LESSON 23: Alchemy of Paint: Transition Metal Chemistry
THINK ABOUT IT
For thousands of years, human beings have expressed themselves through painting. Over time, people have discovered pigments with a wide variety of brilliant colors. Almost all paint pigments contain a transition metal cation.
What types of compounds are made from transition metals?
To answer this question, you will explore
Transition Metal Compounds
Charges on Transition Metal Cations
Transition Metal Compounds
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Transition Metal Compounds
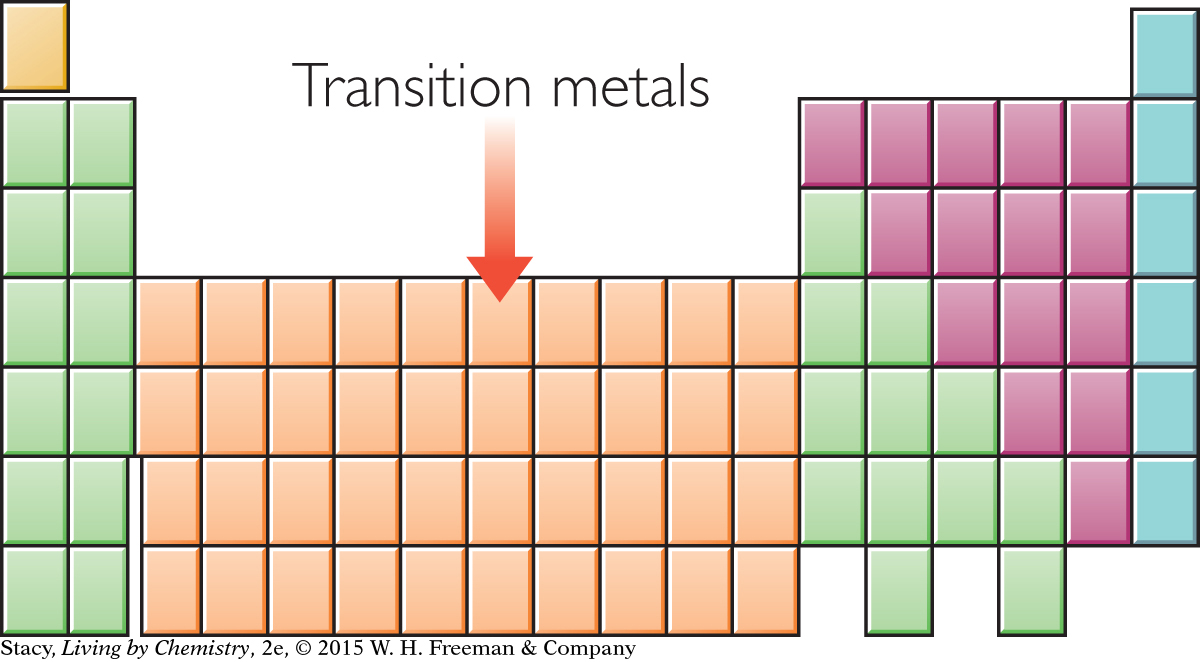
The transition metals are named for their location in the middle of the periodic table. Many of the metals that we use in our daily life, such as copper, iron, nickel, silver, and gold, are located in this part of the periodic table.
