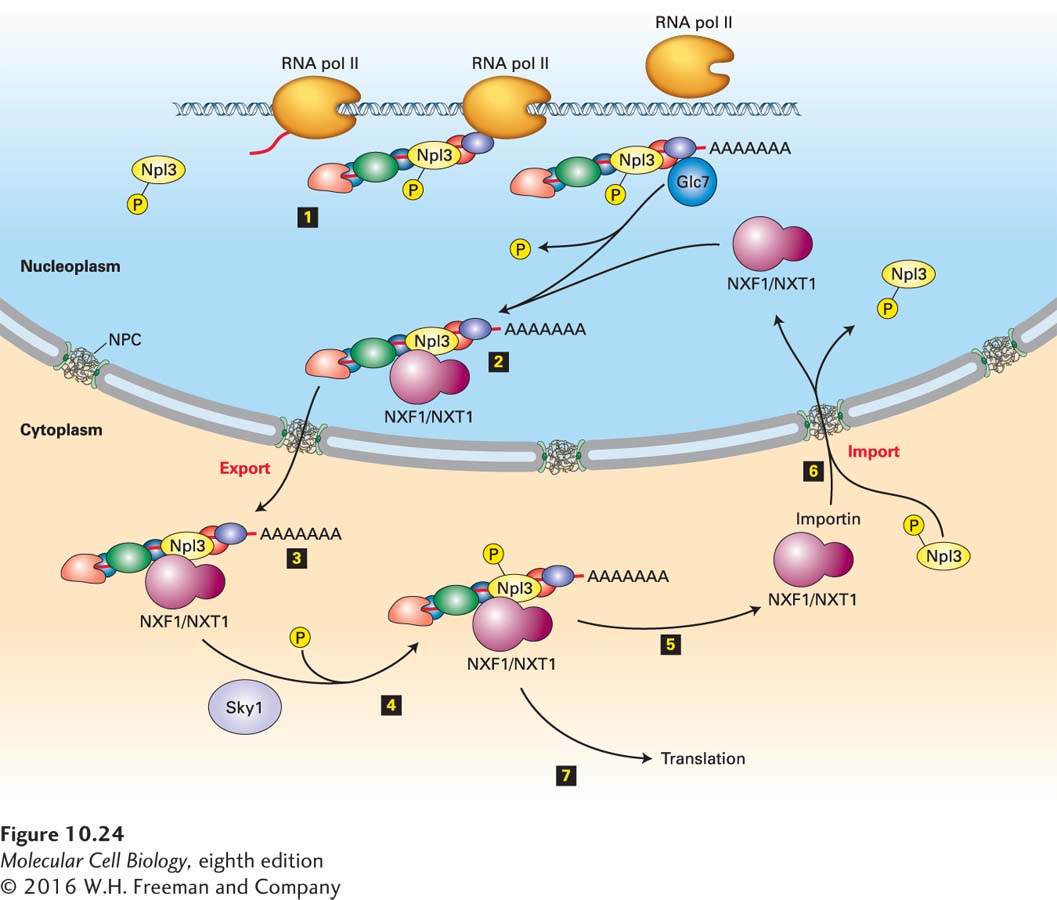
FIGURE 10- e- 0– 1–