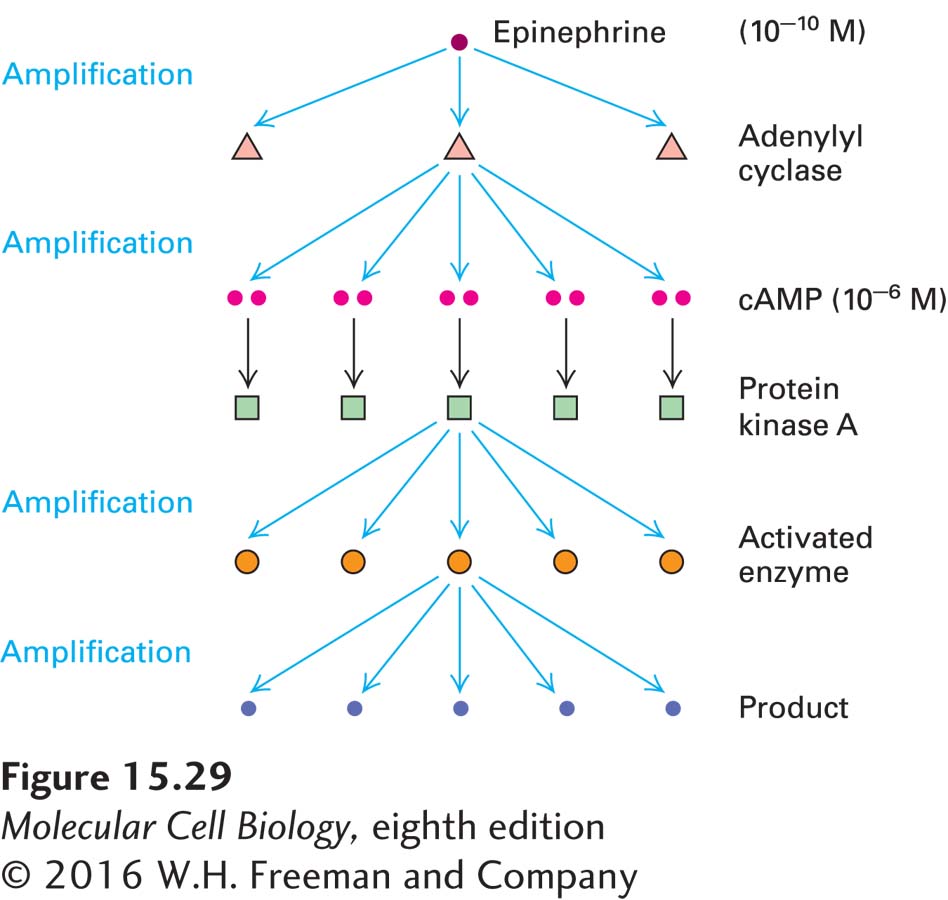
FIGURE 15- 29 Amplification of an extracellular signal by a signal transduction pathway involving cAMP and PKA. The specific example here is the pathway depicted in Figure 15- 7 . Binding of a single epinephrine molecule to one G protein– coupled receptor induces activation of several molecules of adenylyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of cyclic AMP, and each of these enzyme molecules synthesizes a large number of cAMP molecules, the first level of amplification. Two molecules of cAMP activate one PKA, but each activated PKA phosphorylates and activates multiple target proteins. This second level of amplification may involve several sequential reactions in which the product of one reaction activates the enzyme catalyzing the next reaction. The more steps in such a cascade, the greater the signal amplification possible.
[Leave] [Close]