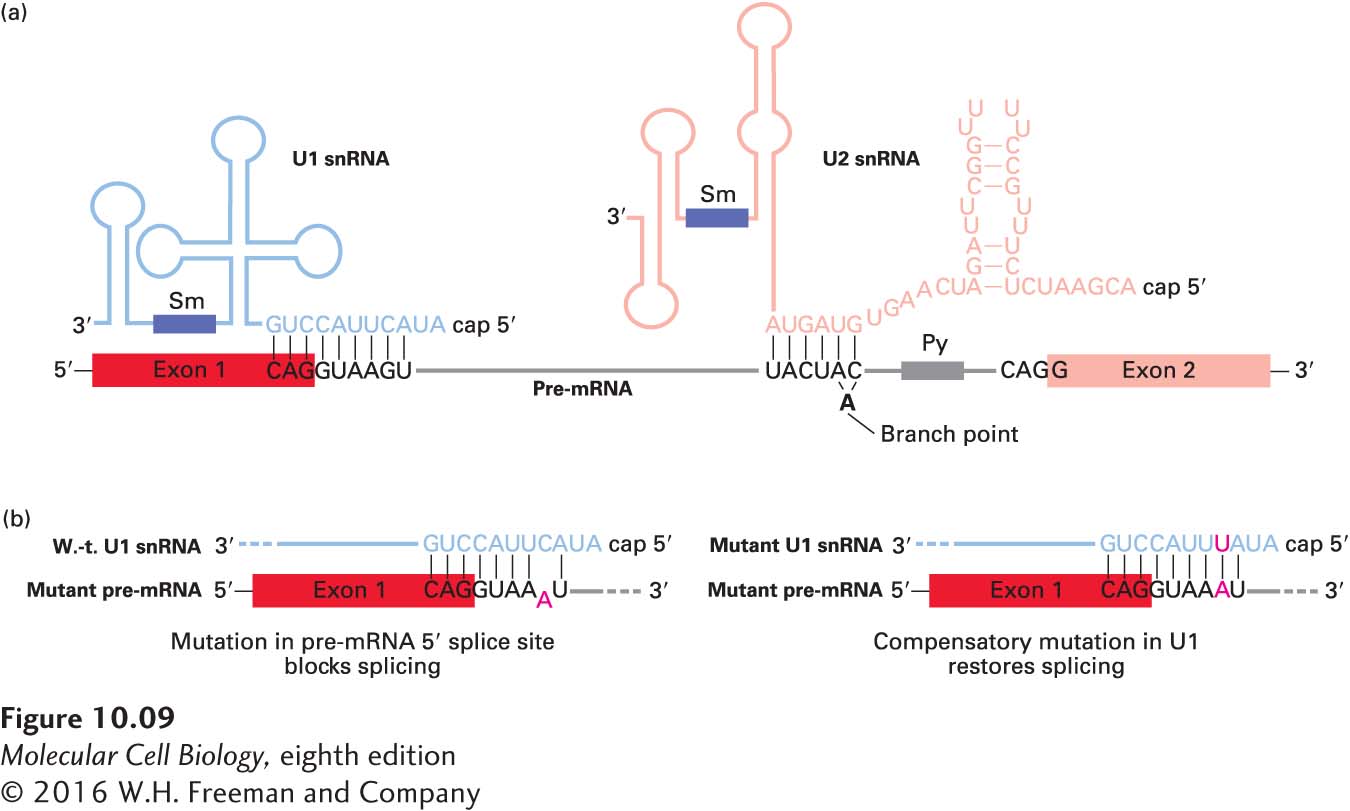
FIGURE 10- 9 Base pairing between pre- mRNA, U1 snRNA, and U2 snRNA early in the splicing process. (a) In this diagram, secondary structures in the snRNAs that are not altered during splicing are depicted schematically. The yeast branch- point sequence is shown here. Note that U2 snRNA base- pairs with a sequence that includes the branch- point A, although this residue is not base- paired. For unknown reasons, antisera from patients with the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) contain antibodies to snRNP proteins, which have been useful in characterizing components of the splicing reaction; the purple rectangles represent sequences that bind snRNP proteins recognized by these anti- Sm antibodies. (b) Only the 5′ ends of U1 snRNAs and 5′ splice sites in pre- mRNAs are shown. (Left) A mutation (A) in a pre- mRNA splice site that interferes with base pairing to the 5′ end of U1 snRNA blocks splicing. (Right) Expression of a U1 snRNA with a compensating mutation (U) that restores base pairing also restores splicing of the mutant pre- mRNA. See M. J. Moore et al., 1993, in R. Gesteland and J. Atkins, eds., The RNA World, Cold Spring Harbor Press, pp. 303– 357; see also Y. Zhuang and A. M. Weiner, 1986, Cell 46:827.
[Leave] [Close]