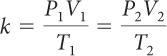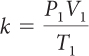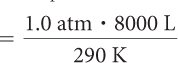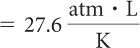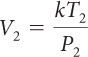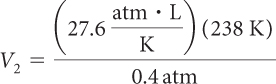LESSON 61: What Goes Up
317
THINK ABOUT IT
In some circumstances, more than two gas variables change at once. For example, if you released a balloon at sea level and it rose into the atmosphere, you would be dealing with three changing gas variables: pressure, temperature, and volume. What effect does this have on the balloon?
What are the relationships among pressure, volume, and temperature for a sample of gas?
To answer this question, you will explore
Changing Pressure, Volume, and Temperature
Combined Gas Law
Changing Pressure, Volume, and Temperature
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Changing Pressure, Volume, and Temperature
VARIATIONS IN PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE WITH ALTITUDE
Both the temperature and the pressure of the atmosphere decrease with altitude. These two conditions (temperature and pressure) will naturally vary as a balloon rises and will affect the overall volume of the balloon. The sample of gas inside the balloon responds to the conditions outside the balloon.
CONSUMER CONNECTION
CONSUMER
CONNECTION
Have you ever wondered why boxes of cake mix sometimes include high-altitude directions? At higher altitudes, water boils at a lower temperature, and the air bubbles from the leavening expand more, causing cakes to expand too much while they’re cooking. To adjust for high altitudes, bakers usually add more water (so the cake doesn’t dry out too much), decrease the amount of leavening, and increase the baking temperature (so the cake won’t have as much time to rise before it sets).

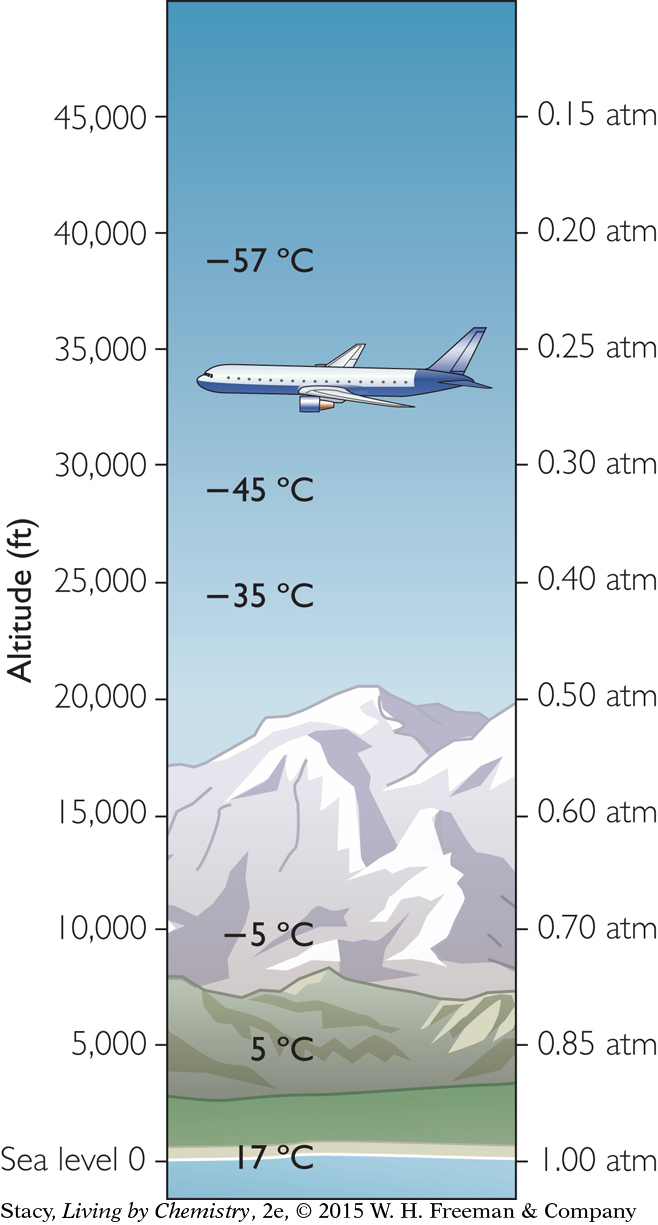
The illustration indicates the approximate average pressure and temperature of the atmosphere at various altitudes. At an altitude of 40,000 ft, the air pressure is only 0.2 atm and the air temperature is around a chilly −57 °C (−70 °F).
