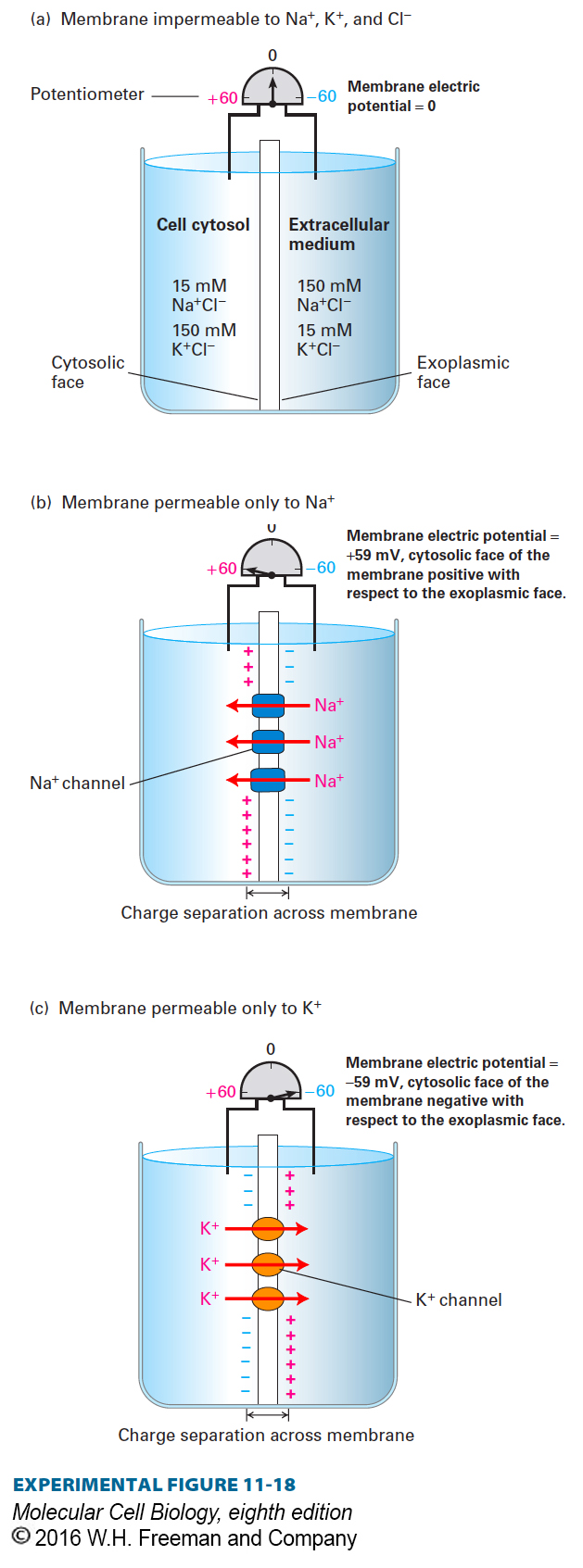
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 11-