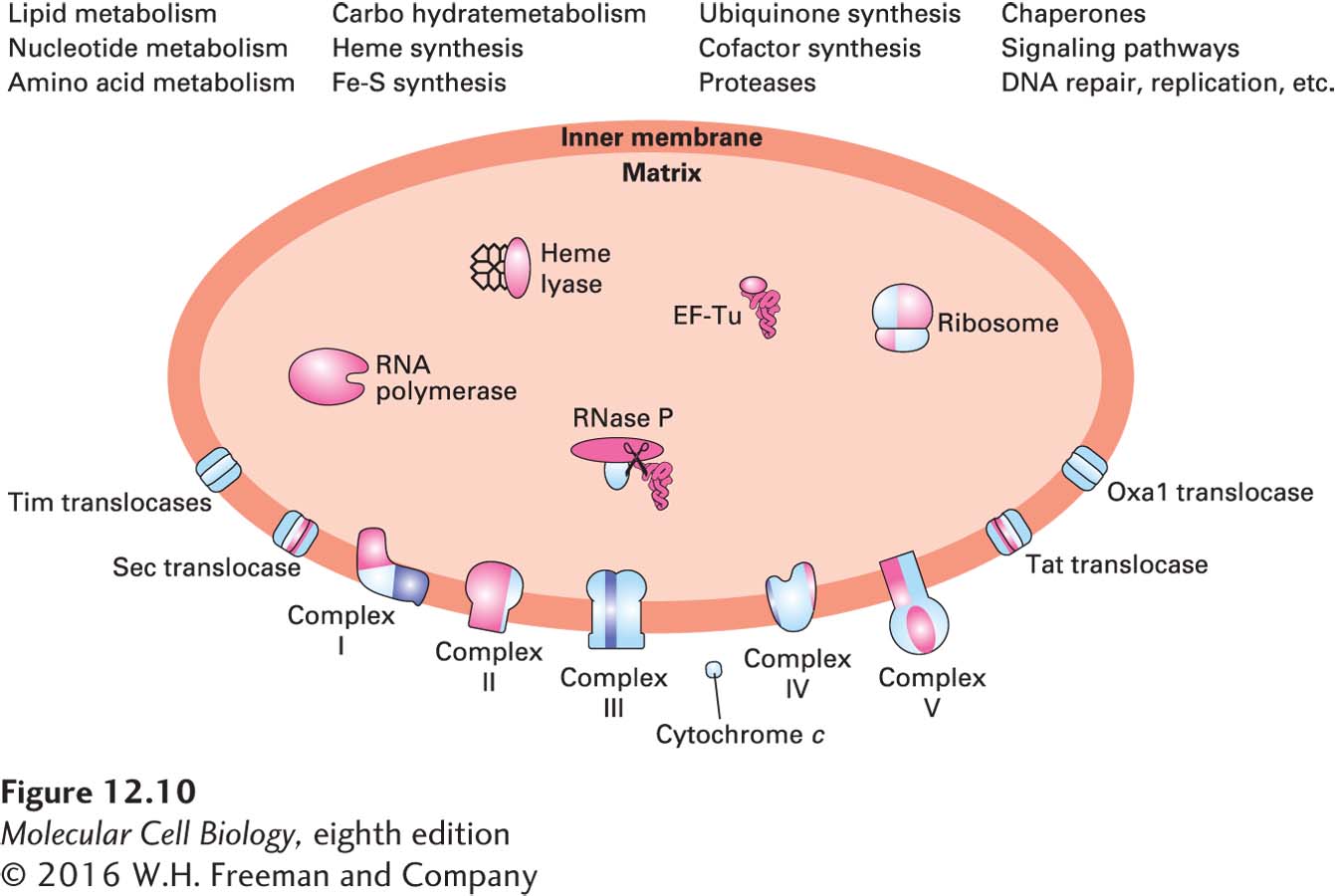
FIGURE 12- s- I– s- e-