WEATHER BALLOONS
Weather balloons are large balloons filled with helium or hydrogen gas that carry instruments aloft to study the atmosphere at high altitudes. As the weather balloon rises, the instruments measure atmospheric conditions like the temperature, relative humidity, and pressure. This information is relayed back to a weather station by a transmitter. Wind speed and wind direction can be calculated from the collected data.
318
METEOROLOGY CONNECTION
METEOROLOGY
CONNECTION
A weather balloon has three parts: the elastic balloon, the instrument package, called a radiosonde, and the parachute. Weather balloons are released twice a day from sites all around the world. There are about 900 release sites worldwide; 95 of these sites are in the United States. Data from weather balloons are fed into National Weather Service supercomputers across the country. This information is used to help predict weather around the country.
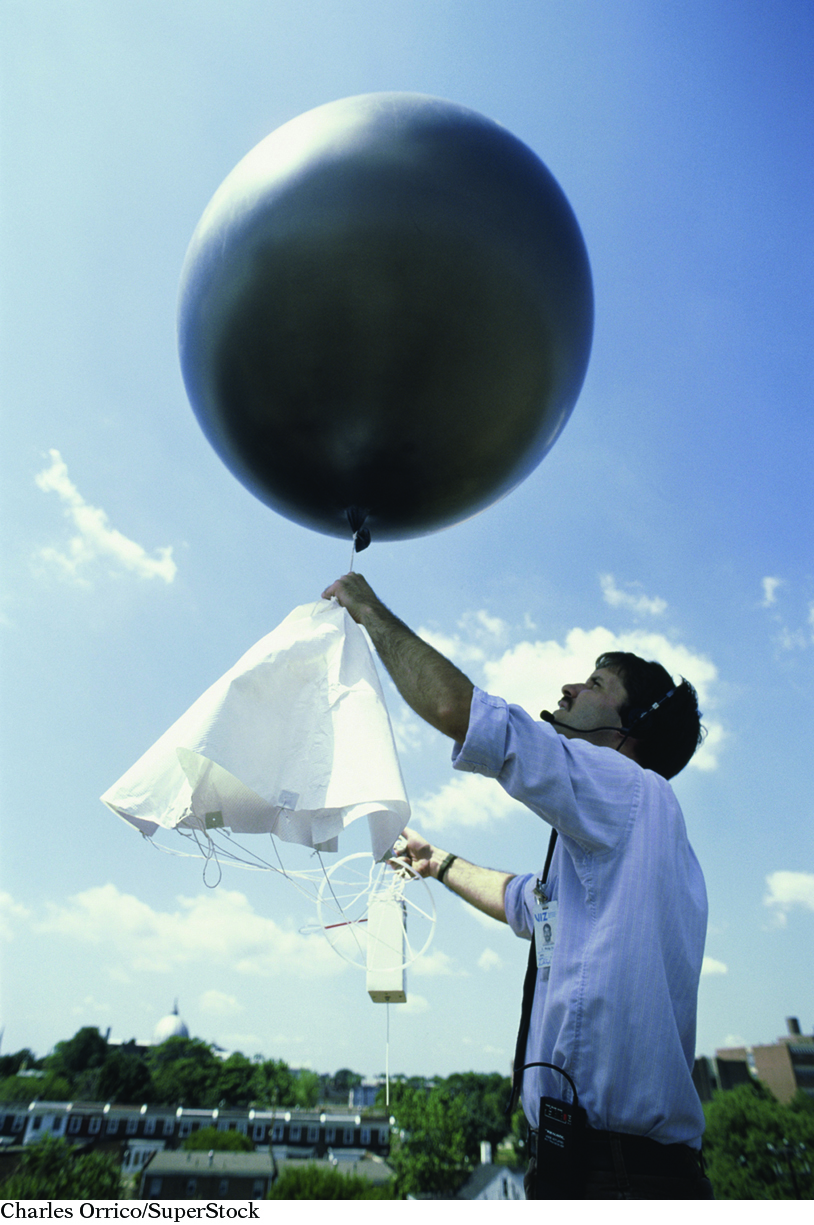

To follow the changes to the gas inside a weather balloon, you must first know the starting conditions of the balloon. Imagine a clear cool morning, where the air temperature is 17 °C and the atmospheric pressure is 1 atm. A team of meteorologists inflates a weather balloon with helium to a volume of 8000 L. If released, this weather balloon will rise no matter what the outside conditions. This is because the balloon is full of helium and helium is less dense than air.
