LESSON 108: Metal Magic: Oxidation
THINK ABOUT IT
If you examine a handful of pennies, chances are some of them will be a bright coppery color and others will be discolored and dull. These tarnished pennies have reacted with the oxygen in the air, just as a fuel does when it burns. But is this a form of combustion?
What happens when metals react with oxygen?
To answer this question, you will explore
Oxidation
Electron Transfer
Oxidation
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Oxidation
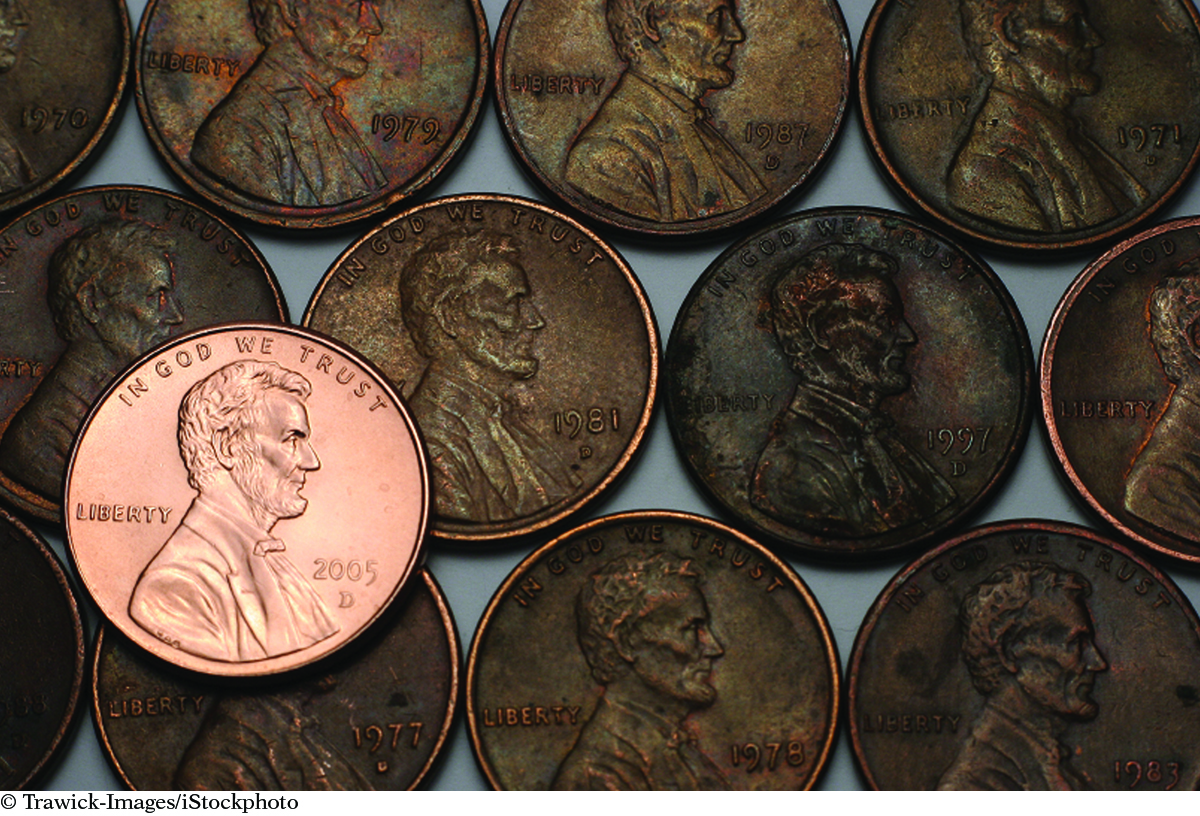

No penny stays bright and shiny forever. Eventually, they all become dark and dull when the copper metal on the surface forms copper (II) oxide and other copper compounds. This reaction happens very slowly at room temperature. The reaction is also exothermic, but it happens so slowly the heat is difficult to detect.
