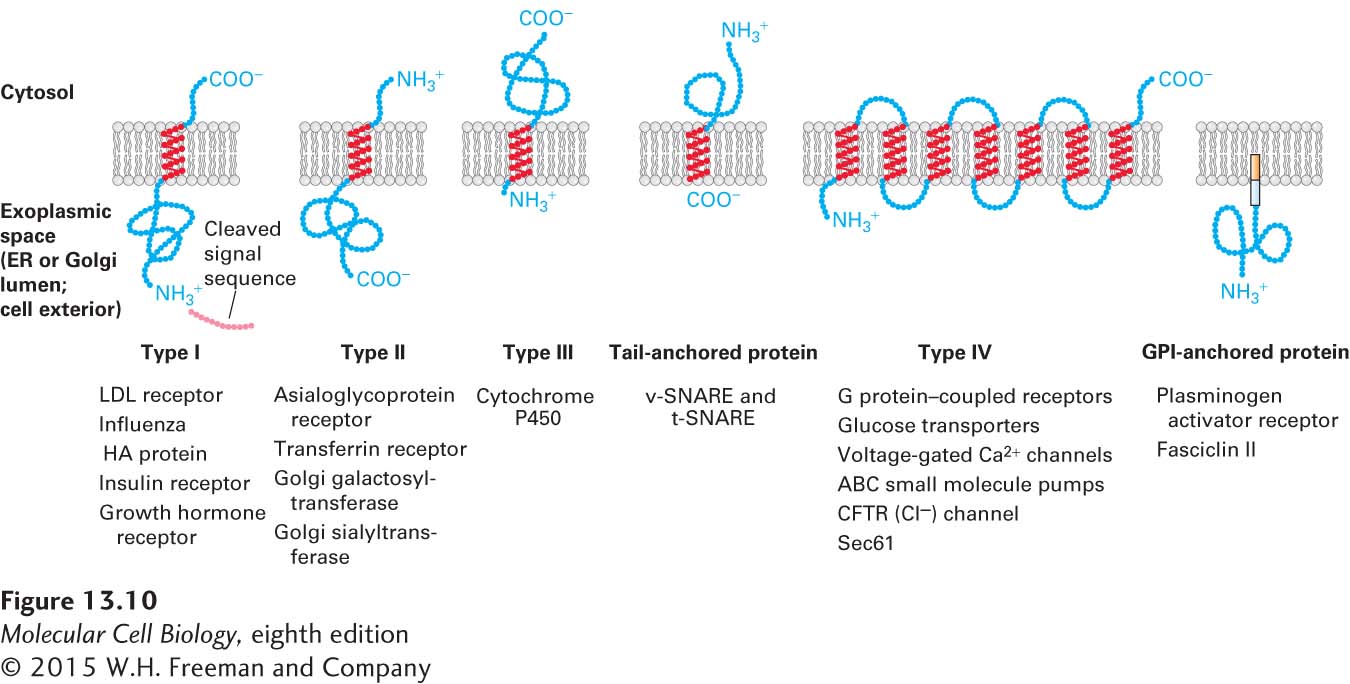
FIGURE 13- 10 Classes of ER membrane proteins. Five topological classes of integral membrane proteins are synthesized on the rough ER, as is a sixth type tethered to the membrane by a phospholipid anchor. These membrane proteins are classified by their orientation in the membrane and the types of signals they contain to direct them there. In the integral membrane proteins, hydrophobic segments of the protein chain form α helices embedded in the membrane bilayer; the regions outside the membrane are hydrophilic and fold into various conformations. All type IV proteins have multiple transmembrane α helices. The type IV topology depicted here corresponds to that of G protein– coupled receptors: seven α helices, the N- terminus on the exoplasmic side of the membrane, and the C- terminus on the cytosolic side. Other type IV proteins may have a different number of helices and various orientations of the N- terminus and C- terminus. See E. Hartmann et al., 1989, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:5786, and C. A. Brown and S. D. Black, 1989, J. Biol. Chem. 264:4442.
[Leave] [Close]