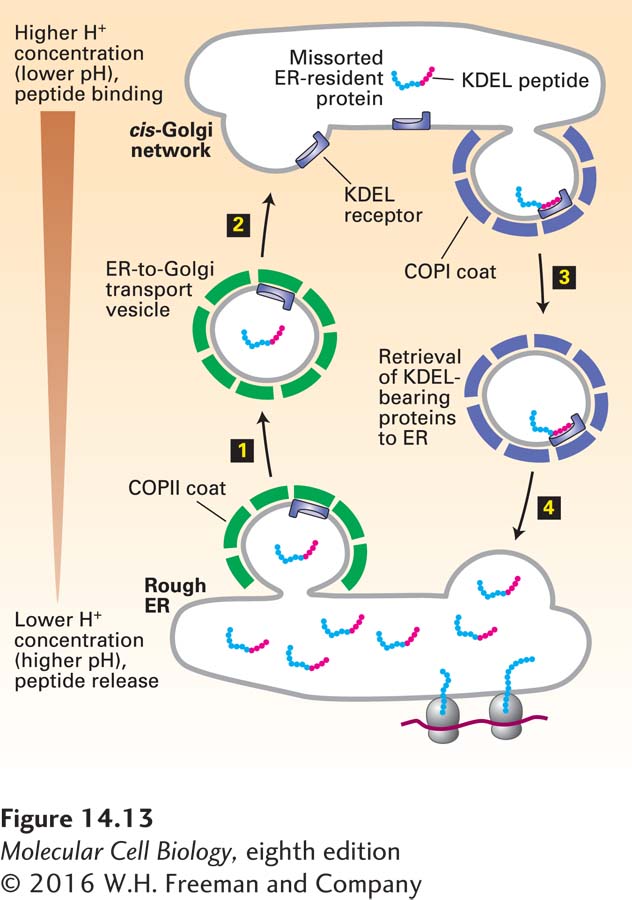
FIGURE 14- 13 Role of the KDEL receptor in retrieval of ER- resident luminal proteins from the Golgi. ER luminal proteins, especially those present at high concentrations, can be passively incorporated into COPII vesicles and transported to the Golgi (steps 1 and 2). Many such proteins bear a C- terminal KDEL (Lys- Asp- Glu- Leu) sequence (red) that allows them to be retrieved. The KDEL receptor, located mainly in the cis-Golgi network and in both COPII and COPI vesicles, binds proteins bearing the KDEL sorting signal and returns them to the ER (steps 3 and 4). This retrieval system prevents depletion of ER luminal proteins such as those needed for proper folding of newly made secretory proteins. The binding affinity of the KDEL receptor is very sensitive to pH. The small difference between the pH of the ER and that of the Golgi favors binding of KDEL- bearing proteins to the receptor in Golgi- derived vesicles and their release in the ER. See J. Semenza et al., 1990, Cell 61:1349.
[Leave] [Close]