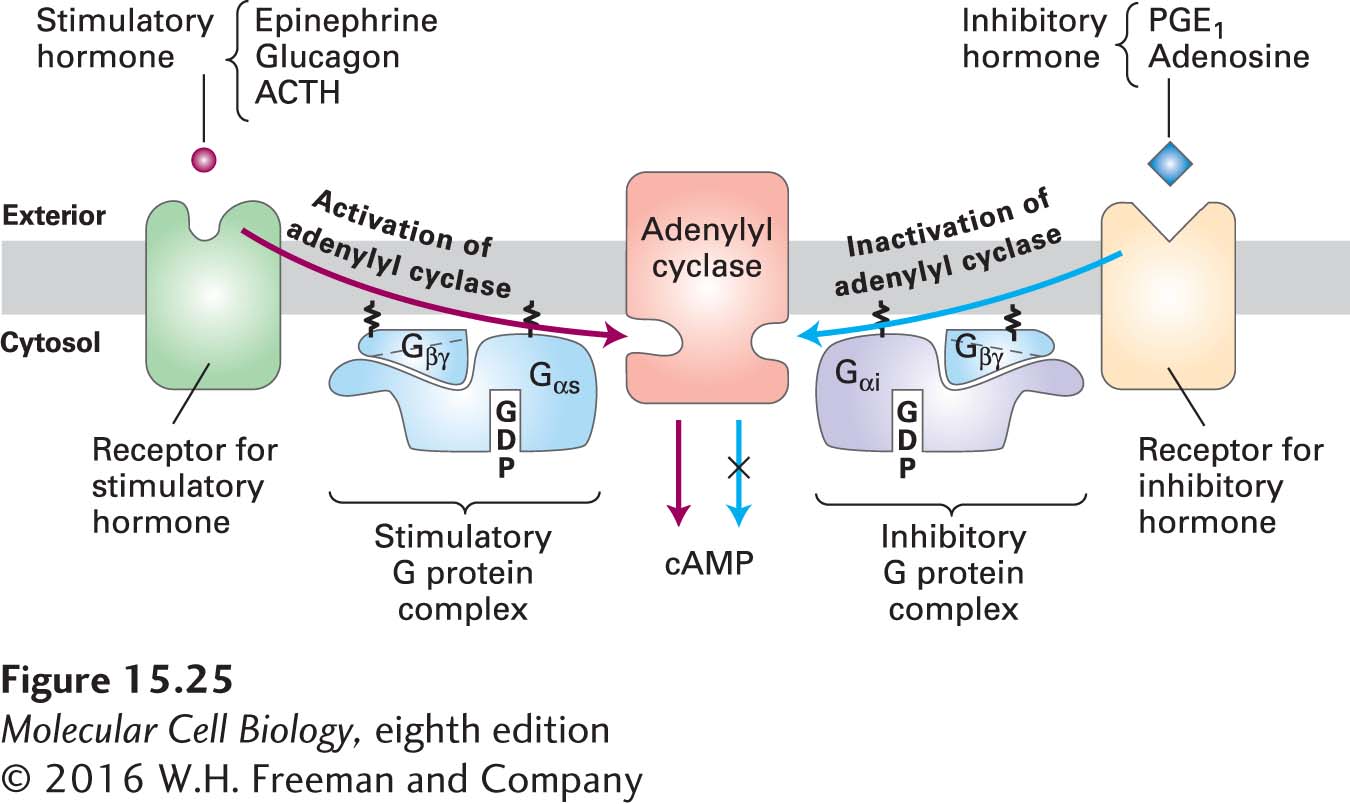
FIGURE 15- 25 Hormone- induced activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in adipose cells. Ligand binding to Gαs-coupled receptors causes activation of adenylyl cyclase, whereas ligand binding to Gαi-coupled receptors causes inhibition of the enzyme. The Gβγ subunit in stimulatory and in inhibitory G proteins is identical; the Gα subunits and their corresponding receptors differ. Ligand- stimulated formation of active Gα·GTP complexes occurs by the same mechanism in both Gαs and Gαi proteins (see Figure 15- 14 ). However, Gαs·GTP and Gαi·GTP interact differently with adenylyl cyclase, so that one stimulates and the other inhibits its catalytic activity. See A. G. Gilman, 1984, Cell 36:577.
[Leave] [Close]