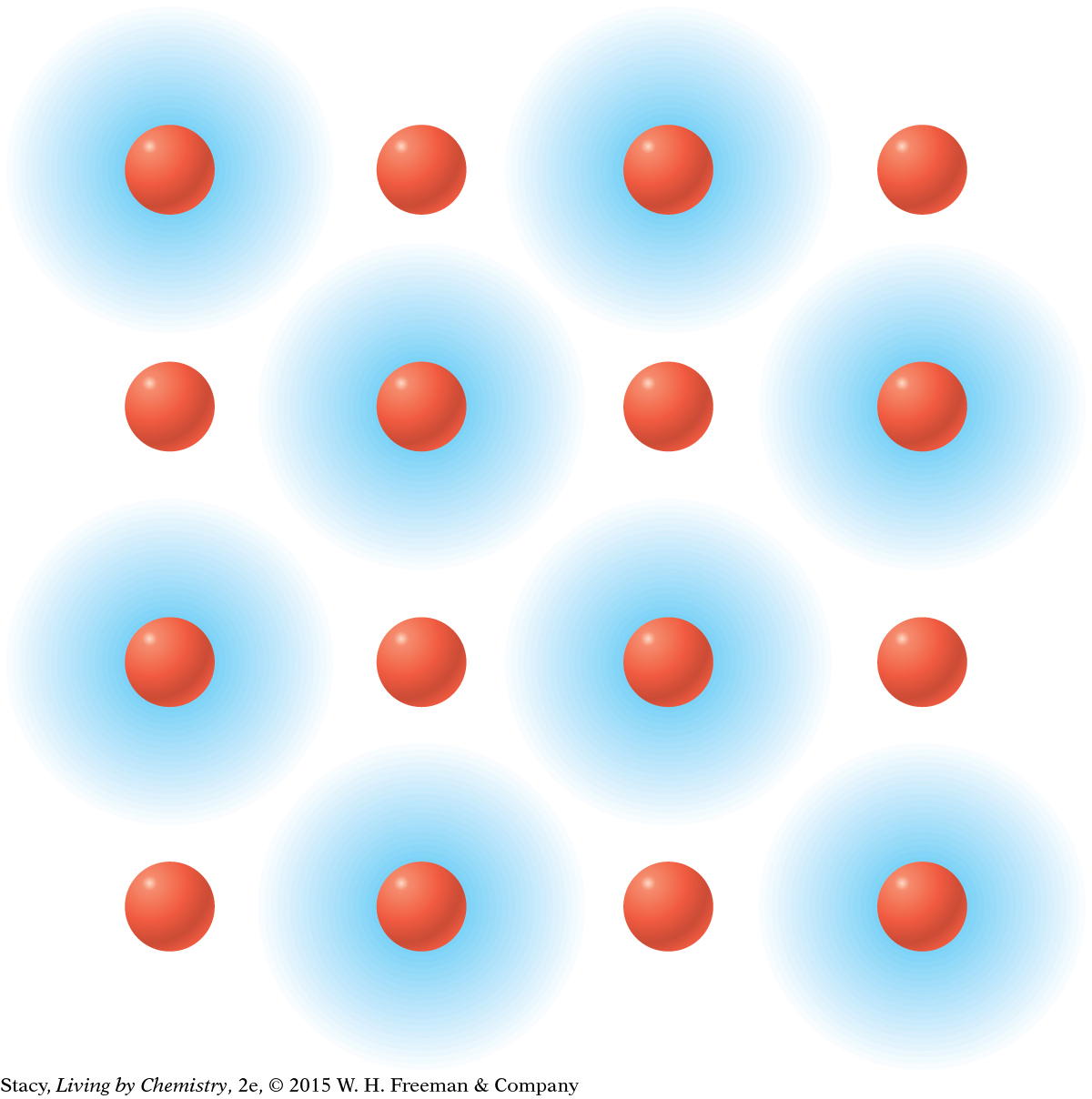 In | MODEL 2: MOLECULAR COVALENT Properties of molecular covalent substances: Some dissolve in water, some do not Do not conduct