HISTORY CONNECTION
HISTORY
CONNECTION
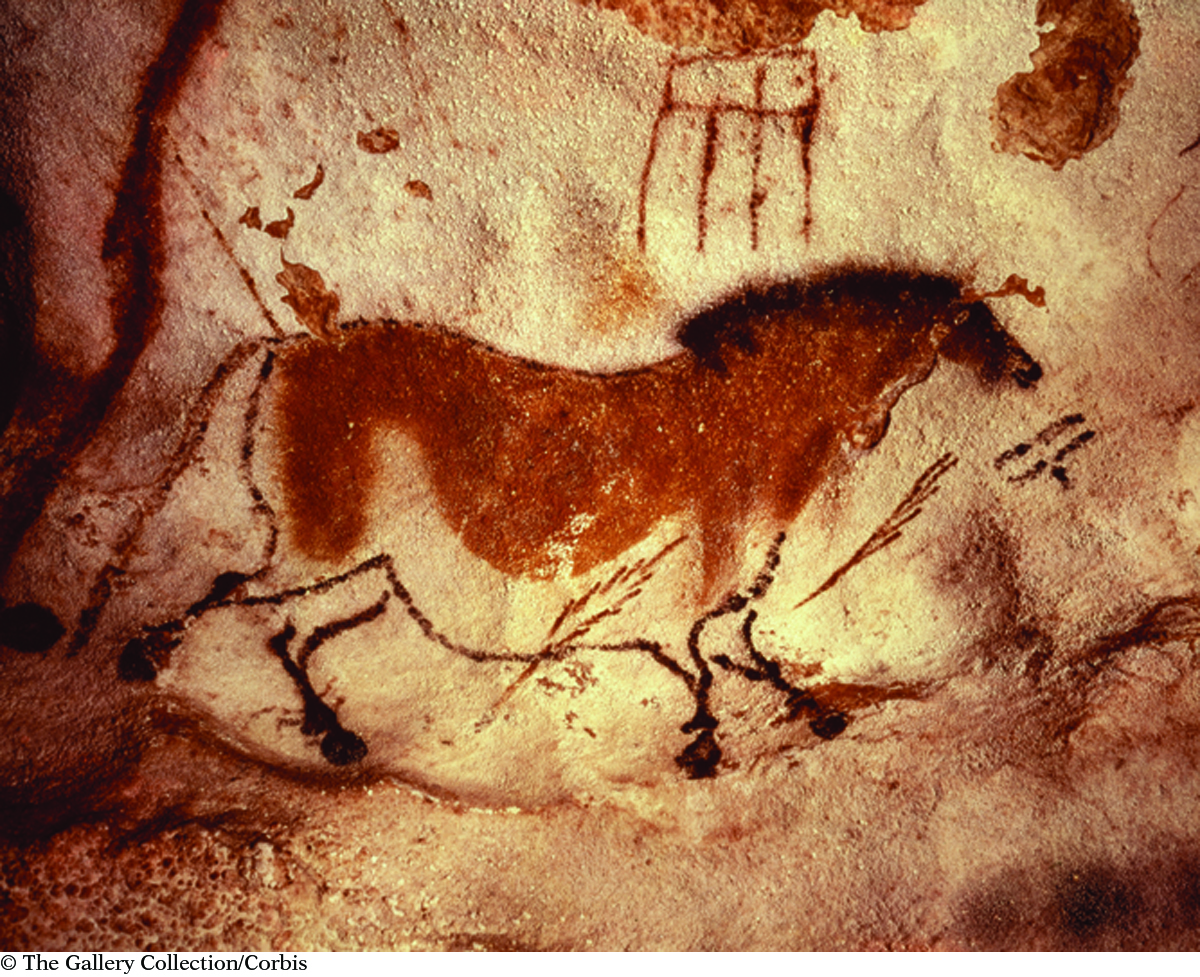
Ionic compounds containing transition metals were used to create ancient cave paintings. This cave painting is from Lascaux, France, and is approximately 17,000 years old.

Transition metal compounds tend to be brightly colored. Hence, they are commonly found as pigments used to color paints. For example, red ochre is a pigment made from iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3. It is thought to be the first pigment ever used by human beings for creating art.
The ancient alchemists worked with the transition metals a great deal, mostly because these metals were closer in their properties to gold than to other metals. As a result, alchemists occasionally discovered paint pigments while trying to create gold.
The table on the next page lists various paint pigments that you can buy at an art store. Examine the data. Pay particular attention to the different charges on the transition metal cations.