The reaction of copper with oxygen is described by this equation.
HEALTH CONNECTION
HEALTH
CONNECTION
Antioxidants are molecules that can slow or prevent the oxidation of other molecules. Antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables can cancel out the cell-damaging effects of free radicals. This is one of the reasons why eating fruits and vegetables can lower a person’s risk for heart disease, neurological disease, and some forms of cancer. Berries are high in antioxidants.

2Cu(s) + O2(g)→2CuO(s)
On the other hand, if magnesium is held to a flame, it reacts rapidly and violently with oxygen, producing an almost blinding light. This metal is also combining with oxygen, but it is a much more exothermic reaction and happens quite rapidly once it gets started.
2Mg(s) + O2(g)→2MgO(s)
Copper and magnesium are just two examples of metals reacting with oxygen. Under the right conditions, all metals will react with oxygen. This process is called oxidation. Both combustion of molecules and tarnishing of metals are forms of oxidation. Compare the oxidation of two metals with a common combustion reaction:
Oxidation of copper: 2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
Oxidation of magnesium 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
Combustion of methane:CH4(g) + 202(g) → CO2(g)+2H2O(g)
The reaction of oxygen with a metal produces a solid, whereas the reaction of oxygen with a molecular substance produces two gases. But the reactions have several characteristics in common. This table shows a comparison of the two types of reactions:
CONSUMER CONNECTION
CONSUMER
CONNECTION
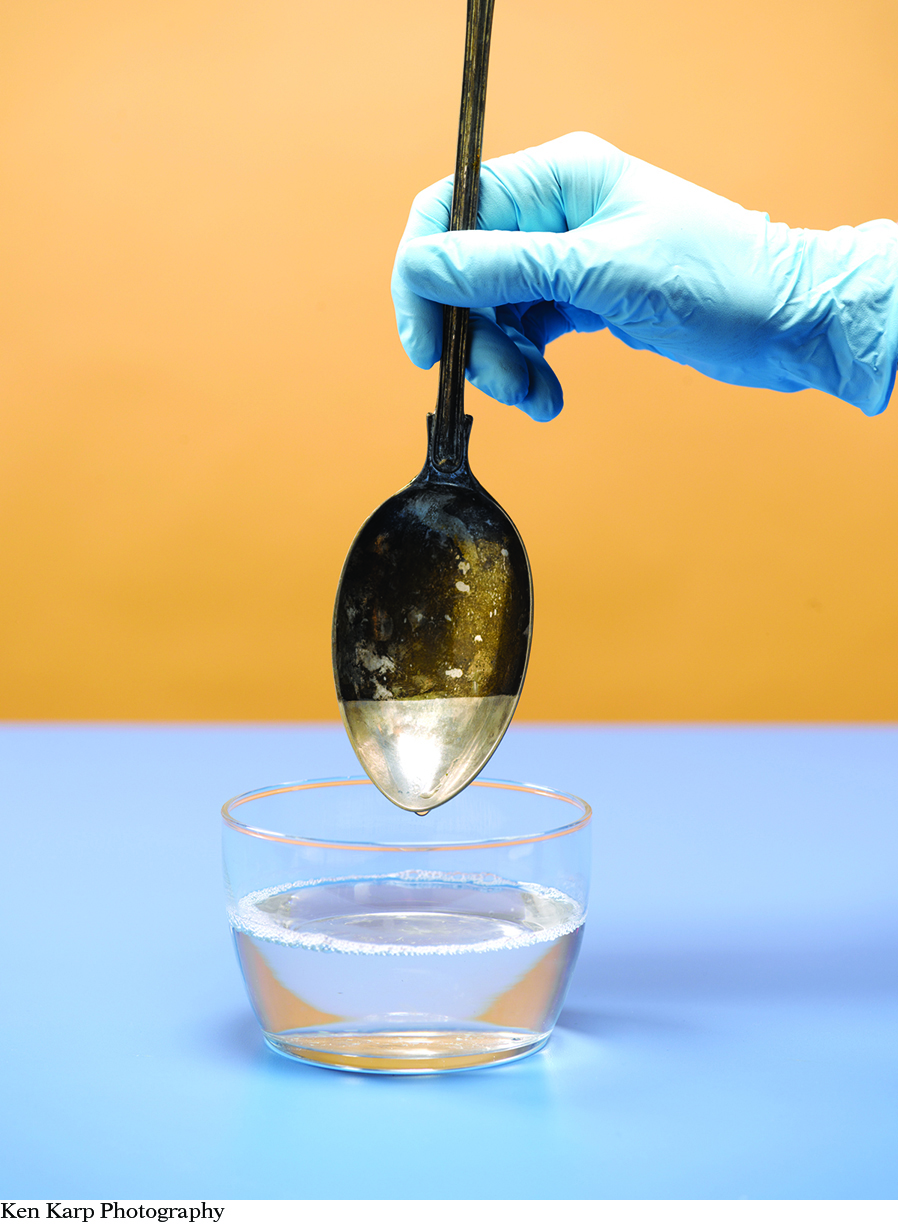
Over time, silver oxidizes and becomes dull. One way to make it shiny again is to place it in a solution of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) with aluminum foil. Within a few minutes, the silver becomes shiny again and the aluminum oxidizes instead.

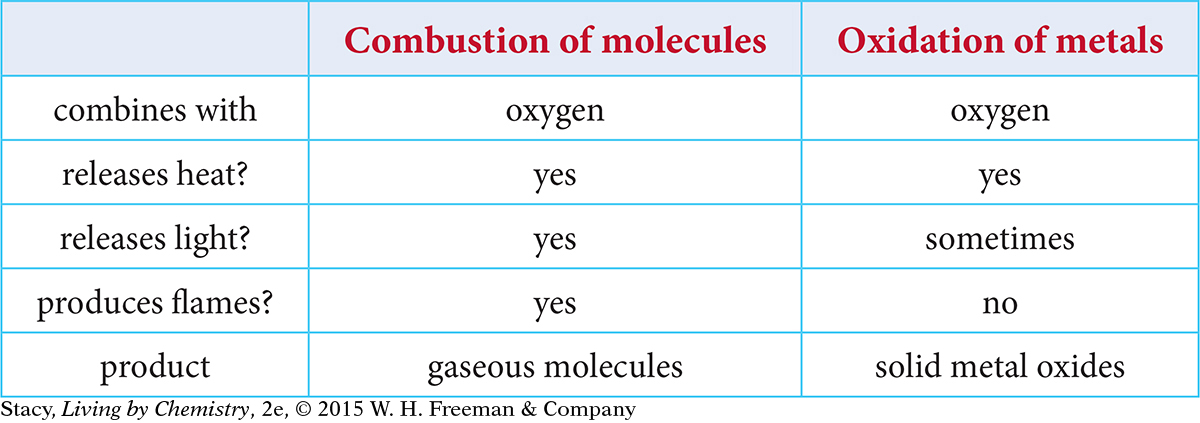
Oxidation of metals transfers energy to the surroundings, just like combustion of molecular covalent compounds. This energy is in the form of heat and sometimes a bright light. However, you can see that the products of oxidation of metals and combustion of molecular compounds are different.
FLAME VERSUS GLOW
Flames are composed largely of superheated gases. When metals oxidize, they might glow with a very bright light, but there is no flame. The bright light is due to the excitation of electrons. Recall that the colored flame tests in Unit 1: Alchemy Lesson 17 were also the result of excited electrons changing energy levels. The bright light from the oxidation of metals may resemble a flame, but it is not a flame.
Electron Transfer
Electron Transfer
All of the oxidation reactions discussed so far involve oxygen. However, oxidation is defined more broadly as any reaction in which an atom transfers electrons to oxygen or another atom. When magnesium oxide is formed, the magnesium atoms transfer electrons to the oxygen atom. When this happens, we say that the magnesium has been oxidized.
