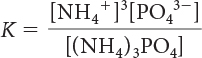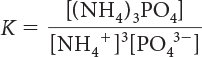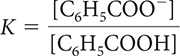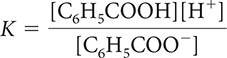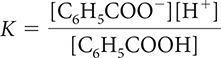STANDARDIZED TEST PREPARATION
Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer.
Use the following to answer Exercises 1–3.
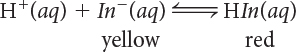
Question 1
1. Which correctly identifies the acid and base forms of the indicator?
H+ is the acid form of the indicator; HIn− is the base form of the indicator.
In− is the acid form of the indicator; HIn is the base form of the indicator.
HIn is the acid form of the indicator; In− is the base form of the indicator.
HIn is the acid form of the indicator; H+ is the base form of the indicator.
Question 2
2. Which statement correctly describes the color of the solution containing the indicator when it is orange?
Only the H+ ions are present in the solution.
Only In− anions are present in the solution.
Only the HIn molecules are present in the solution.
There is a mixture of both the In− anions and HIn molecules in solution.
Question 3
3. What will happen to the reaction as H+ ions are added to the solution?
The color of the solution will change from red to yellow.
The color of the solution will change from yellow to red.
The color of the solution will remain yellow.
The color of the solution will remain red.
Question 4
4. For the cabbage juice indicator, what might be the pH of the solution when the color is red?
2
7
9
12
Question 5
5. Which of these is a reversible process?
lighting a safety match
burning a log on a fire
water freezing to become ice
baking a cake
Question 6
6. Carbon dioxide binds to hemoglobin, Hb, in your blood to form [CO2 : hemoglobin] in a reversible process. Which of the following correctly represents a balanced chemical equation for this process?
[CO2 : hemoglobin] ⇋ CO2 + hemoglobin
CO2 + hemoglobin ⇋ [CO2 : hemoglobin]
CO2 + hemoglobin → [CO2 : hemoglobin]
I only
II only
III only
Both I and II
Question 7
7. The particle views below show 10 molecules of each of three sweeteners with their relative sweetness. Which statement correctly describes sucrose?
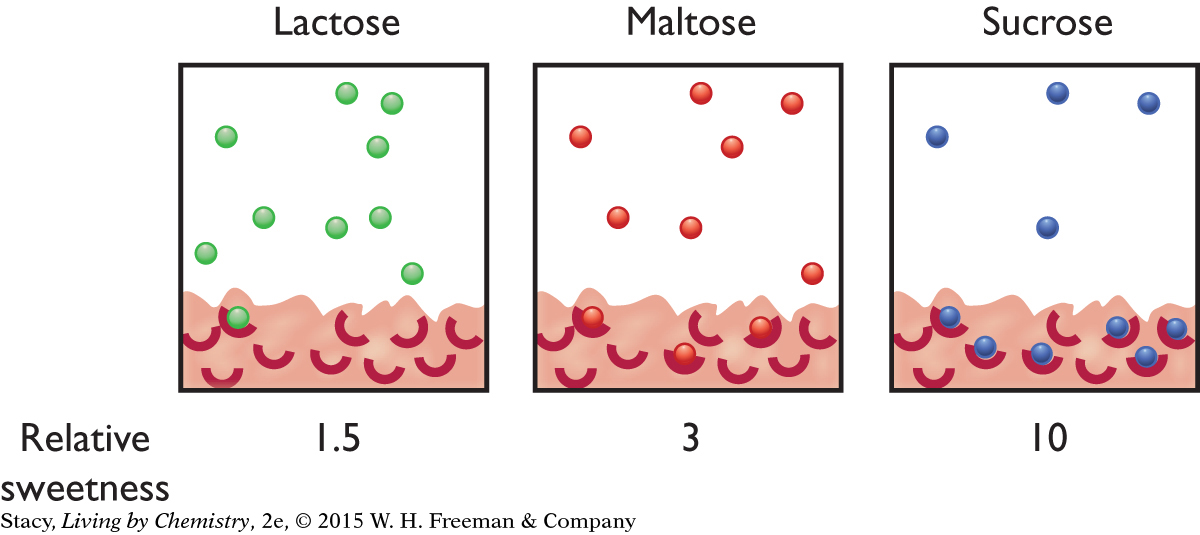
Sucrose molecules are detected as sweeter because more are attached to the receptors.
