LESSON 100: You’re Fired!
THINK ABOUT IT
An automobile engine burns gasoline or ethanol. In a fireplace, you burn paper and wood. In a barbecue grill, you burn charcoal, lighter fluid, and an occasional marshmallow. While many substances burn, others—like sodium chloride, table salt, and water—do not.
What types of substances burn?
To answer this question, you will explore
Substances That Burn
Combustion Reactions
Substances That Burn
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Substances That Burn
HISTORY CONNECTION
HISTORY
CONNECTION
From the 1880s until the 1930s, photographers would ignite a sample of magnesium to produce the flash needed to take a picture. For safety and simplicity, flash bulbs, which contained magnesium wire or thin sheets of magnesium foil, were then invented. In the 1980s, these bulbs were replaced with electronic flashes.

A wide variety of substances can burn, or combust. Solids, such as wood and coal, liquids, such as methanol or kerosene, and gases, such as methane or hydrogen, all combust. Something besides phase must determine whether or not a material can burn.
Use the table to compare substances that combust with those that do not combust.
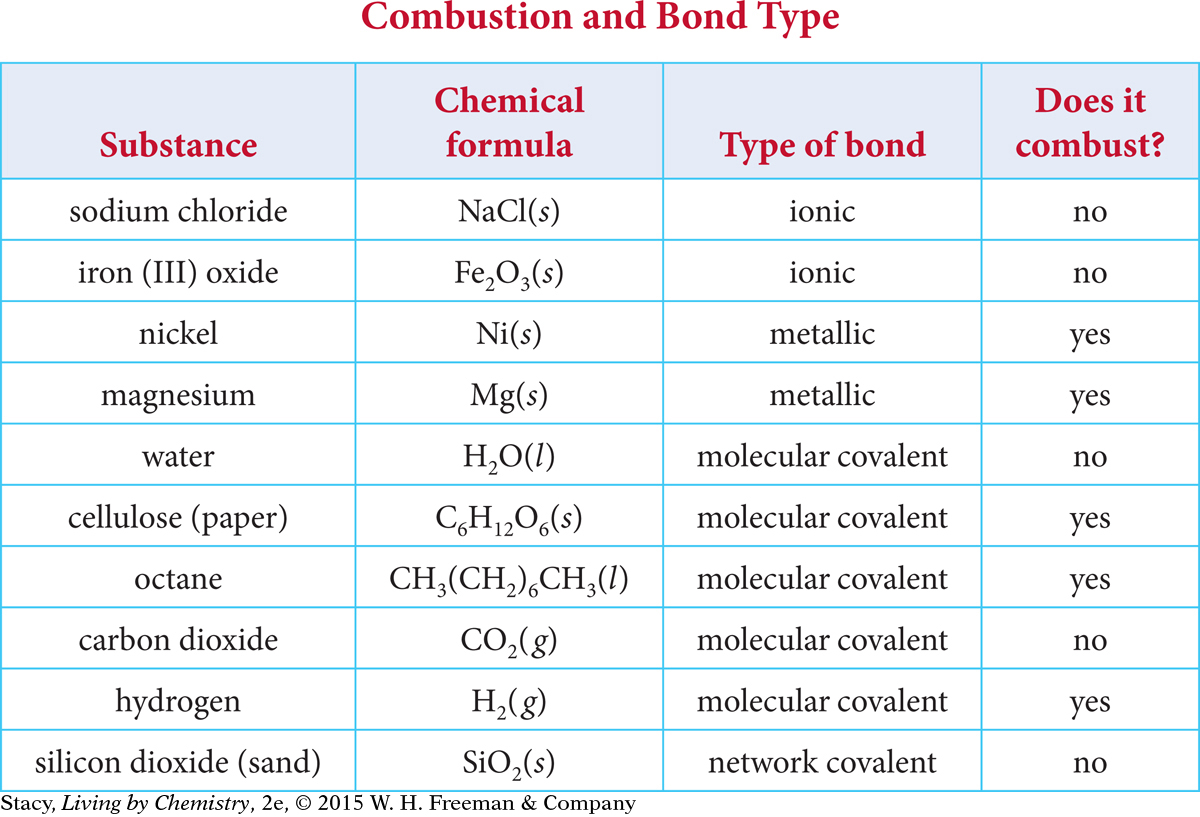
Using the information in the table, it is possible to make some generalizations about whether or not a substance will combust.