CONFLICTING OUTCOMES
Consider the effect of changing conditions on the volume of the rising weather balloon. Charles’s law indicates that the volume of the balloon will shrink with decreasing temperature. However, Boyle’s law indicates that as the air pressure outside the balloon decreases, the balloon will expand in volume.
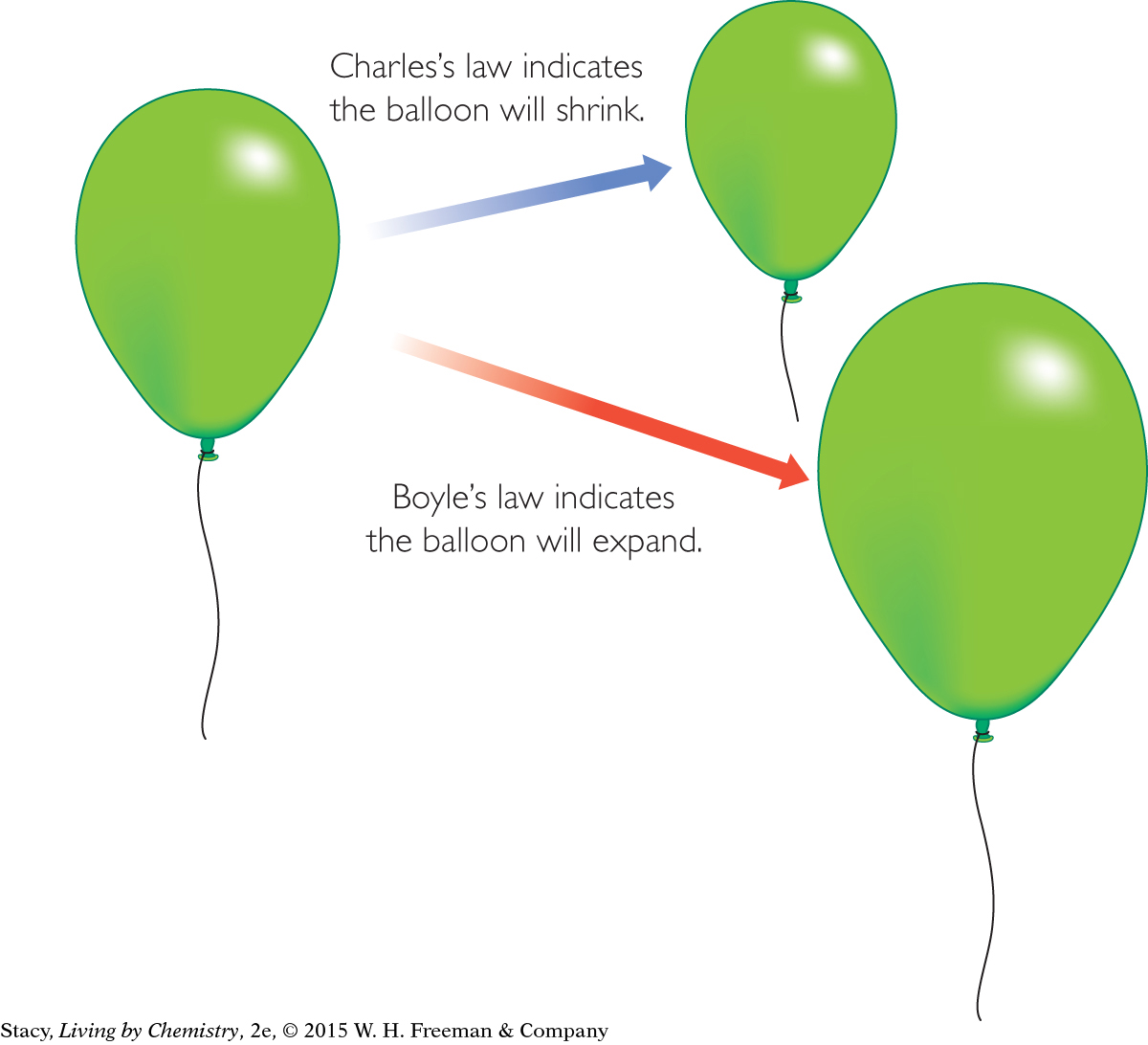
There are two conflicting outcomes. Will the balloon expand or shrink?
