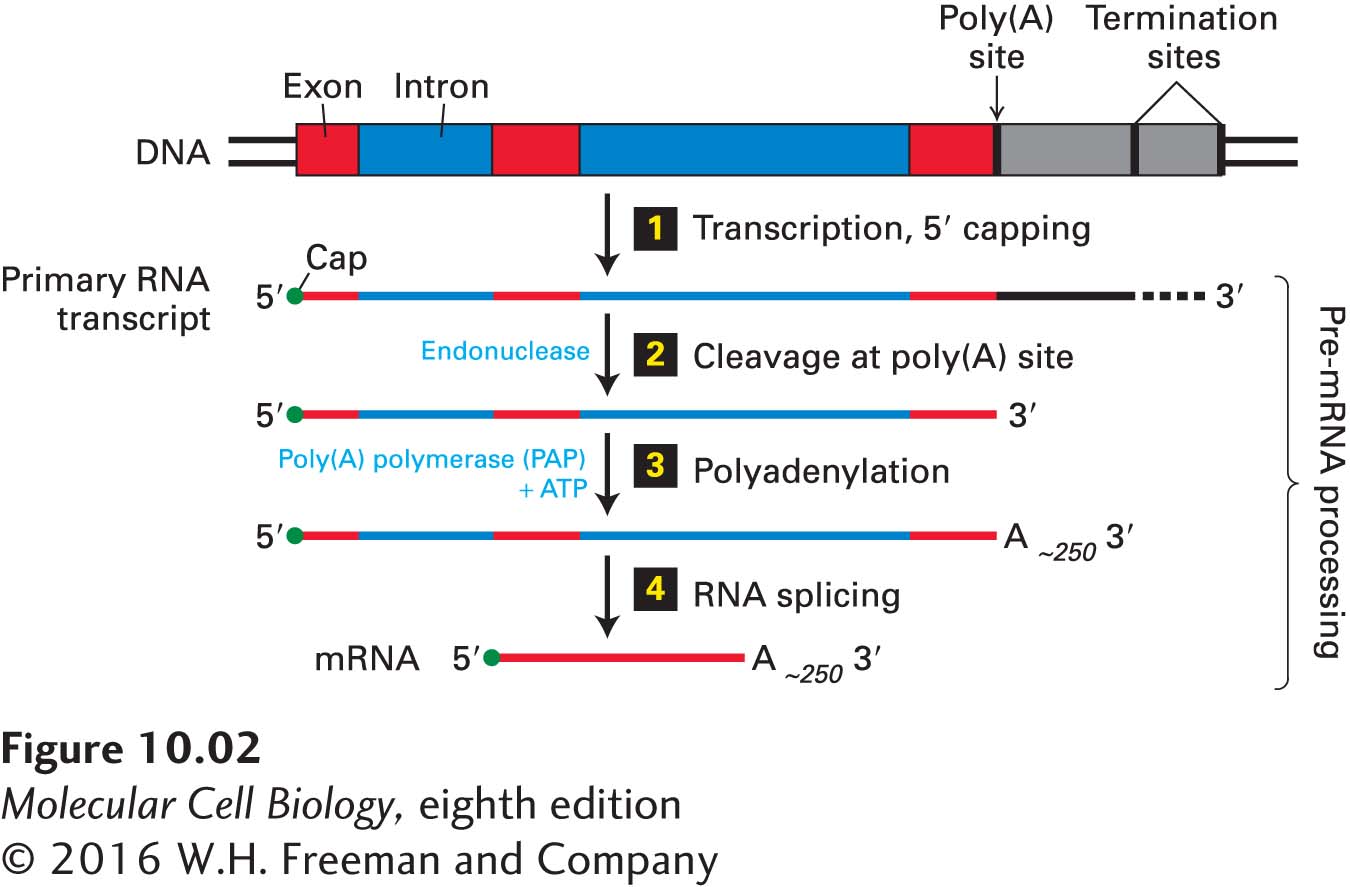
FIGURE 10- 7-