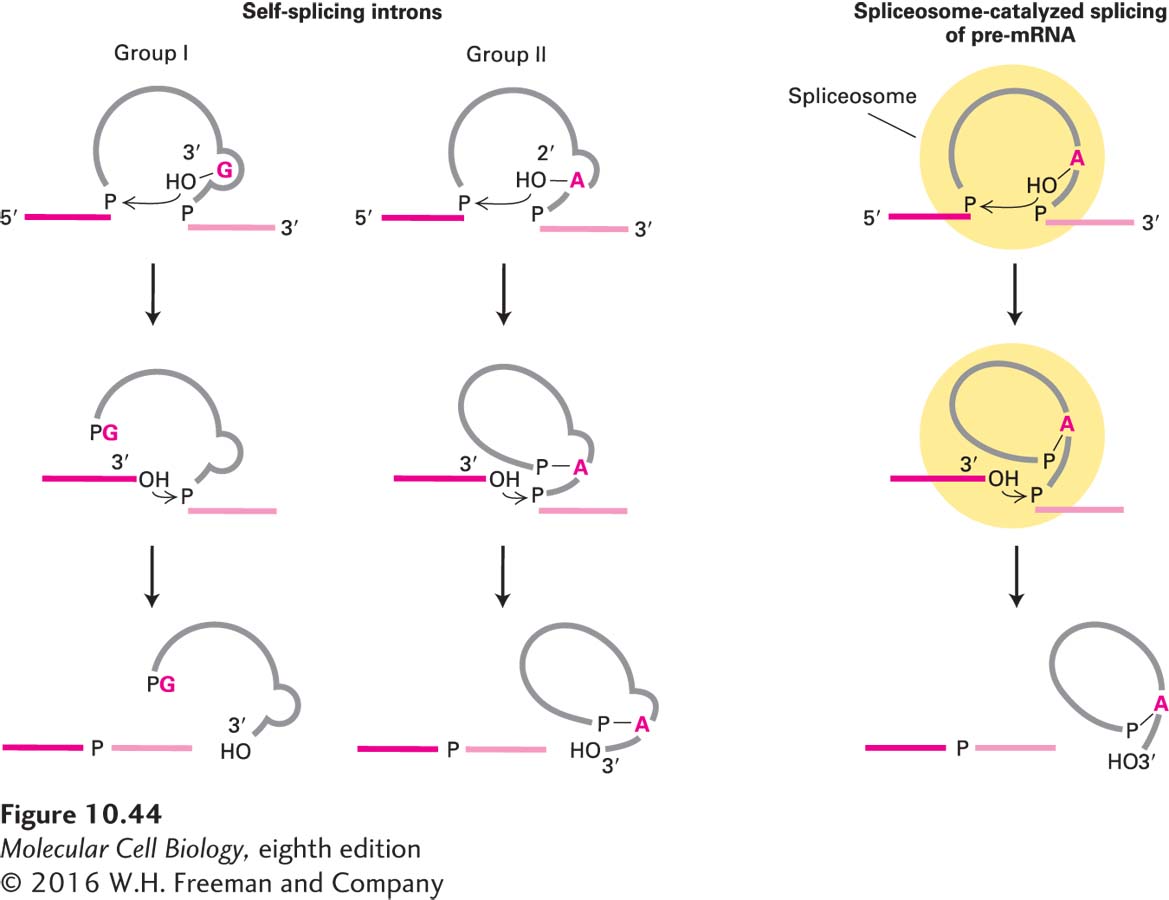
FIGURE 10- f- e- e- h- e- 0- d-