Most ionic compounds do not combust.
Most molecular covalent compounds do combust, especially those that contain carbon and hydrogen.
Most elemental metals combust.
Water and carbon dioxide do not combust.
Combustion Reactions
Combustion Reactions
Combustion is a chemical reaction in which an element or a compound reacts with oxygen and releases energy in the form of heat and light. When molecular covalent substances containing mainly carbon and hydrogen burn, they produce carbon dioxide and water. When metallic substances combust, they produce a metal oxide.
These are the chemical equations for the combustion of methane and of magnesium.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat + light
2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s) + heat + light
Oxygen is always a reactant in a combustion reaction. The other reactant in a combustion reaction is usually called a fuel. In these reactions, methane and magnesium are considered the fuels.
Notice that both reactions have heat and light on the product side of the equation. Remember, heat is not a substance, but chemists sometimes include it in the equation to keep track of energy changes.
HISTORY CONNECTION
HISTORY
CONNECTION
Around 1680, Irish physicist Robert Boyle experimented with creating a ready source of fire by coating a small piece of wood with sulfur to be struck against phosphorus-coated paper. Yet it was not till the mid-1800s that efficient manufacturing of the safety match was developed by Johan Lundstrom of Sweden.

If a compound is already combined with oxygen, it is not likely to combust and combine with more oxygen. This is why some molecular covalent compounds like water, H2O, and carbon dioxide, CO2, do not burn. Other examples include sulfur trioxide, SO3(g), and nitrogen dioxide, NO2(g).
FIRE—A SPECIAL TYPE OF COMBUSTION
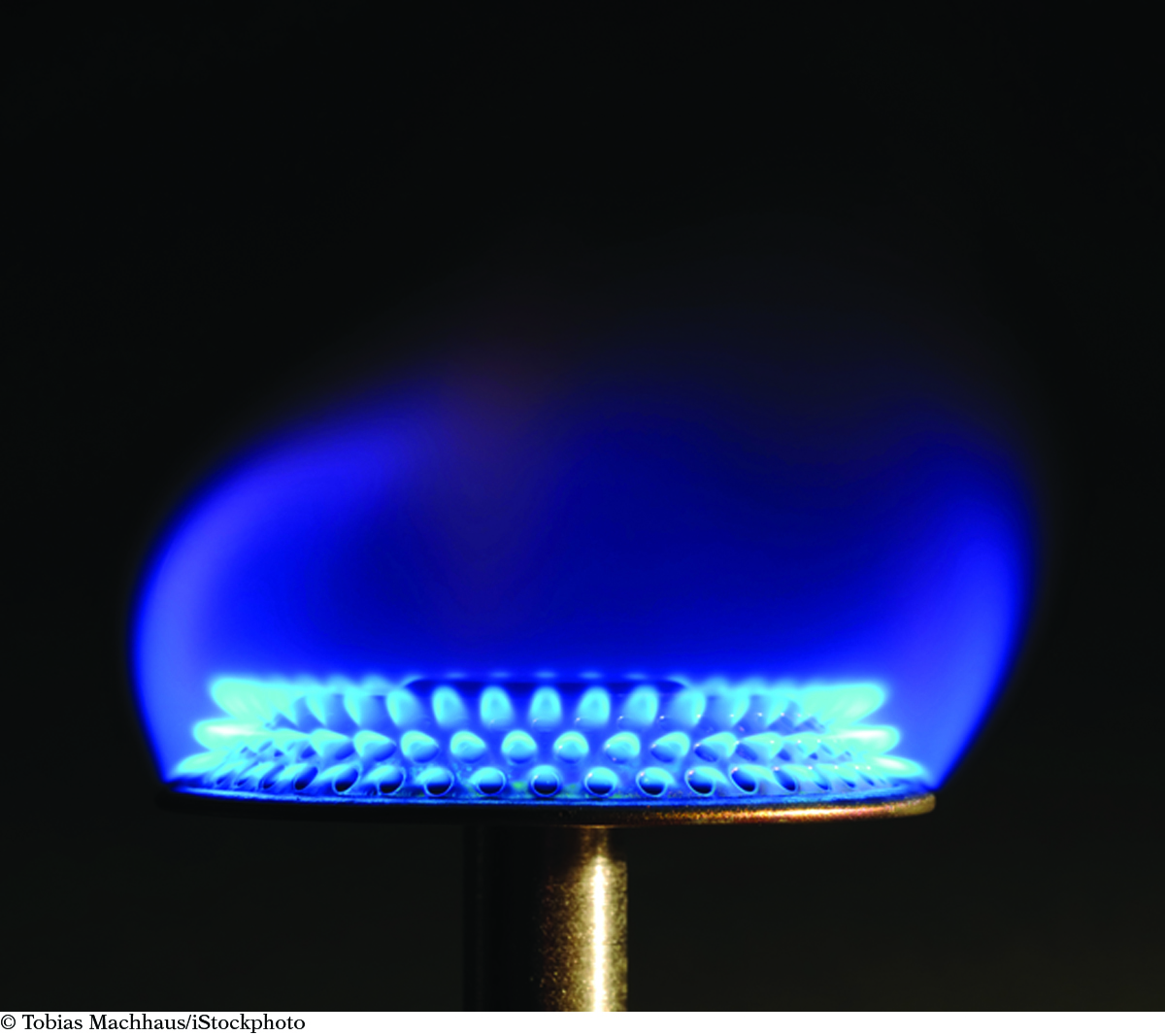

The photo shows the flame produced when methane burns. When we call something a fire, it is because a flame is present during the combustion reaction. The combustion of methane produces a fire.
