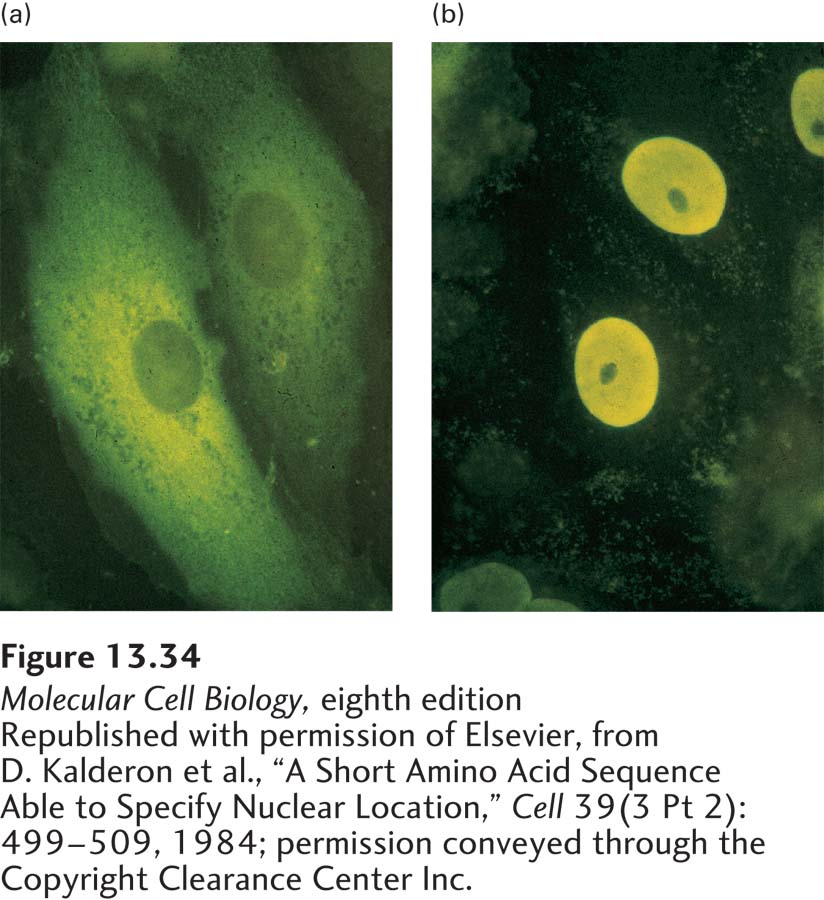
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 13- 34 Nuclear- localization signals (NLSs) direct proteins to the cell nucleus. Cytoplasmic proteins can be transported to the nucleus if they are fused to a nuclear- localization signal. (a) Normal pyruvate kinase, here visualized by immunofluorescence after cultured cells were treated with a specific antibody (yellow), is localized to the cytoplasm. This very large cytosolic protein functions in carbohydrate metabolism. (b) When a chimeric pyruvate kinase containing the SV40 NLS at its N- terminus was expressed in cells, it was localized to the nucleus. The chimeric protein was expressed from a transfected engineered gene produced by fusing a viral gene fragment encoding the SV40 NLS to the pyruvate kinase gene.
[Republished with permission of Elsevier, from D. Kalderon et al., “A Short Amino Acid Sequence Able to Specify Nuclear Location,” Cell 39(3 Pt 2):499– 509, 1984; permission conveyed through the Copyright Clearance Center Inc.]
[Leave] [Close]