electricity Some are liquids or gases Made entirely of nonmetal atoms 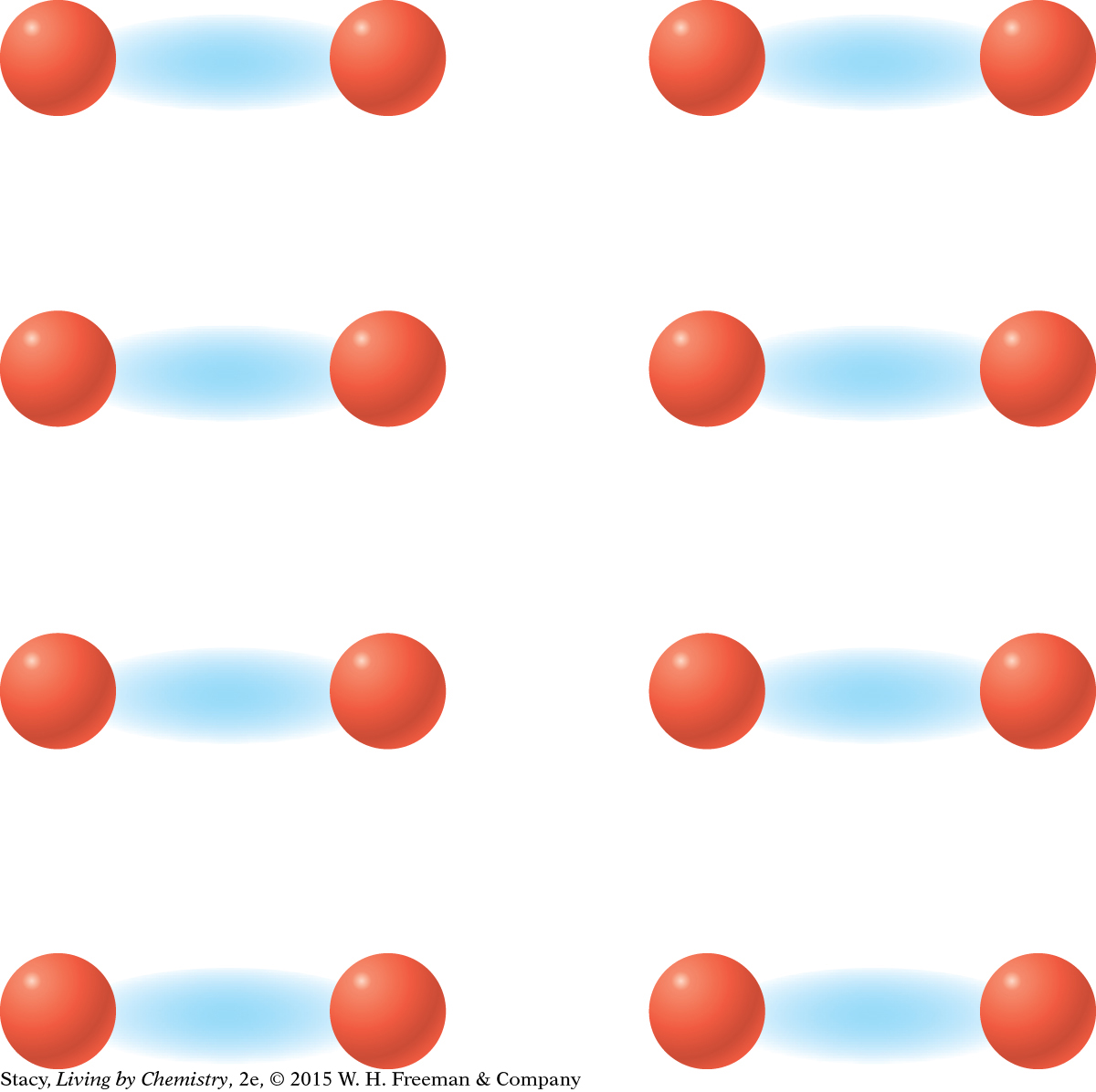 In |
MODEL 3: METALLIC Properties of metallic substances: Do not dissolve