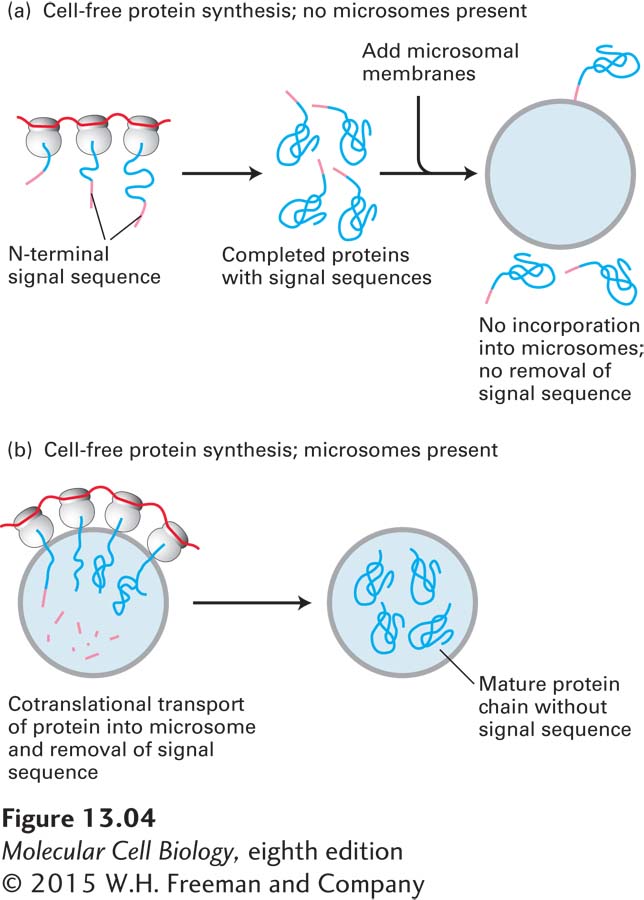
FIGURE 13- 4 Translation and translocation occur simultaneously. Cell- free experiments demonstrate that translocation of secretory proteins into microsomes is coupled to translation. Treatment of microsomes with EDTA, which chelates Mg2+ ions, strips them of associated ribosomes, allowing isolation of ribosome- free microsomes, which are equivalent to ER membranes (see Figure 13- 3 ). Protein synthesis is carried out in a cell- free system containing functional ribosomes, tRNAs, ATP, GTP, and cytosolic enzymes, to which mRNA encoding a secretory protein is added. The secretory protein is synthesized in the absence of microsomes (a) but is translocated across the vesicle membrane and loses its signal sequence (resulting in a decrease in molecular weight) only if microsomes are present during protein synthesis (b).
[Leave] [Close]