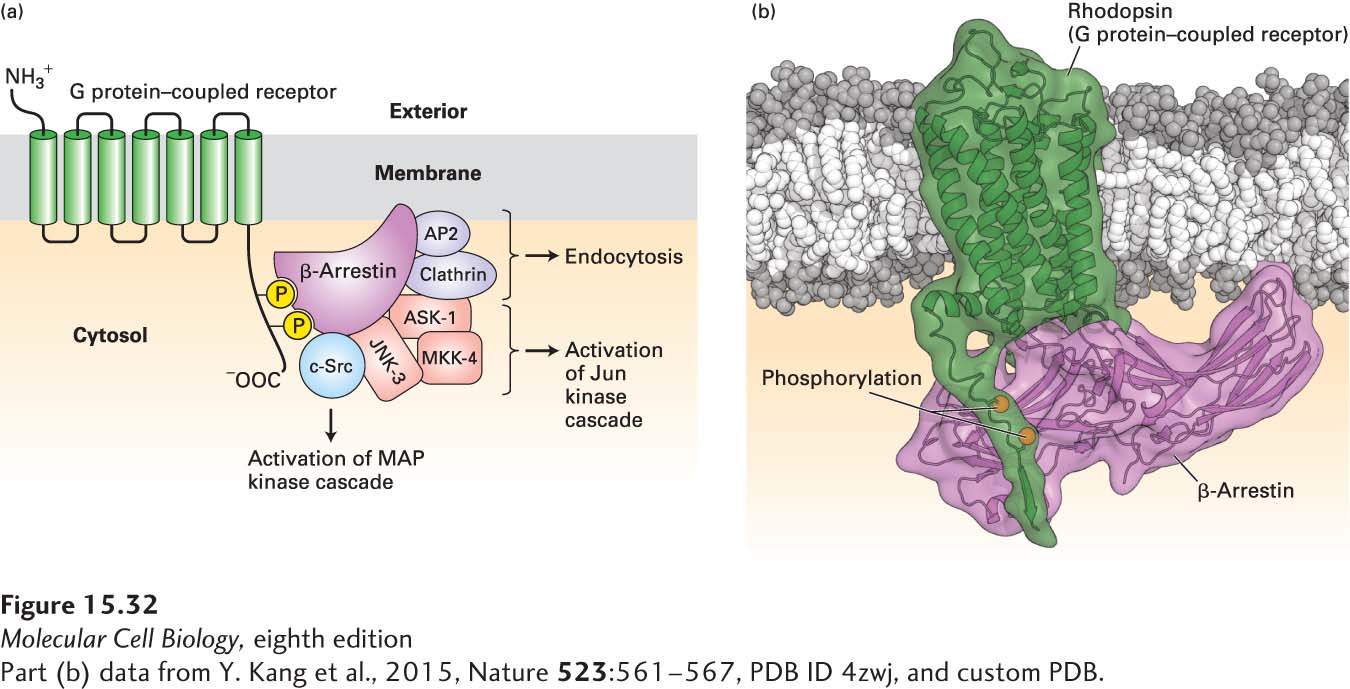
FIGURE 15- 32 Binding of β-arrestin to phosphorylated GPCRs triggers receptor desensitization and activation of several different signal transduction proteins. (a) β-Arrestin binds to specific phosphorylated serine and threonine residues in the C- terminal segment of G protein– coupled receptors (GPCRs). Clathrin and AP2, two other proteins bound by β-arrestin, promote endocytosis of the receptor (see Figure 14- 29 ). β-Arrestin also functions in transducing signals from activated receptors by binding to and activating several cytosolic protein kinases. Src activates the MAP kinase pathway, leading to phosphorylation of key transcription factors (see Chapter 16). Interaction of β-arrestin with three other proteins, including JNK- 3 (a Jun N- terminal kinase), results in phosphorylation and activation of another transcription factor, Jun. See W. Miller and R. J. Lefkowitz, 2001, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13:139, and K. Pierce et al., 2002, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:639. (b) Three- dimensional structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin. Arrestin binds to segments of the C- terminal cytosolic alpha helix of activated rhodopsin that includes the two phosphorylated resides as well as to parts of transmembrane helix 7.
[Part (b) data from Y. Kang et al., 2015, Nature 523:561- 567, PDB ID 4zwj, and custom PDB.]
[Leave] [Close]