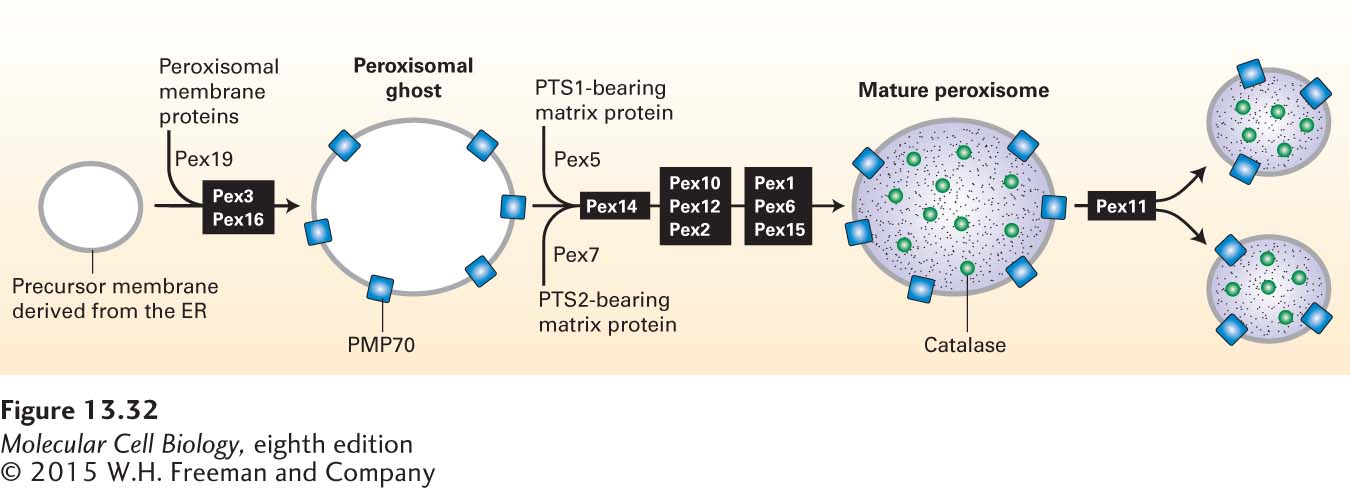
FIGURE 13- 32 Model of peroxisomal biogenesis and division. The first stage in the de novo formation of peroxisomes is the incorporation of peroxisomal membrane proteins into precursor membranes derived from the ER. Pex19 acts as the receptor for membrane- targeting sequences. A complex of Pex3 and Pex16 is required for proper insertion of proteins (e.g., PMP70) into the forming peroxisomal membrane. Insertion of all peroxisomal membrane proteins produces a peroxisomal ghost, which is capable of importing proteins targeted to the matrix. The pathways for importing PTS1- and PTS2- bearing matrix proteins differ only in the identity of the cytosolic receptor (Pex5 and Pex7, respectively) that binds the targeting sequence (see Figure 13- 30 ). Complete incorporation of matrix proteins yields a mature peroxisome. Although peroxisomes can form de novo as just described, under most conditions, the proliferation of peroxisomes involves the division of mature peroxisomes, a process that depends on the Pex11 protein.
[Leave] [Close]