Combined Gas Law
Combined Gas Law
For a sample of gas, the relationship among gas pressure, temperature, and volume can be expressed in a mathematical equation called the combined gas law.
Combined Gas Law
If you know the temperature, T, pressure, P, and volume, V, of a gas, you can determine k. Then you can use k to determine the volume of the gas for other pressures and temperatures.
319
Example
Weather Balloon at 25,000 Ft
A weather balloon is filled at sea level with 8000 L of helium. The pressure at sea level is 1 atm and the temperature is 17 °C. Calculate the volume of the balloon at 25,000 ft when the atmospheric pressure has decreased to 0.4 atm.
Solution
| P1 = 1.0 atm | P2 = 0.4 atm |
| V1 = 8000 L | V2 = ? |
| T1 = 290 K | T2 = 290 K |
Because pressure, volume, and temperature are all changing, you need to use the combined gas law. The first step in using the combined gas law is to make note of all the values for P, V, and T. Notice that we already know five out of the six values. Remember to convert °C to K. Then it is a matter of solving for V2.
| Use the combined gas law. |
|
| Determine the proportionality constant, k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Use k to solve for V2. |
|
|
|
|
| V2 = 16,422 L |
The balloon has expanded to about 16,000 L at this altitude.
[For a review of this math topic, see MATH Spotlight: Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Digits on page A-1.]
PRESSURE VERSUS TEMPERATURE
The example shows that decreasing air pressure has a greater effect on a weather balloon than decreasing temperature does. The volume of the balloon continues to expand as the balloon goes up in altitude, in spite of the decreasing temperature. The balloon eventually ruptures. There is a parachute on every weather balloon so that the weather instruments can be carried safely to the ground.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
320
What are the relationships among pressure, volume, and temperature for a sample of gas?
KEY TERM
combined gas law
If there is a situation involving a gas in which volume, temperature, and pressure are all changing, then you can use the combined gas law to determine the effects of changing two variables on the third variable. The value of the proportionality constant, k, is equal to PV/T. Therefore, P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2. Remember that the combined gas law works only in situations where the amount of gas involved remains the same.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What is the combined gas law? When do you apply it?
Does the temperature of the atmosphere have any effect on the volume of a weather balloon as it rises? Explain.
Reason and Apply
A gas collected in a flexible container at a pressure of 0.97 atm has a volume of 0.500 L. The pressure is changed to 1.0 atm. The amount of gas and the temperature of the gas do not change.
Will the volume of the gas increase or decrease? Explain.
Which equation should you use to calculate the new volume of the gas?
Calculate the volume of the gas at a pressure of 1.0 atm.
The gas pressure in an automobile tire was 1.0 atm at 21 °C. After an hour of driving, the tire heated up to 55 °C. Assume that the tire remained at constant volume and no gas escaped from the tire.
Did the gas pressure inside the tire increase or decrease? Explain.
Which equation should you use to calculate the new gas pressure of the tire?
Calculate the gas pressure of the tire at 55 °C.
The helium inside a balloon has a volume of 1.5 L, a pressure of 1.0 atm, and a temperature of 25 °C. The balloon floats up into the sky where the air pressure is 0.95 atm and the temperature is 20 °C.
Will the volume of the balloon increase or decrease? Explain.
Which equation should you use to calculate the new volume of the balloon?
Calculate the volume of the balloon at 20 °C and 0.95 atm.
Someone leaves a steel tank of nitrogen gas in the sun. The gas pressure inside the tank was 150 atm at 27 °C to begin with. After several hours, the internal temperature rises to 55 °C. What is the gas pressure in the tank now?
A car airbag is an example of a trapped gas. The airbag is designed to inflate to 65 L if you have an accident in a location where the temperature is 25 °C and the air pressure is 1.0 atm.
Determine the size of the airbag if you have an accident in the mountains where the temperature is −5 °C and the air pressure is 0.8 atm.
Suppose that you have an accident in a location in which the airbag inflates to 60 L. What has to be true about the temperature and air pressure in this location?