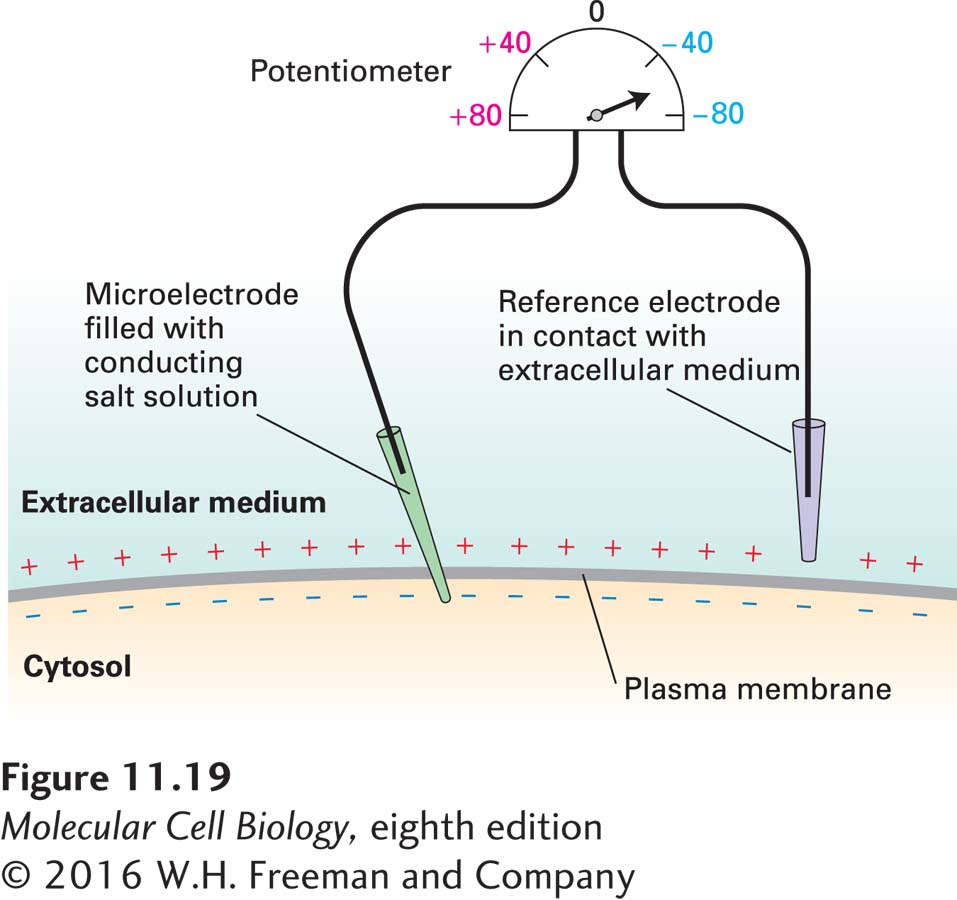
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 11- l—