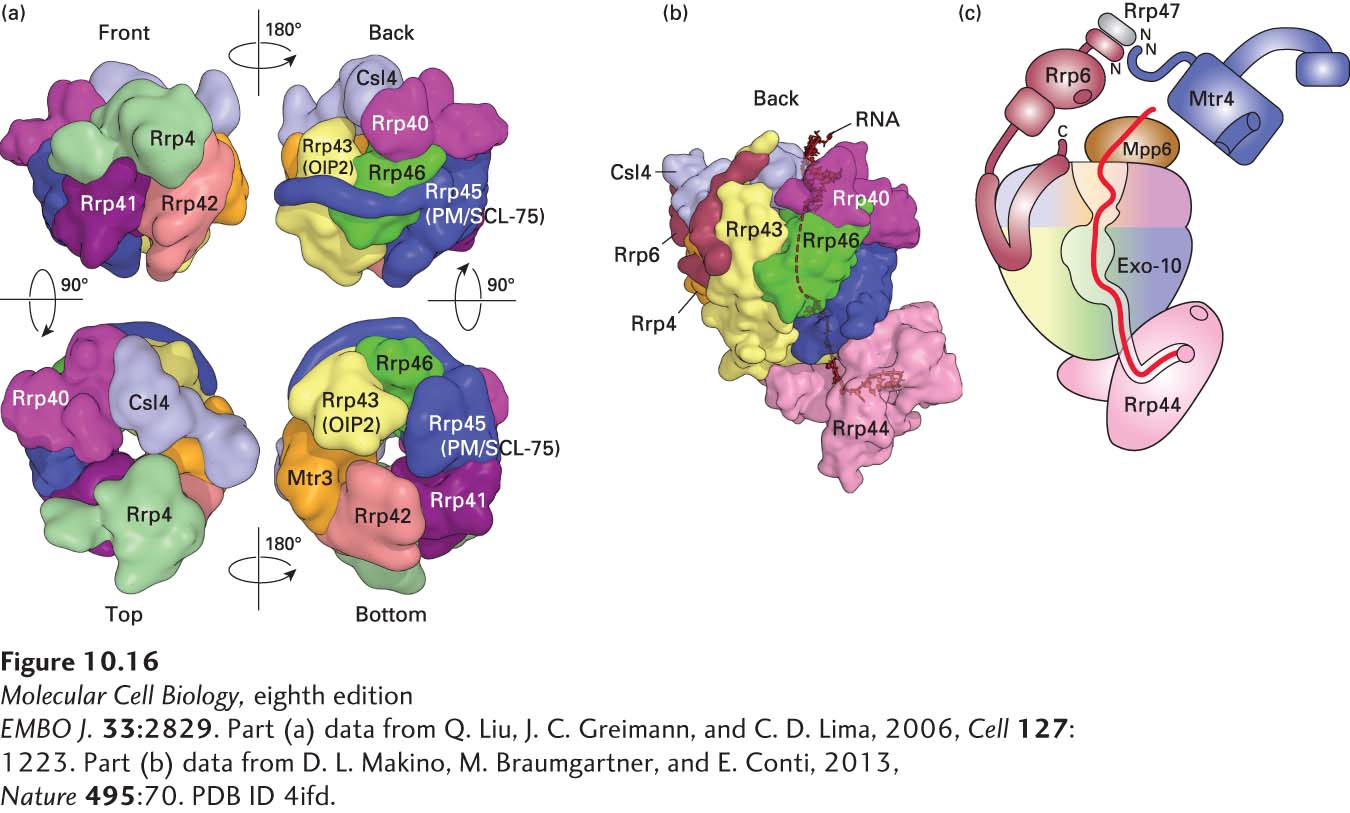
FIGURE 10- 16 Structure of the exosome. (a) Catalytically inactive exosome core. A nine- subunit, 286- kDa human exosome core was assembled in vitro from subunits Rrp41, Rrp45, Rrp42, Mtr3, Rrp43, Rrp46, Rrp4, Rrp40, and Csl4 expressed at a high level in E. coli (see Figure 6- 29 ). Its structure was determined to a resolution of 3.35 Å by x- ray crystallography. (b) The 10- subunit, catalytically active cytoplasmic exosome. The orientation is similar to that of the upper right image in part (a), but rotated slightly counterclockwise. Processive 3′→5′ exonuclease activity is provided by the tenth subunit, Rrp44 (pink), associated with the bottom of the core. The C- terminus of an eleventh subunit, Rrp6, in the nuclear exosome is shown in maroon. RNA with a double- stranded region at the top and a 3′ single- stranded region that enters the core pore is shown in black. (c) Diagram of the 14- subunit nuclear exosome. Exo- 10 represents the 10- subunit complex shown in (b). A heterodimer of Rrp6 and Rrp47 associates with Csl4 at the top of the exosome core through the C- terminal domain of Rrp6, as shown in (b). The N- terminus of an RNA helicase, Mtr4 (blue), associates with the heterodimerization domain of Rrp6 and Rrp47. Another subunit associated with the top, Mpp6, also associates with the Mtr4 RNA helicase in the human nuclear exosome, but its structure and the details of the Mpp6- Mtr4 interaction remain to be determined. The path of single- stranded RNA through the exosome is diagrammed in red. The exonuclease active site in the processive exonuclease Rrp44 is indicated by a pink circle. An endonuclease active site in Rrp44 is represented by the pink oval. A non- processive 3′→5′ exonuclease active site in Rrp6 is represented by a maroon oval. See B. Schuch et al., 2014.
EMBO J. 33:2829. [Part (a) data from Q. Liu, J. C. Greimann, and C. D. Lima, 2006, Cell 127:1223. Part (b) data from D. L. Makino, M. Braumgartner, and E. Conti, 2013, Nature 495:70. PDB ID 4ifd.]
[Leave] [Close]