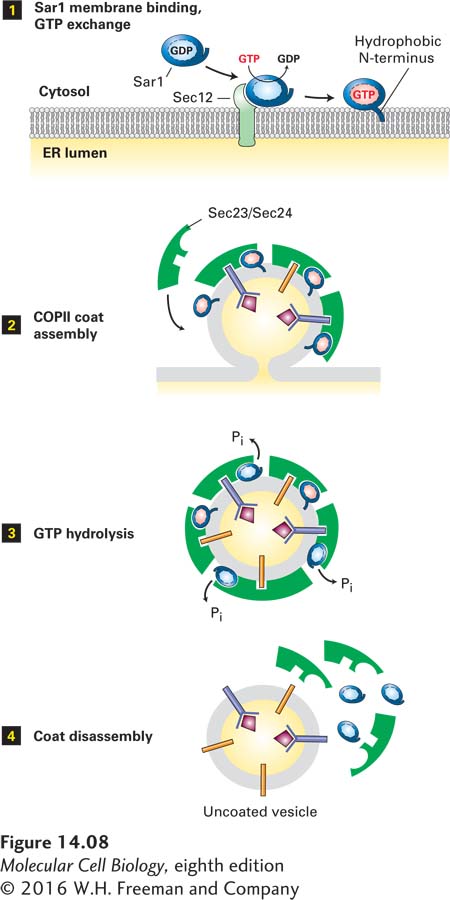
FIGURE 14- 8 Model for the role of Sar1 in the assembly and disassembly of the COPII coat. Step 1: Interaction of soluble GDP- bound Sar1 with the GEF Sec12, an ER integral membrane protein, catalyzes exchange of GTP for GDP on Sar1. The hydrophobic N- terminus of the GTP- bound form of Sar1 extends outward from the protein’s surface and anchors Sar1 to the ER membrane. Step 2: Sar1 attached to the membrane serves as a binding site for the Sec23/Sec24 coat protein complex. Membrane cargo proteins are recruited to the forming vesicle bud by binding of specific short sequences (sorting signals) in their cytosolic regions to sites on the Sec23/Sec24 complex. Some membrane cargo proteins also act as receptors that bind soluble proteins in the lumen. The coat is completed by assembly of a second type of coat complex composed of Sec13 and Sec31 (not shown). Step 3: After the vesicle coat is complete, the Sec23 coat subunit promotes GTP hydrolysis by Sar1. Step 4: Release of Sar1·GDP from the vesicle membrane causes disassembly of the coat. See S. Springer et al., 1999, Cell 97:145.
[Leave] [Close]