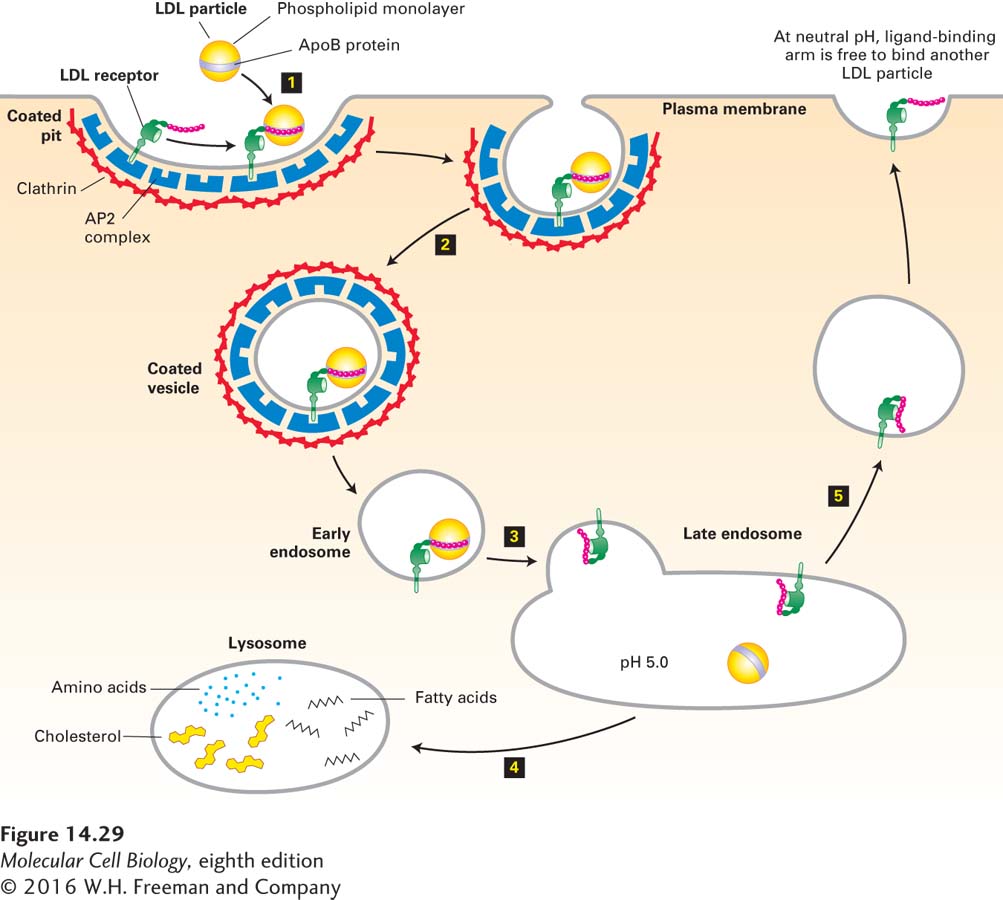
FIGURE 14- 29 Endocytic pathway for internalizing low- density lipoprotein (LDL). Step 1: A cell- surface LDL receptor binds to an ApoB protein embedded in the phospholipid outer layer of an LDL particle. Interaction between the NPXY sorting signal in the cytosolic tail of the LDL receptor and the AP2 complex incorporates the receptor- ligand complex into a forming endocytic vesicle. Step 2: Clathrin- coated pits containing receptor- LDL complexes are pinched off by the same dynamin- mediated mechanism used to form clathrin/AP1- coated vesicles on the trans-Golgi network (see Figure 14- 19 ). Step 3: After the vesicle coat is shed, the uncoated endocytic vesicle (early endosome) fuses with a late endosome. The acidic pH in this compartment causes a conformational change in the LDL receptor that leads to release of the bound LDL particle. Step 4: The late endosome fuses with a lysosome, and the proteins and lipids of the free LDL particle are broken down into their constituent parts by enzymes in the lysosome. Step 5: The LDL receptor is recycled to the cell surface, where at the neutral pH of the exterior medium, the receptor undergoes a conformational change so that it can bind another LDL particle. See M. S. Brown and J. L. Goldstein, 1986, Science 232:34, and G. Rudenko et al., 2002, Science 298:2353.
[Leave] [Close]