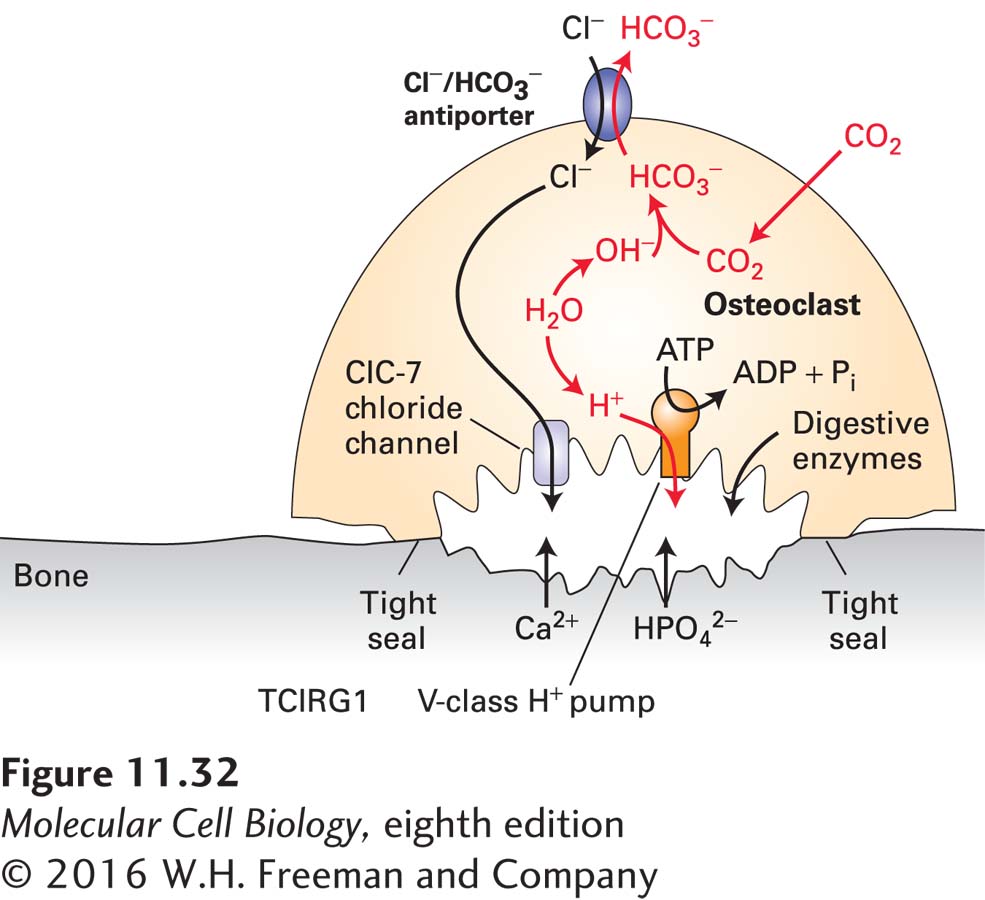
FIGURE 11- V- C- V- C- s- C-