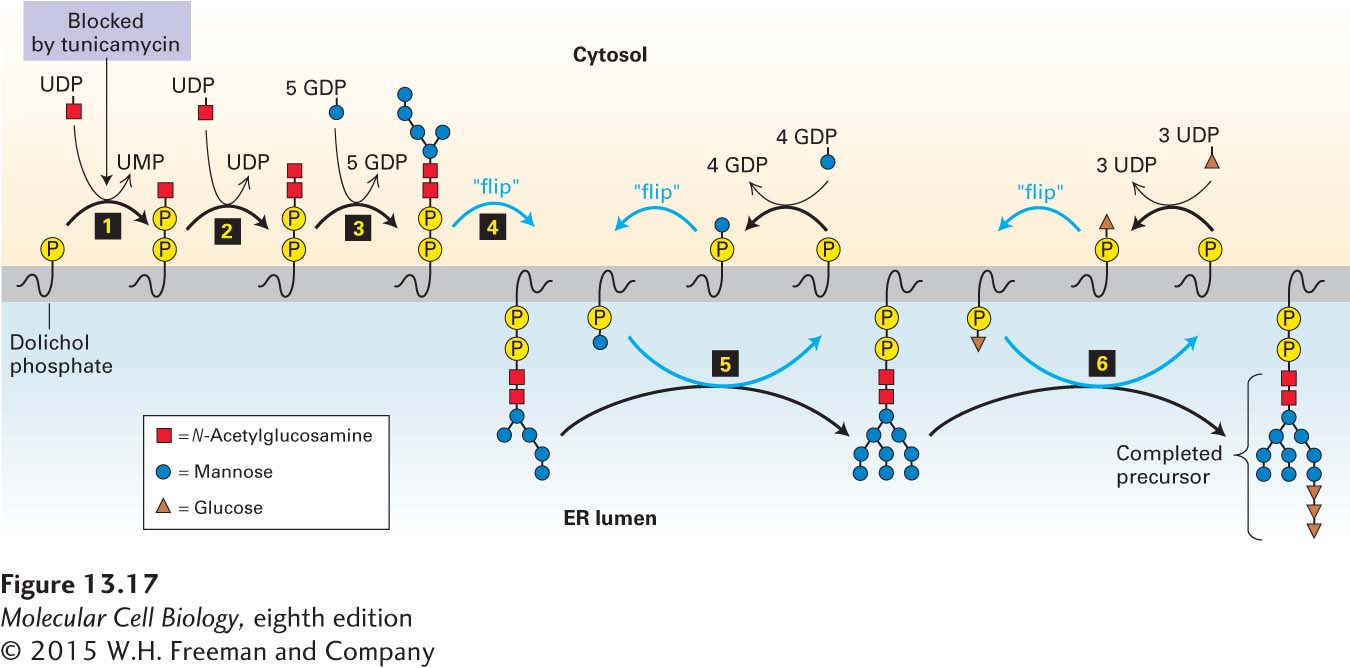
FIGURE 13- 17 Biosynthesis of the oligosaccharide precursor. Dolichol phosphate is a strongly hydrophobic lipid, containing 75– 95 carbon atoms, that is embedded in the ER membrane. Two N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and five mannose residues are added one at a time to a dolichol phosphate on the cytosolic face of the ER membrane (steps 1–3). The nucleotide- sugar donors in these and later reactions are synthesized in the cytosol. Note that the first sugar residue is attached to dolichol by a high- energy pyrophosphate linkage. Tunicamycin, which blocks the first enzyme in this pathway, inhibits the synthesis of all N-linked oligosaccharides in cells. After the seven- residue dolichol pyrophosphoryl intermediate is flipped to the luminal face (step 4), the remaining four mannose residues and all three glucose residues are added one at a time (steps 5–6). In the later reactions, the sugar to be added is first transferred from a nucleotide sugar to a carrier dolichol phosphate on the cytosolic face of the ER; the carrier is then flipped to the luminal face, where the sugar is transferred to the growing oligosaccharide, after which the “empty” carrier is flipped back to the cytosolic face. See C. Abeijon and C. B. Hirschberg, 1992, Trends Biochem. Sci. 17:32.
[Leave] [Close]