Sucrose molecules have weaker intermolecular attractions with receptors than maltose molecules.
More sucrose molecules remain in the saliva than either maltose or lactose molecules.
Sucrose molecules are the sweetest because they bind to all available receptors.
Question 8
8. An octane molecule is reversibly held weakly to a smell receptor in the nose. What might be responsible for reversibly holding octane to smell receptors?
hydrogen bonds
covalent bonds
dipole-dipole interactions
intermolecular forces
Question 9
9. Which correctly describes a reversible process?
The forward and reverse reactions can occur at the same time.
A reversible process proceeds in both the forward and reverse directions.
In a reversible chemical reaction system, the products and the starting substances are both present.
All of the above are true of a reversible process.
Question 10
10. Which chemical process might this graph represent?
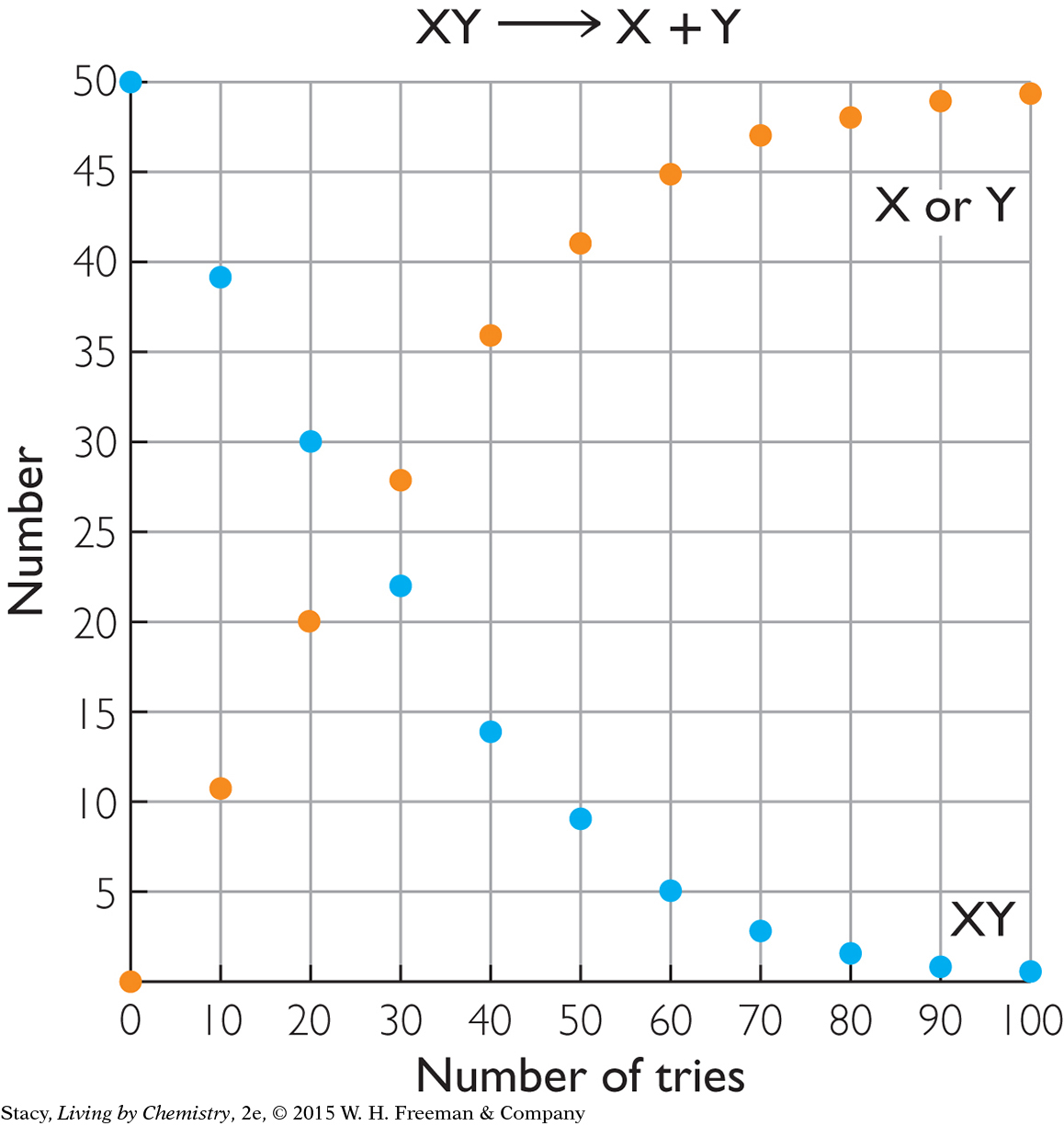
a salt such as NaCl, which dissolves partially to Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq) to form a saturated solution
a strong acid such as HBr, which separates to H+(aq) + Br−(aq)
an acid-base indicator, HIn, which separates to H+(aq) + In−(aq)
a molecule bound to a receptor, which separates to a molecule and the empty receptor
Question 11
11. Consider this chemical reaction: AB ⇋ A + B. In a rigid container, 25 mol of AB decompose to reach equilibrium. The amounts of A and B are measured over time, and the values are recorded in the table below. At 240 s, which statement is correct?
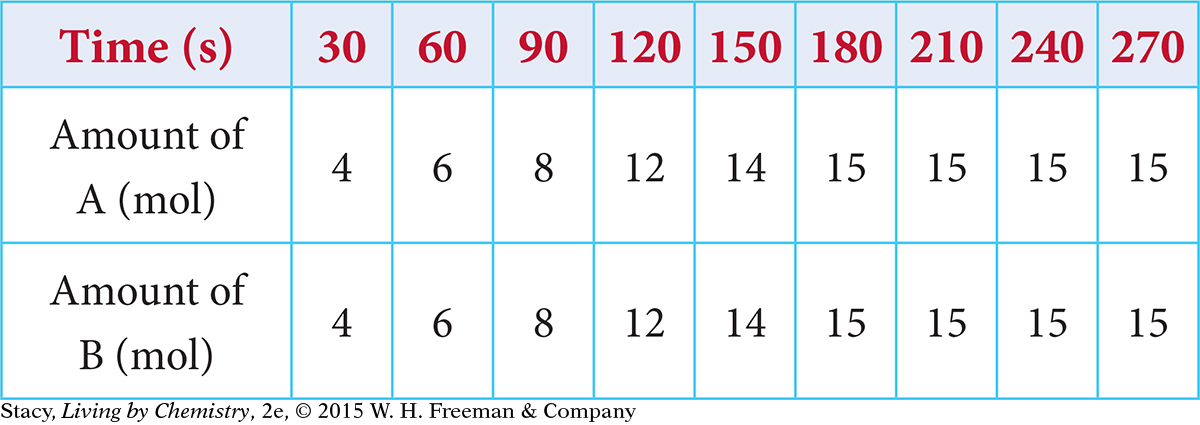
The concentrations of AB, A, and B are equal.
The concentration of A is greater than the concentration of AB.
The concentration of AB is greater than the concentration of B.
The system is not at equilibrium.