Big Idea
Big Idea
When an atom or ion is oxidized, it loses electrons.
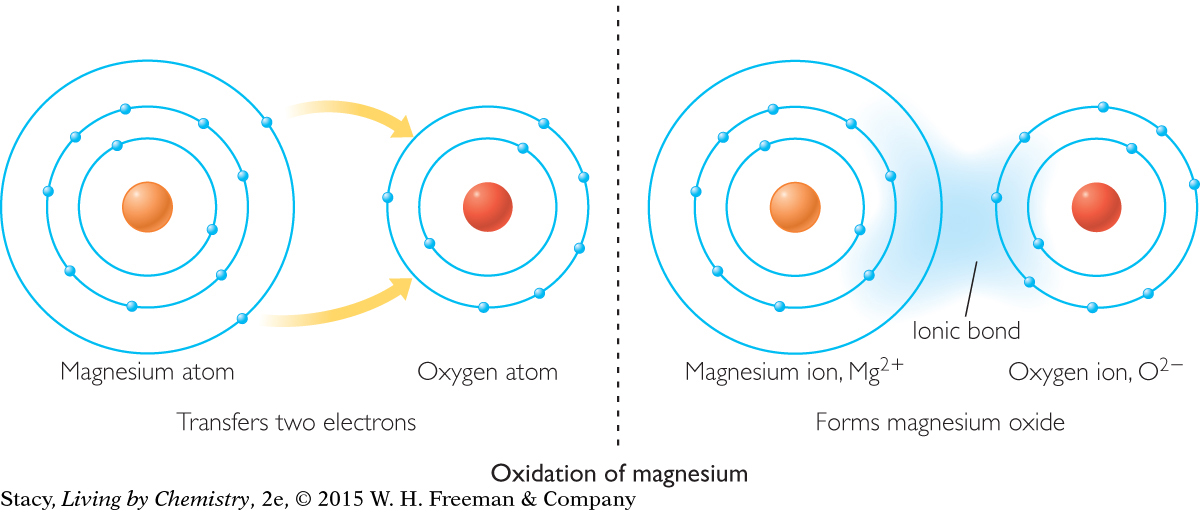
The shell models show a magnesium atom being oxidized. When magnesium is oxidized, it forms Mg2+ ions.
Recall that metal elements generally have one, two, or three electrons in their valence electron shells. Having such a small number of electrons in the valence shell makes it more likely that metal atoms will lose electrons, forming cations that have a charge of +1, +2, or +3. Through electron transfer, metal atoms form ionic bonds with nonmetal atoms.
Molecular covalent compounds also transfer electrons to oxygen when they react. Therefore, combustion reactions are considered oxidation reactions.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What happens when metals react with oxygen?
KEY TERM
oxidation
Metal atoms react with oxygen to form metal oxides. When metal oxides form, heat is released, and sometimes, an intense bright light is emitted. This process is called oxidation. Molecular substances can also be oxidized, as is the case in combustion. However, no flames are present when metals oxidize. This is partly what differentiates the oxidation of metals from the oxidation of molecular substances. Oxidation occurs whenever an atom, ion, or molecule transfers electrons to another atom, ion, or molecule.
Exercises
Reading Questions
How does oxidation of a metal compare to combustion of a covalent compound?
Explain what happens when magnesium metal is oxidized.
Reason and Apply
Write balanced equations for the reactions of calcium, chromium, and lithium with oxygen. Identify the charge on the cation and the charge on the anion for each product.
Ca(s) + O2(g) → CaO(s)
Cr(s) + O2(g) → Cr2O3(s)
Li(s) + O2(g) → Li2O3(s)
Circle the elements that are oxidized in the chemical equations in part a.
Draw shell models for lithium and oxygen atoms to show the transfer of electrons during oxidation.
Draw shell models for silicon and oxygen atoms to show the transfer of electrons during oxidation.