Notice that the chemical names are a bit unusual. In the middle of each chemical name for a transition metal compound is a Roman numeral: I, II, III, or IV (meaning 1, 2, 3, or 4). This Roman numeral indicates what the charge is on the transition metal cation. Thus, cobalt (II) oxide has a +2 charge on the cobalt ion, and manganese (IV) carbonate has a +4 charge on the manganese ion.
FINE ART CONNECTION
FINE ART
CONNECTION
Some paint pigments have more complicated chemical compositions than the compounds shown in the table. For example, the pigment Egyptian blue, shown below, is calcium copper silicate, with the formula CaCuSi4O10. There are three different cations and one type of anion.

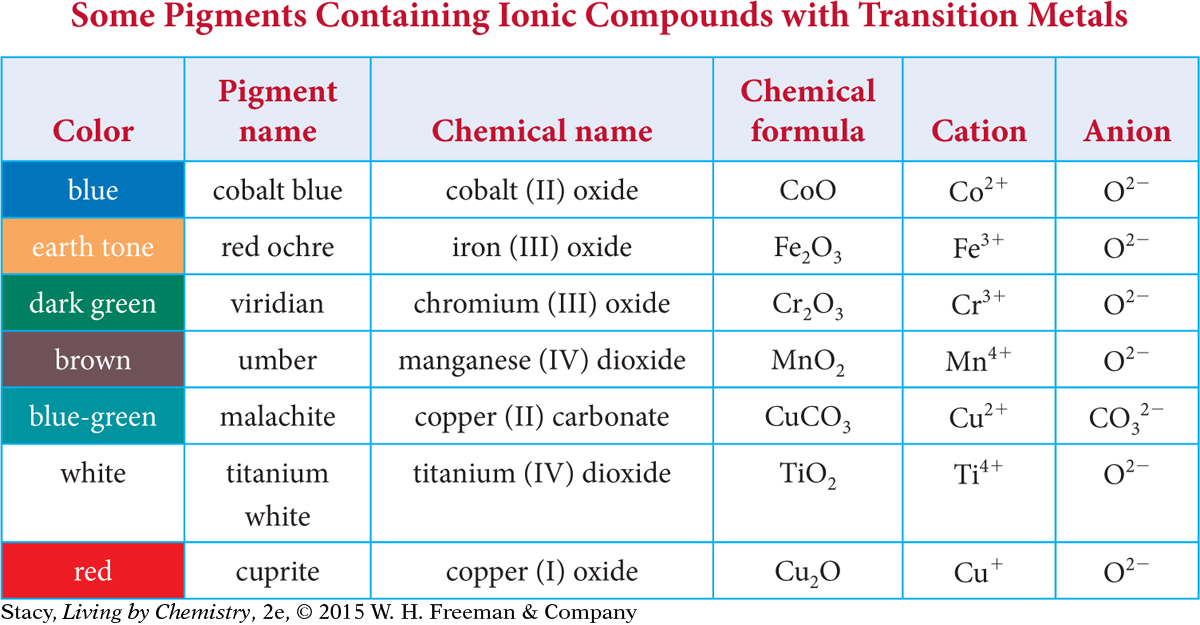
Note that copper, Cu, has a charge of +1 in copper (I) oxide, Cu2O, and a charge of +2 in copper (II) carbonate, CuCO3.
There is an older naming system for the transition metal ionic compounds. In this system, Fe2O3 and FeO were called ferric oxide and ferrous oxide. The “-ic” ending indicated the higher ion charge and the “-ous” ending referred to the lower ion charge. So Co2+ was cobaltous and Co3+ was cobaltic.
Charges on Transition Metal Cations
Charges on Transition Metal Cations
Recall that you can determine the charges on the main group metals and nonmetals from their positions on the periodic table. For example, all of the alkali metals, Group 1A, form cations with +1 charges. All of the halogens, Group 7A, form anions with –1 charges. However, you cannot simply determine the charge of a transition metal ion from its location on the periodic table. Instead, it is necessary to use chemical formulas to determine the charge of the ion.
