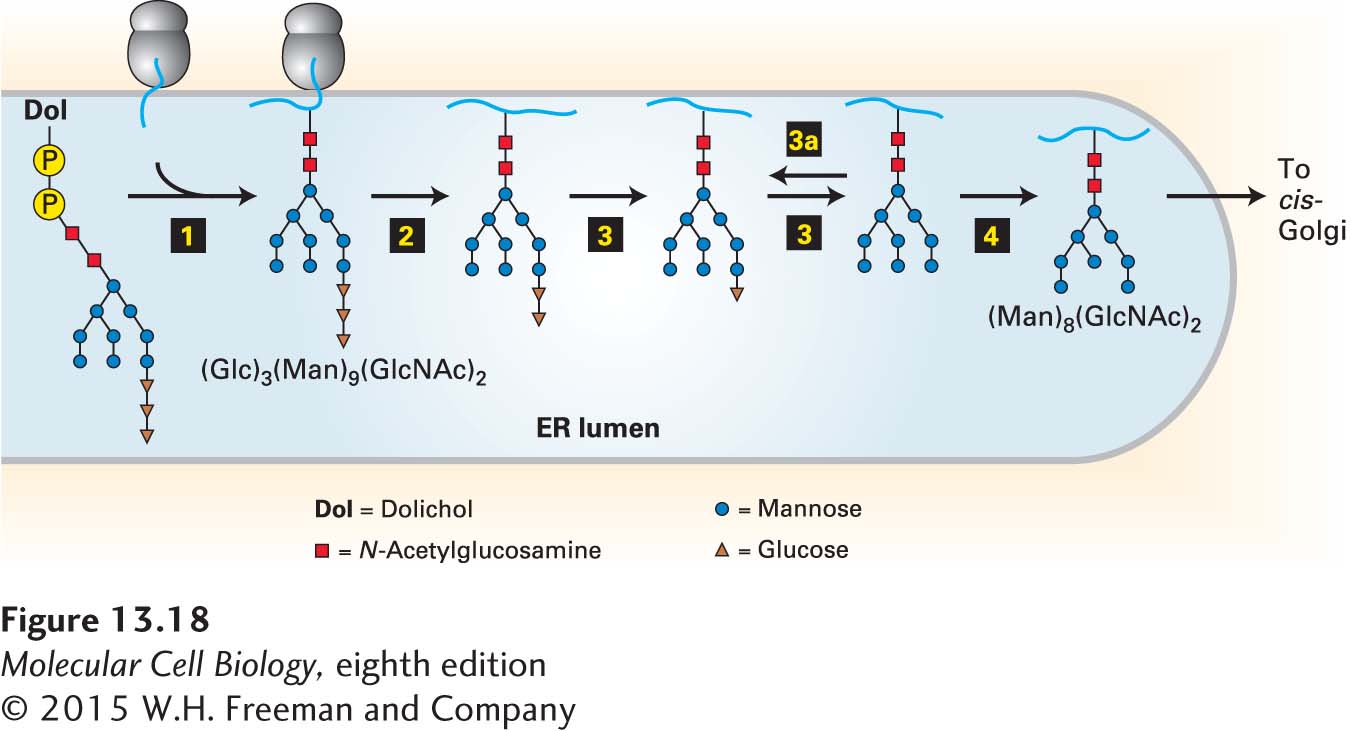
FIGURE 13- 18 Addition and initial processing of N-linked oligosaccharides. In the rough ER of vertebrate cells, the Glc3Man9(GlcNAc)2 precursor is transferred from the dolichol carrier to a susceptible asparagine residue on a nascent protein as soon as the asparagine crosses to the luminal side of the ER (step 1). In three separate reactions, first one glucose residue (step 2), then two glucose residues (step 3), and finally one mannose residue (step 4) are removed. Re- addition of one glucose residue (step 3a) plays a role in the correct folding of many proteins in the ER, as discussed later. The process of N-linked glycosylation of a soluble secretory protein is shown here, but the luminal portions of an integral membrane protein can be modified on asparagine residues by the same mechanism. See R. Kornfeld and S. Kornfeld, 1985, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 45:631, and M. Sousa and A. J. Parodi, 1995, EMBO J. 14:4196.
[Leave] [Close]