Use this graph to answer Exercises 12–14. The graph represents the chemical reaction:
A2(g) + 3B2(g) ⇋ 2AB3(g)
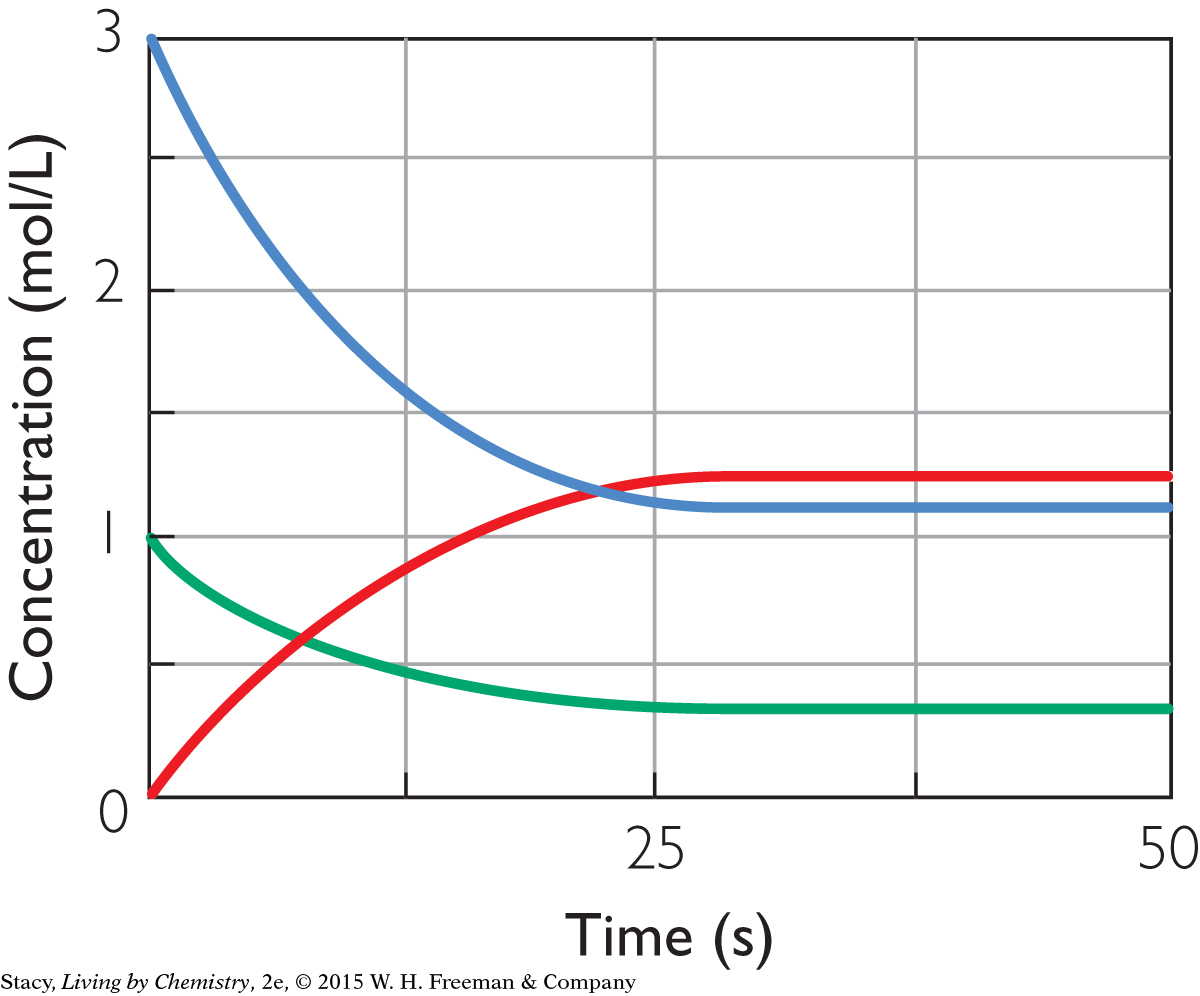
Question 12
12. Given that the initial concentration of A2 is 1.0 M and the initial concentration of B2 is 3.0 M, what are the equilibrium concentrations of the starting substances and the products?
[A2] = 0.37 M [B2] = 1.1 M [AB3] = 1.2 M
[A2] = 0.40 M [B2] = 1.5 M [AB3] = 0.50 M
[A2] = 1.0 M [B2] = 1.5 M [AB3] = 0.50 M
[A2] = 1.2 M [B2] = 1.1 M [AB3] = 0.37 M
Question 13
13. Which correctly describes the reaction process at equilibrium?
The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
The concentration of the starting substances equals the concentration of the products.