To determine the charges on transition metal cations, you use the charges on ions that you do know and apply the rule of zero charge. For example, iron combines with oxygen to form both Fe2O3 and FeO. Oxygen is a main group anion, so you can use the periodic table to determine that oxygen atoms form ions with a –2 charge. The rule of zero charge states that the charges on the ions in the compound should add up to zero. Working backward, you can determine the charge on the iron cations in each compound.
Important to Know
Unlike the main group metals, most transition metals can form several ions with different charges.
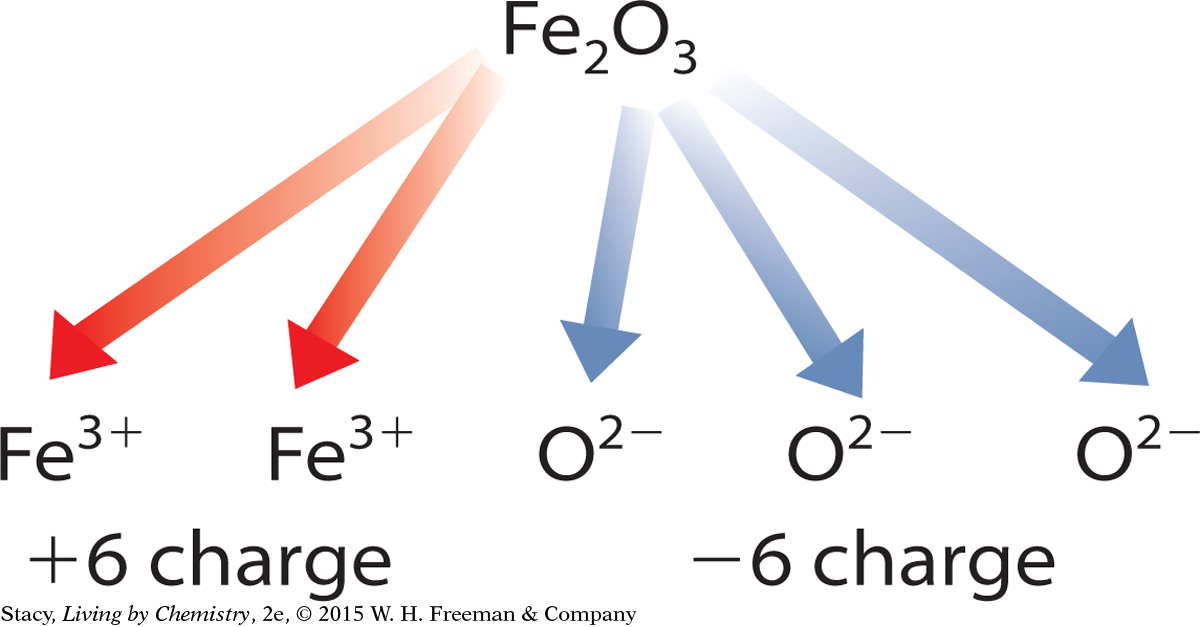
The charges on the three oxygen anions add up to –6. Each iron cation must have a charge of +3.