in water Conduct electricity Bendable, malleable solids Made entirely of metal atoms 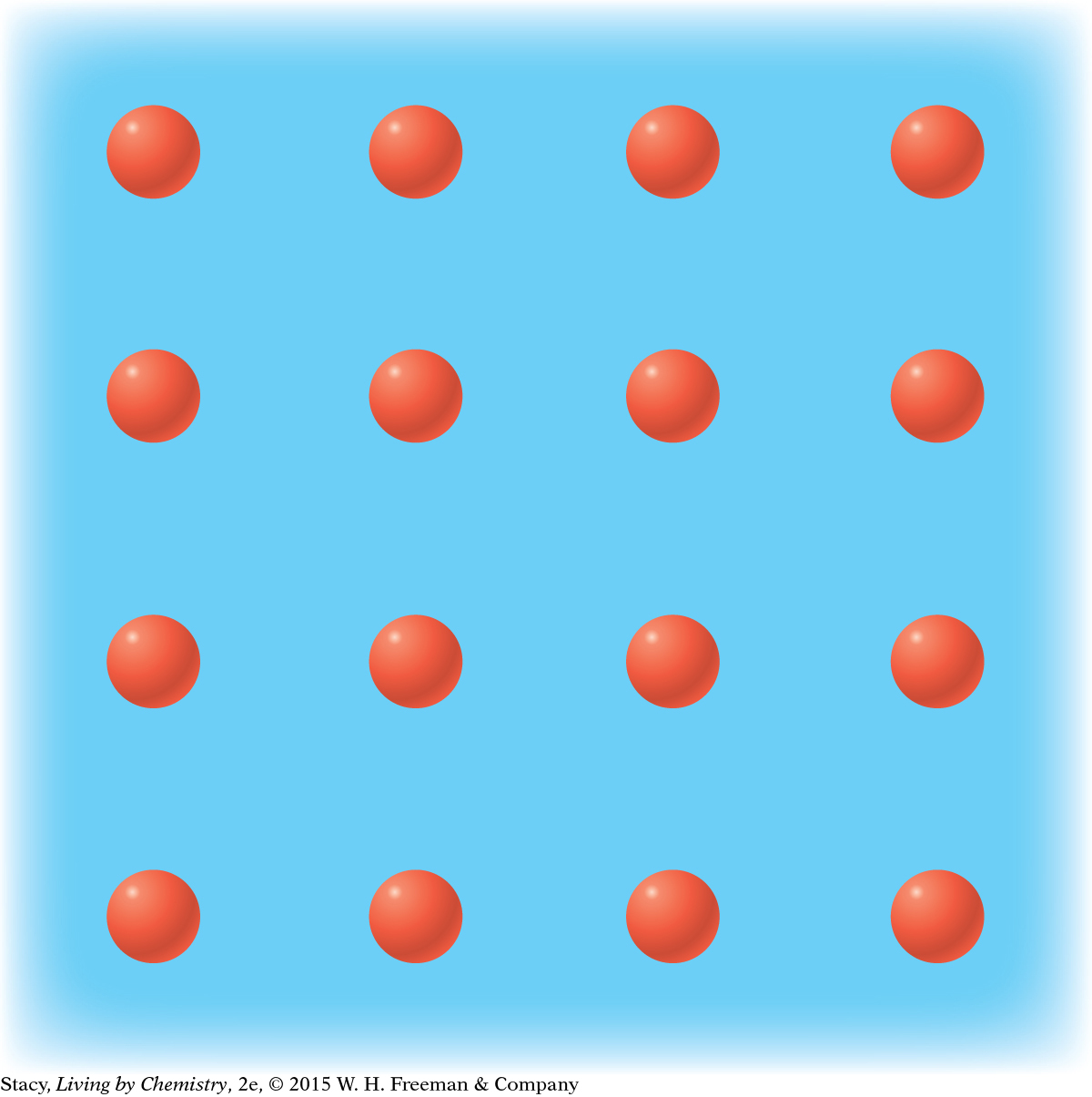 In | MODEL 4: NETWORK COVALENT Properties of