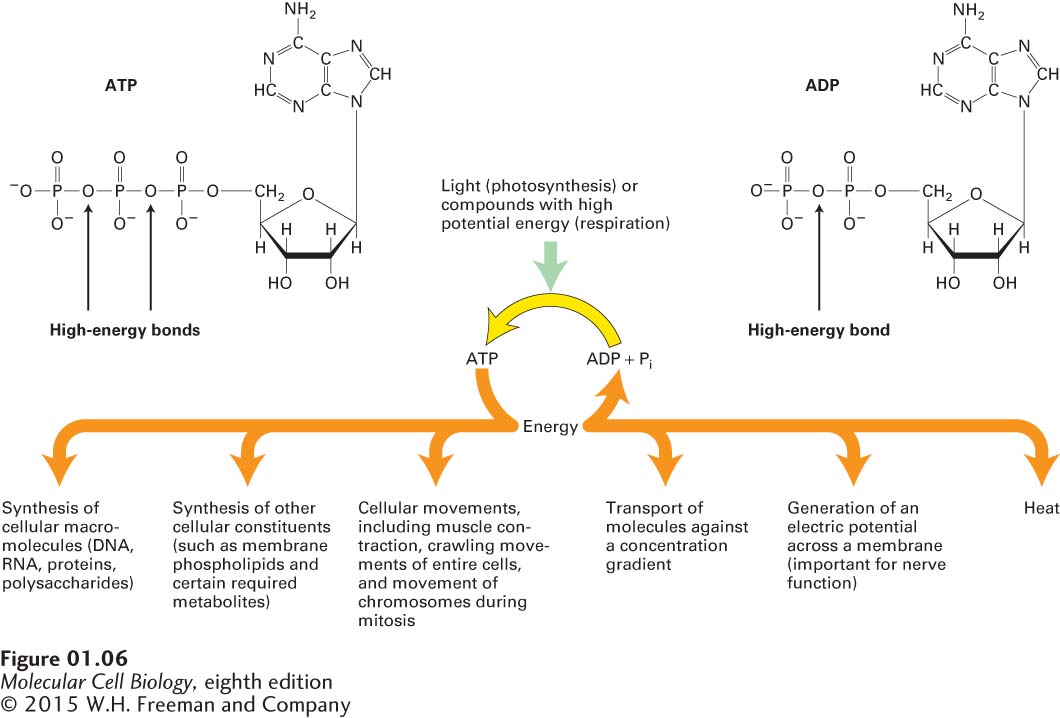
FIGURE 1-