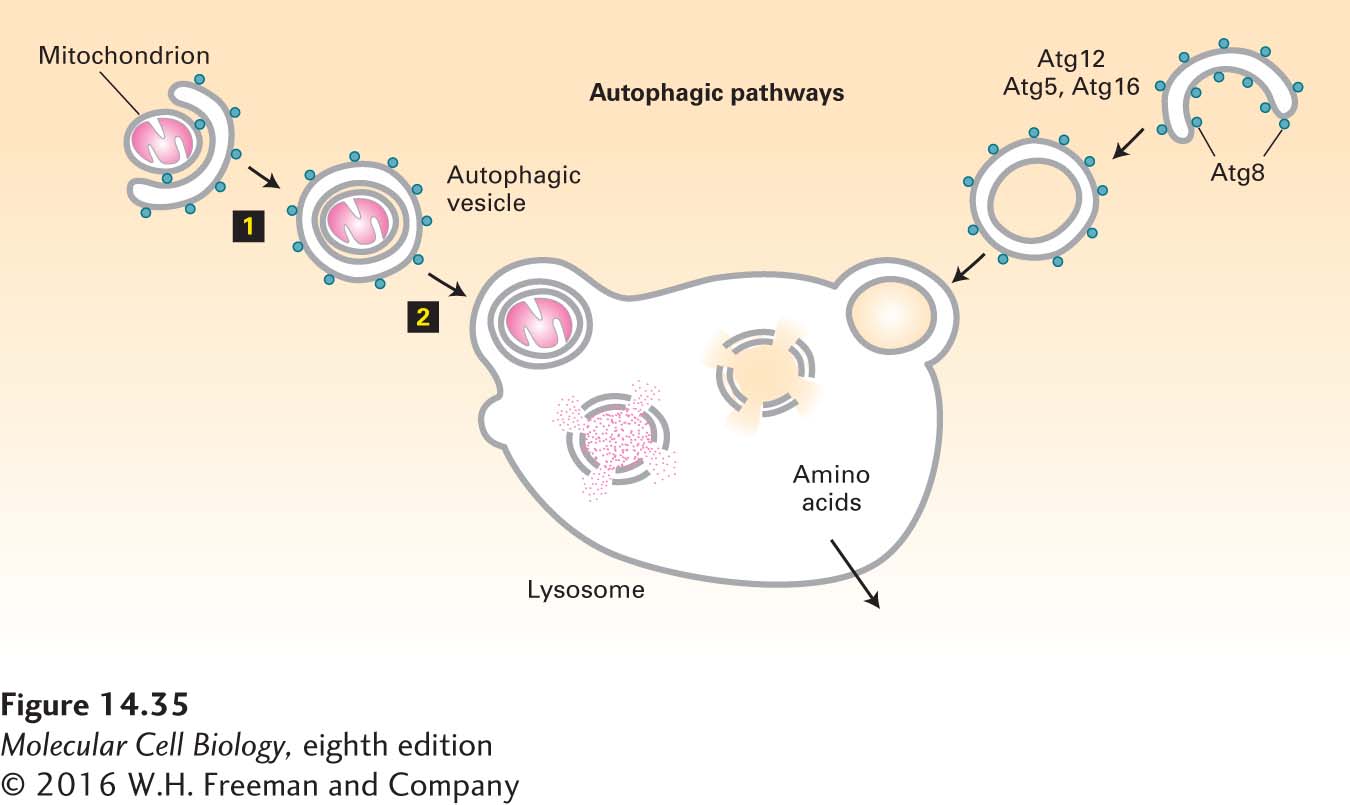
FIGURE 14- 35 The autophagic pathway. The autophagic pathway allows cytosolic proteins and organelles to be delivered to the lysosome interior for degradation. In the autophagic pathway, a cup- shaped structure forms around a portion of the cytosol (right) or an organelle such as a mitochondrion (left). Continued addition of membrane eventually leads to the formation of an autophagosome that envelops its contents in two complete membranes (step 1). Fusion of the outer membrane with the membrane of a lysosome releases a single- membrane vesicle and its contents into the lysosome interior (step 2). After degradation of the protein and lipid components by hydrolases in the lysosome interior, the released amino acids are transported across the lysosomal membrane into the cytosol. Proteins known to participate in the autophagic pathway include Atg8, which forms a coat structure around the autophagosome.
[Leave] [Close]