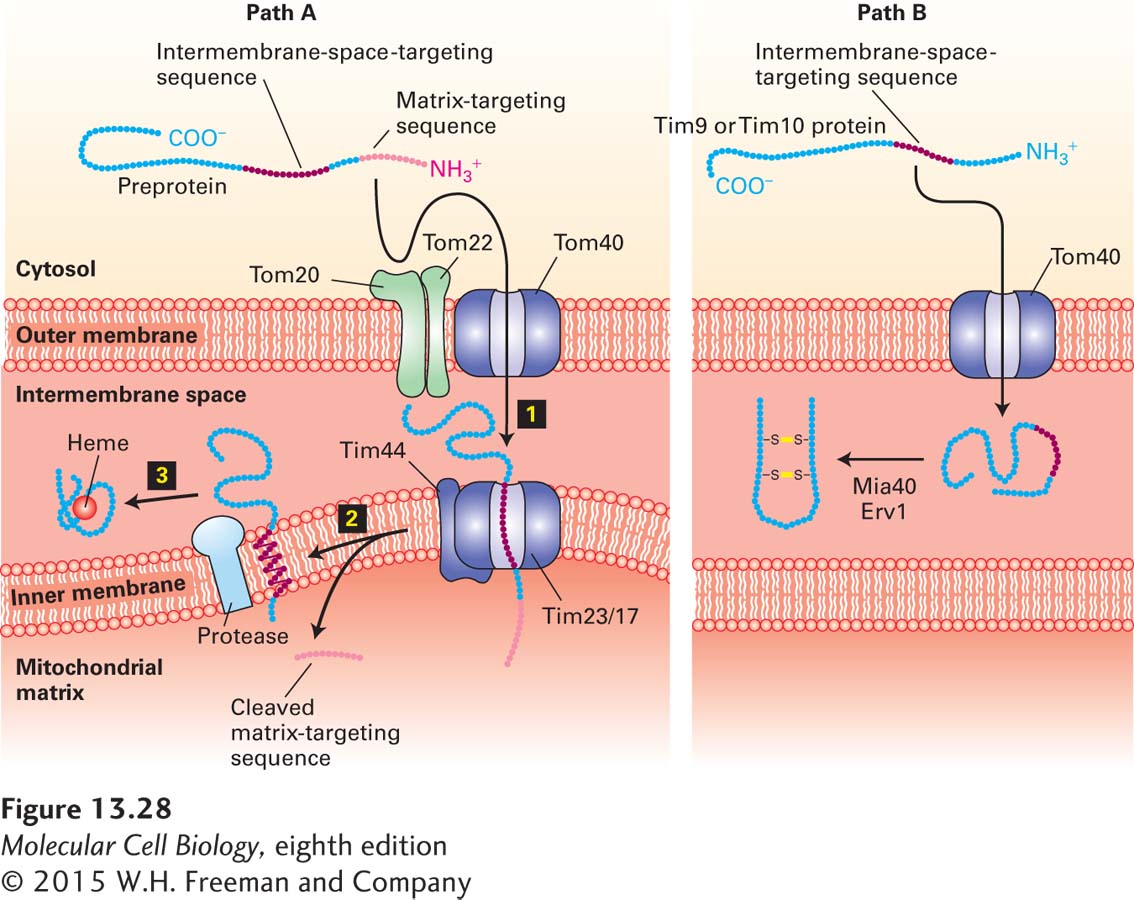
FIGURE 13- 28 Two pathways to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Pathway A, the major one for delivery of proteins from the cytosol to the intermembrane space, is similar to pathway A for delivery to the inner membrane (see Figure 13- 26 ). The major difference is that the internal targeting sequence in these proteins, such as cytochrome b2, is recognized by an inner- membrane protease, which cleaves the protein on the intermembrane- space side of the membrane. The released protein then folds and binds to its heme cofactor within the intermembrane space. Pathway B is a specialized pathway for delivery of the proteins Tim9 and Tim10 to the intermembrane space. These proteins readily pass through the Tom40 general import pore, and once they are in the intermembrane space, they fold and form disulfide bonds that prevent reverse translocation through Tom40. The disulfide bonds are generated by Erv1 and are transferred to Tim9 and Tim10 by Mia40. See R. E. Dalbey and A. Kuhn, 2000, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 16:51; N. Pfanner and A. Geissler, 2001, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2:339; and K. Tokatlidis, 2005, Cell 121:965– 967.
[Leave] [Close]