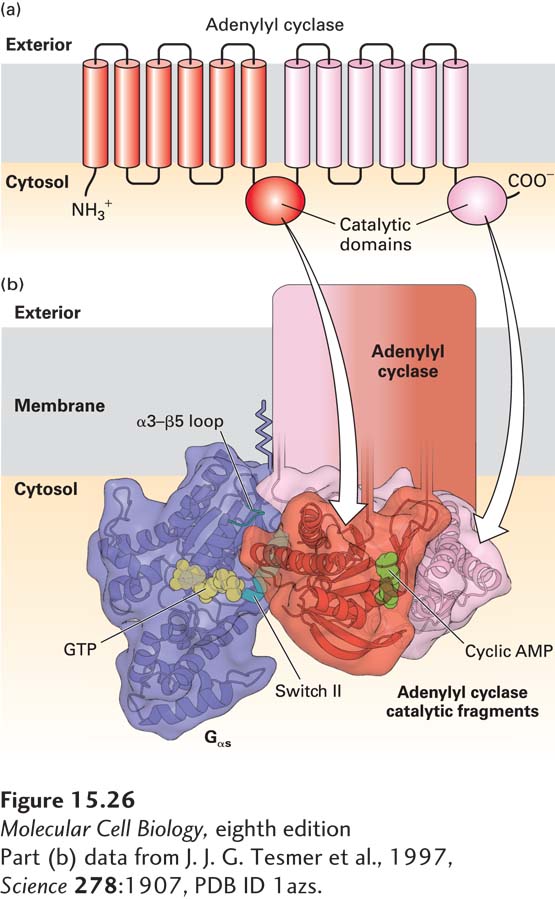
FIGURE 15- 26 Activation of the catalytic domain of mammalian adenylyl cyclase by binding to Gαs·GTP. (a) Schematic diagram of mammalian adenylyl cyclase. The membrane- bound enzyme contains two similar catalytic domains, which convert ATP to cAMP, on the cytosolic face of the membrane, and two integral membrane domains, each of which is thought to contain six transmembrane α helices. (b) Model of the three- dimensional structure of Gαs·GTP complexed with two fragments of catalytic domains that reconstituted in vitro one functional adenylyl cyclase catalytic domain, as determined by x- ray crystallography. A newly- formed cAMP is shown in green. The α3– β5 loop and the helix in the switch II region (blue) of Gαs·GTP interact simultaneously with a specific region of adenylyl cyclase. GTP (yellow) is bound to the GTP- binding domain, which is similar in structure to Ras (see Figure 15- 5 ). The two adenylyl cyclase fragments are shown in red and pink.
[Part (b) data from J. J. G. Tesmer et al., 1997, Science 278:1907, PDB ID 1azs.]
[Leave] [Close]