|
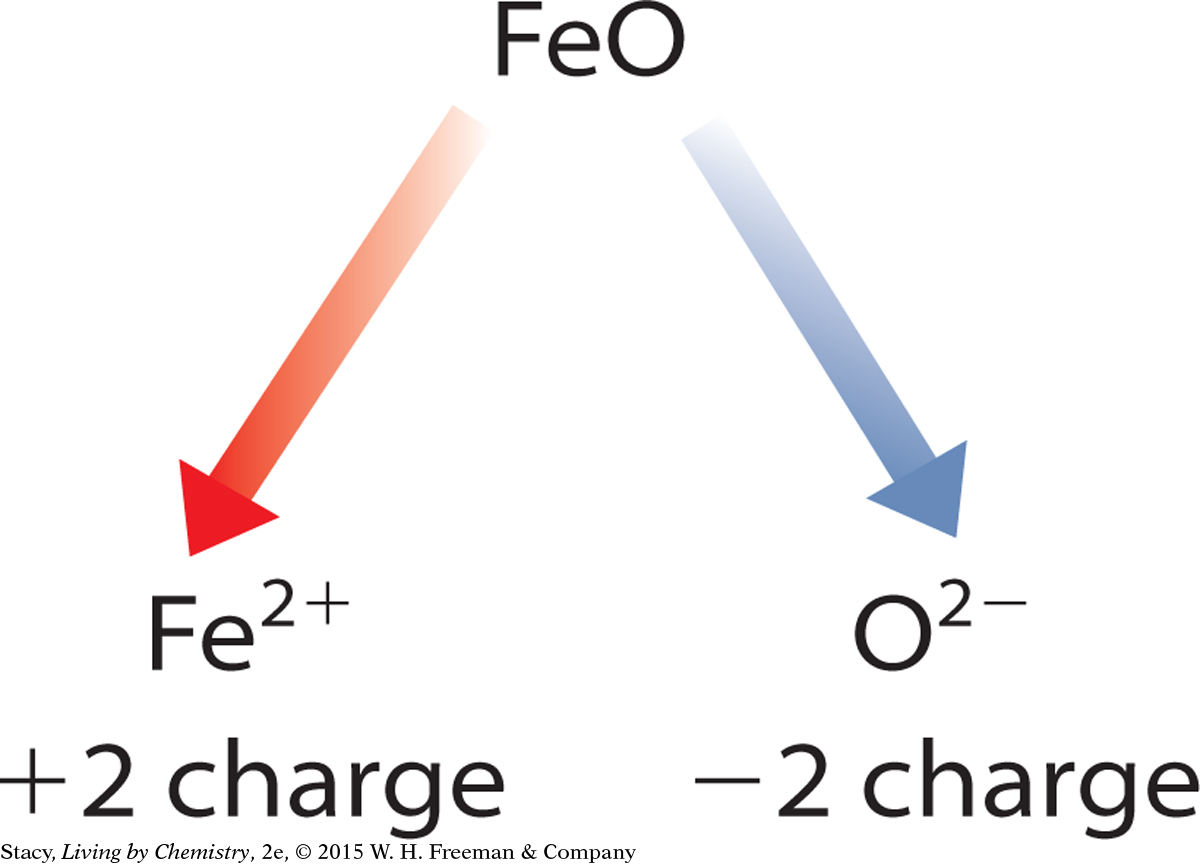
The charge on the single oxygen anion is –2. The iron cation must have a charge of +2.
|
These two different iron compounds are formally named iron (III) oxide and iron (II) oxide.
CONSUMER CONNECTION
CONSUMER
CONNECTION
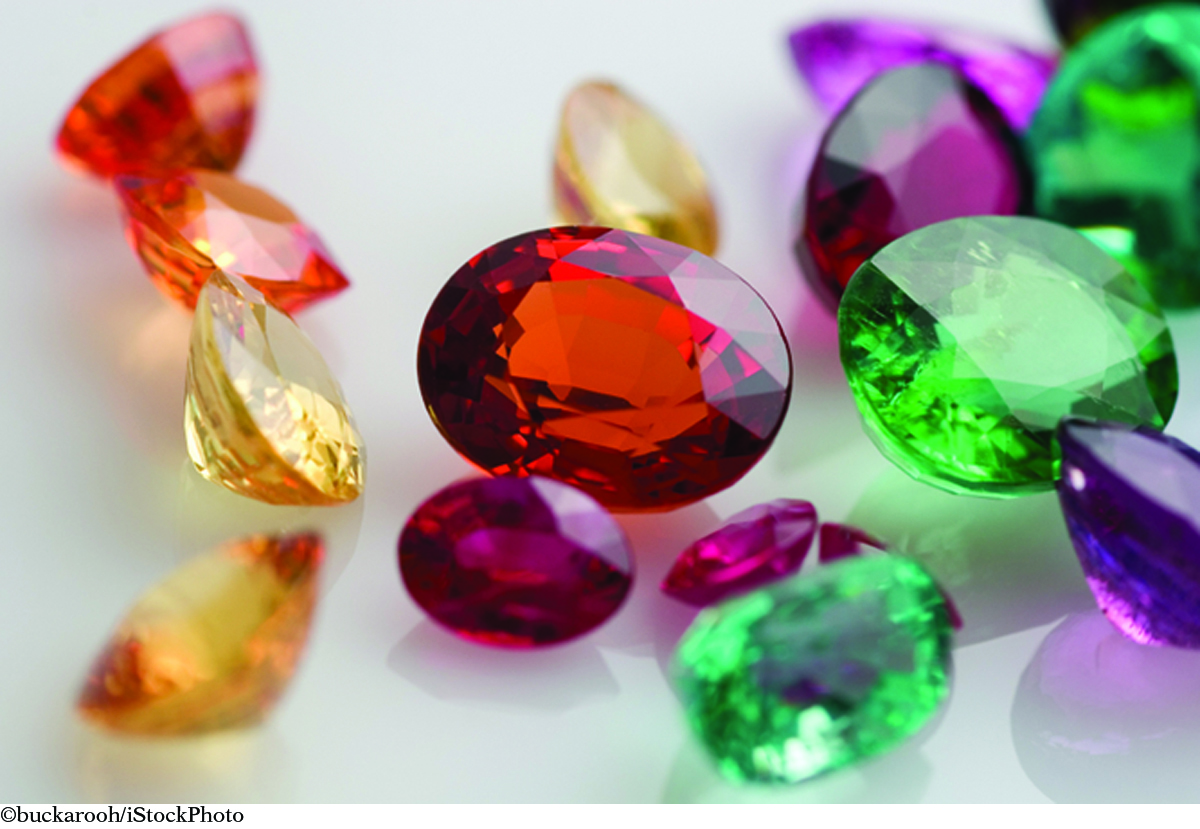
Transition metal ions are responsible for colors in different-colored gem stones. For example, chromium ions, Cr3+, are present in red ruby, green emerald, and pink topaz. Iron ions, Fe3+, are present in citrine and yellow sapphire, while Fe2+ ions make sapphires blue. The transition metals in crystals absorb certain colors of light while allowing other colors to pass through and be seen.

Example
Transition Metal Compounds
Determine the charge on the transition metal cation in each of the compounds given. Then name the compound.
Ag2S
Fe(NO3)3
Solution
You can determine the charge on each transition metal cation from the charges on the anions using the rule of zero charge.
Sulfur anions have a charge of –2. So each silver cation must have a charge of +1, Ag+. The compound name is silver (I) sulfide.
The polyatomic ion is nitrate with a –1 charge. There are three nitrate ions, so the iron cation must have a charge of +3, Fe3+. The compound name is iron (III) nitrate.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What types of compounds are made from transition metals?
Transition metals bond with nonmetal atoms to form ionic compounds. Unlike the main group atoms, most transition metals can have more than one ion charge. The best way to determine the charge on a transition metal cation is to work backward from the anion, whose charge is known. When naming ionic compounds, a Roman numeral is used to indicate the charge on the transition metal cation. Colorful paint pigments are frequently composed of transition metal compounds.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What does the Roman numeral in a chemical name indicate?
Explain how you determine the charge on a transition metal cation from the chemical formula.
Reason and Apply
Determine the charge on the transition metal cation in each of the compounds listed. Then name each compound.
HgS
CuCO3
NiCl2
Co(NO3)3
Cu(OH)2
FeSO4
Write the cation and anion in each compound, then determine the correct chemical formula.
copper (II) sulfide
nickel (II) nitrate
iron (II) carbonate
cobalt (II) sulfate
iron (III) carbonate
chromium (VI) oxide
Cobalt violet is a paint pigment discovered in 1859. If the cation for this compound is Co2+ and the anion is PO43–, what is the chemical formula?