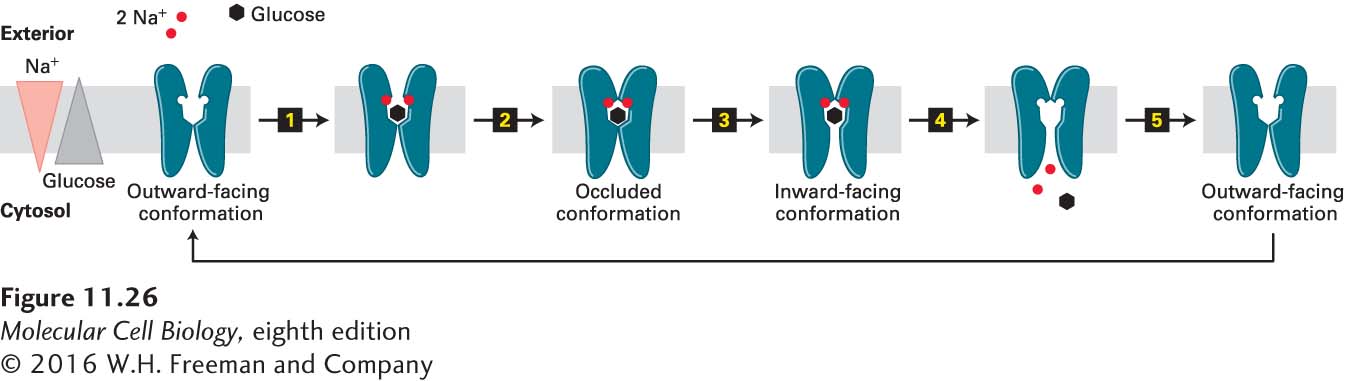
FIGURE 11- o- e- d- d- d- 7–