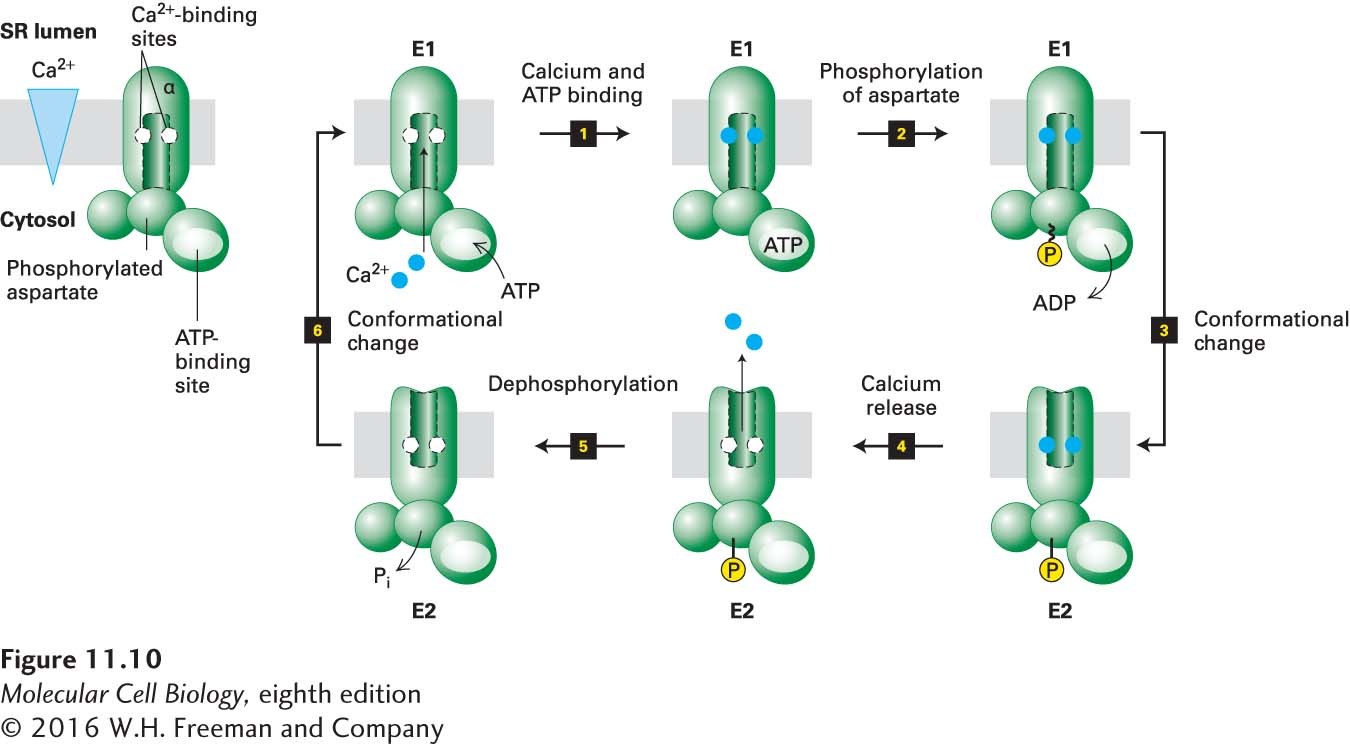
FIGURE 11- 10 Operational model of the Ca2+ ATPase in the SR membrane of skeletal muscle cells. Only one of the two catalytic α subunits of this P- class pump is depicted. E1 and E2 are alternate conformations of the protein in which the Ca2+-binding sites are accessible from the cytosolic and exoplasmic (SR lumen) faces of the membrane, respectively. An ordered sequence of steps, as diagrammed here, is essential for coupling ATP hydrolysis with the transport of Ca2+ ions across the membrane. In the figure, ~P indicates a high- energy aspartyl phosphate bond; –P indicates a low- energy bond. Because the affinity of Ca2+ for the cytosolic- facing binding sites in E1 is 1000- fold greater than its affinity for the exoplasmic- facing sites in E2, this pump transports Ca2+ unidirectionally from the cytosol to the SR lumen. See the text and Figure 11- 11 for more details. See C. Toyoshima and G. Inesi, 2004, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73:269– 292.
[Leave] [Close]