The rate of the forward reaction is faster than the rate of the reverse reaction.
The concentrations of the starting substances are greater than the concentration of the products.
Question 14
14. How long did it take for this reaction to reach equilibrium?
6 s
12 s
25 s
50 s
Use this table to answer Exercises 15–18.
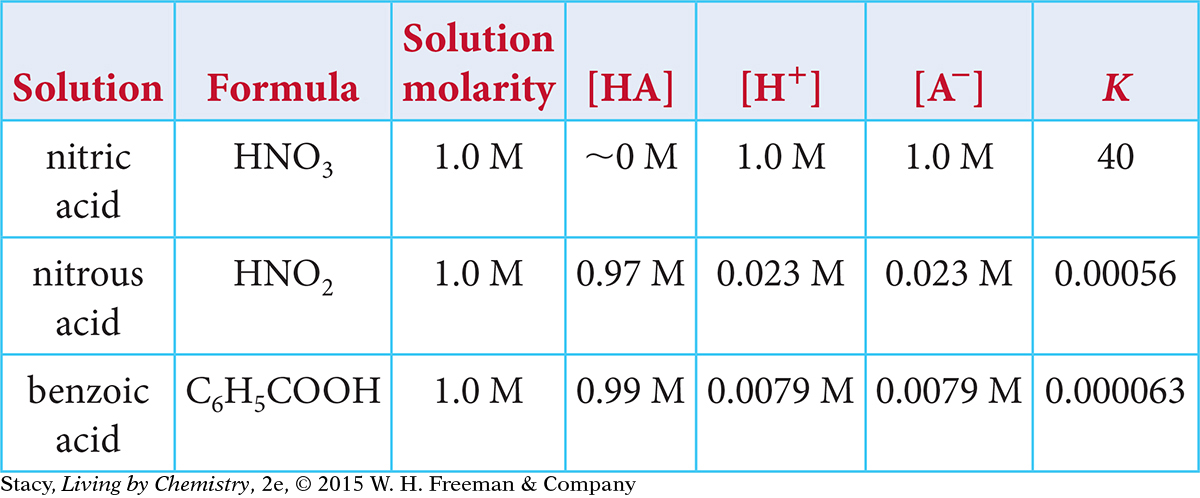
Question 15
15. Which is the correct chemical equation for the dissociation of nitrous acid, HNO2?
HNO2(aq) ⇋ H+(aq) + NO2−(aq)
H+(aq) + NO2−(aq) ⇋ HNO2(aq)
HNO2(aq) → H+(aq) + NO2−(aq)
H+(aq) + NO2−(aq) → HNO2(aq)
Question 16
16. Which correctly describes the dissociation of benzoic acid at equilibrium?
There are equal concentrations of C6H5COO− and H+ ions.
There are more C6H5COOH molecules than C6H5COO− and H+ ions.
The pH of the solution will be between 2 and 3.
All of the above are true statements.
Question 17
17. Which correctly describes the three reactions based on the value of their equilibrium constants?
Both nitrous acid and benzoic acid dissolve and partially dissociate in water.
Both nitrous acid and benzoic acid dissolve and completely dissociate in water.
Both nitrous acid and nitric acid dissolve and partially dissociate in water
Both nitrous acid and nitric acid dissolve and completely dissociate in water.
Question 18
18. Which of the following is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the dissociation of benzoic acid?
Question 19
19. The dissociation of alizarin yellow indicator, a weak acid, is given below.
HIn(aq) ⇋ H+(aq) + In−(aq) K = 3.4 × 10−11
What is the pH value of a 1.0 M solution of alizarin yellow, HIn?
pH = 3.3
pH = 5.2
pH = 10.5
pH = 10.7
Question 20
20. Which is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the following reaction?
(NH4)3PO4(s) ⇋ 3NH4+(aq) + PO43–(aq)
K = [(NH4)3PO4]
K = [NH4+]3 [PO43–]