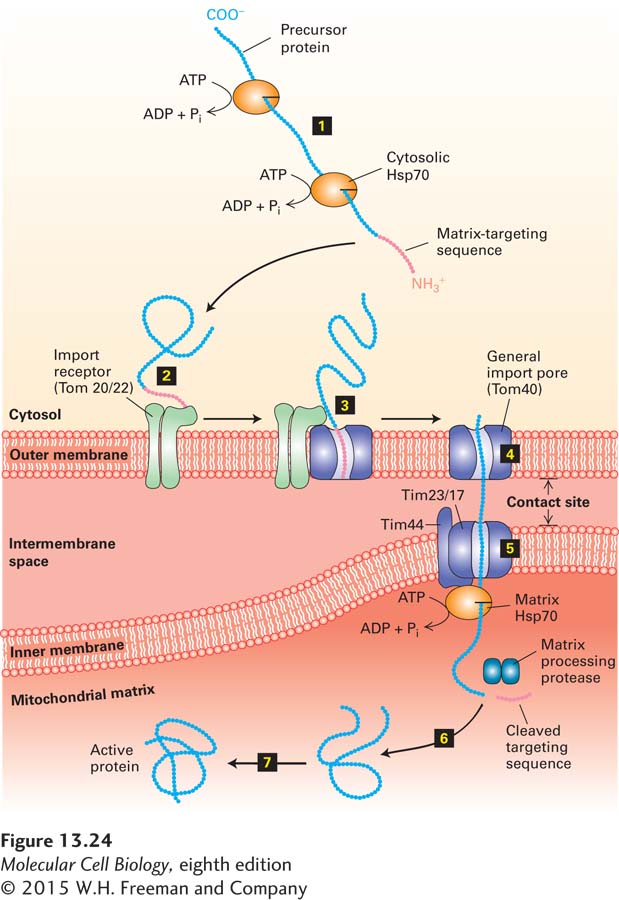
FIGURE 13- 24 Protein import into the mitochondrial matrix. Precursor proteins synthesized on cytosolic ribosomes are maintained in an unfolded or partially folded state by bound chaperones, such as cytosolic Hsp70 (step 1). After a precursor protein binds to an import receptor near a site of contact with the inner membrane (step 2), it is transferred into the general import pore (step 3). The translocating protein then moves through this channel and an adjacent channel in the inner membrane (steps 4–5). Note that translocation occurs at rare “contact sites” at which the inner and outer membranes appear to touch. Binding of the translocating protein by matrix Hsp70 and subsequent ATP hydrolysis by Hsp70 helps drive import into the matrix. Once the targeting sequence is removed by a matrix protease and Hsp70 is released from the newly imported protein (step 6), the protein folds into its mature, active conformation within the matrix (step 7). Folding of some proteins depends on matrix chaperonins. See G. Schatz, 1996, J. Biol. Chem. 271:31763, and N. Pfanner et al., 1997, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:25.
[Leave] [Close]