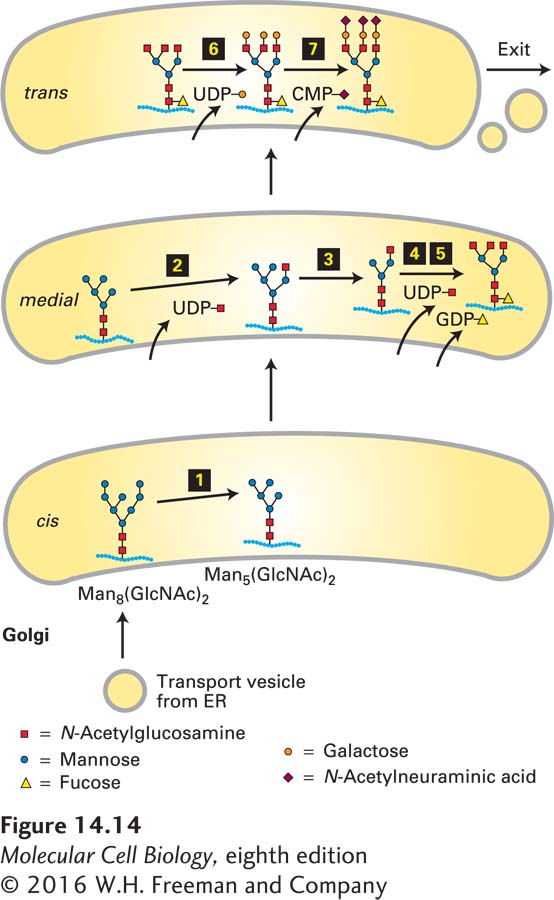
FIGURE 14- 14 Processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains on glycoproteins within cis- , medial- , and trans-
[Leave] [Close]