Not all combustion reactions produce fire. The burning of magnesium produces a bright light but no flame. The light produced is so bright that it can damage your eyes. Most elemental metals are combustible but do not produce fire.
Ash is often left over after a fire. For molecular compounds, ash is composed of unburned or partially burned reactants. After combustion of metallic substances, the product may look like ash, but it is actually the metal oxide product of the reaction.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What types of substances burn?
KEY TERM
combustion
The process of burning is also referred to as combustion. Combustion is the combining of compounds or elements with oxygen through a chemical reaction that produces energy in the form of heat and light. Most ionic compounds do not combust. Most molecular covalent compounds are combustible. When molecular substances that are made mostly of hydrogen and carbon combust, they produce carbon dioxide and water. When metals combust, they form metal oxides, producing heat and light but no flame.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What should you look for in a chemical formula to decide if a compound or element will not combust?
Name three things that are true of every combustion reaction.
Reason and Apply
Which of the substances listed below will combust? Explain your reasoning.
Na2SO4(s)
Cu(s)
MgO(s)
Na(s)
C2H6O(l)
Ar(g)
Balance the following equations for combustion reactions. Circle the fuel for each reaction.
C2H6(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
C6H12O6(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
C21H24N2O4(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + NO2(g)
C2H5SH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + SO2(g)
What are the products of these combustion reactions? Write balanced chemical equations for each reaction.
C7H6O(l) + O2(g) →
CH3COCH3(l) + O2(g) →
H2C2O4(s) + O2(g) →
Ca(s) + O2(g) →
Li(s) + O2(g) →
Si(s) + O2(g) →