network covalent substances: Do not dissolve in water Do not conduct electricity Extremely hard solids Made entirely of nonmetal atoms 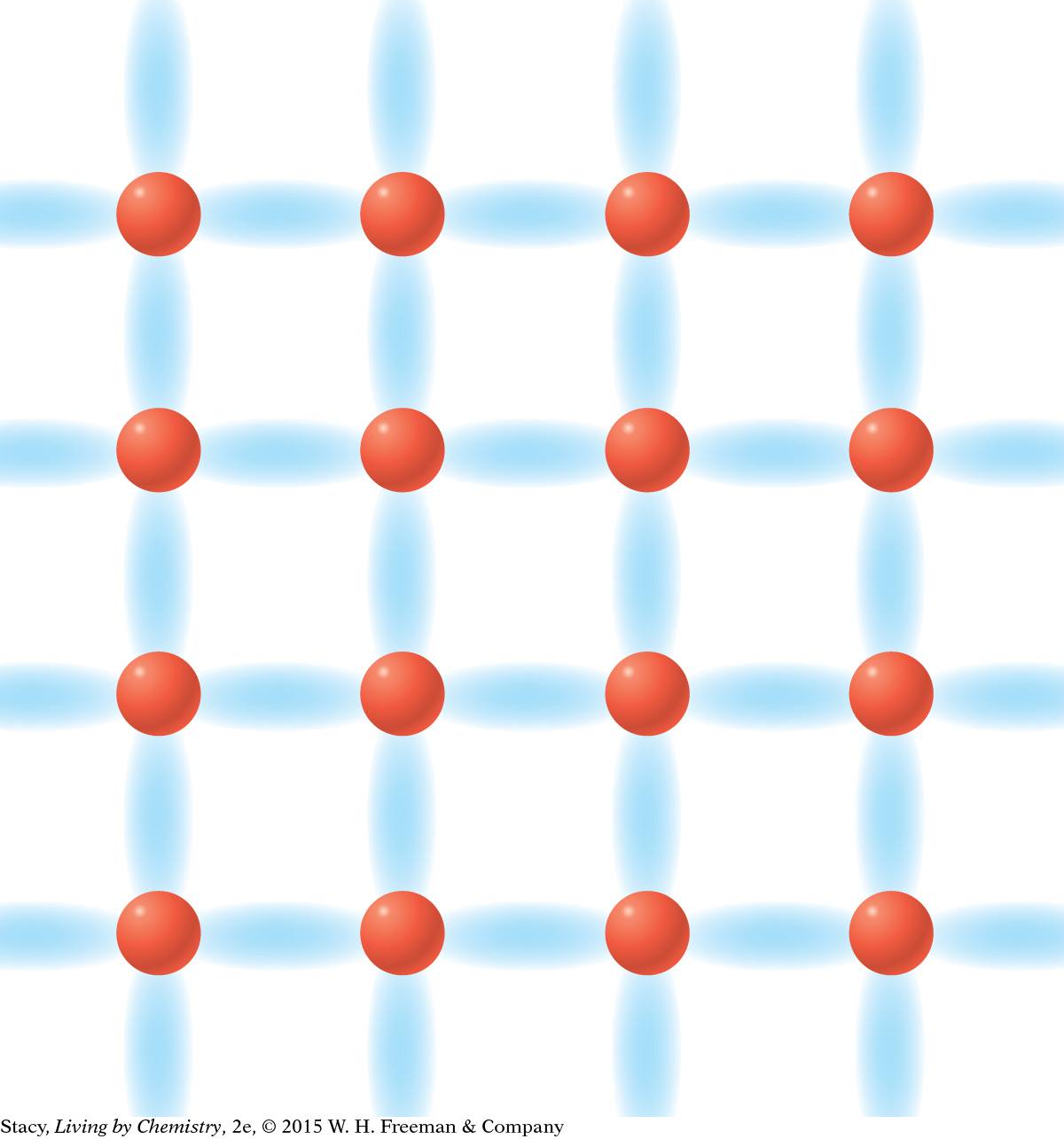 |