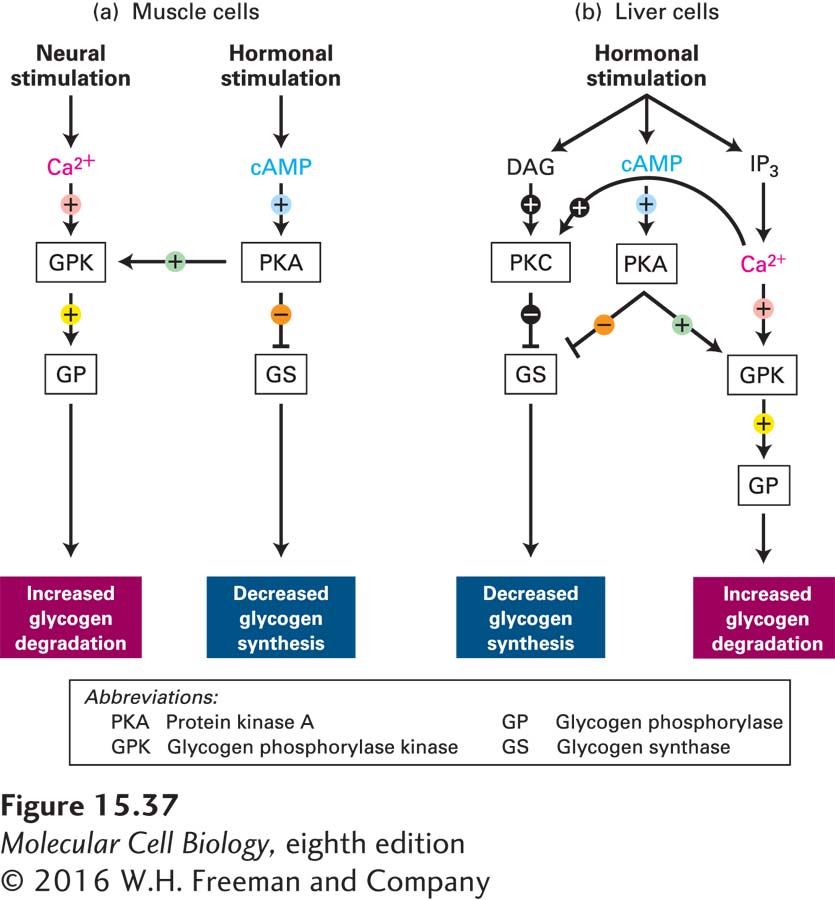
FIGURE 15- 37 Integrated regulation of glycogenolysis by Ca2+ and cAMP/PKA pathways. (a) Neuronal stimulation of striated muscle cells or epinephrine binding to β-adrenergic receptors on their surfaces leads to increased cytosolic concentrations of the second messengers Ca2+ or cAMP, respectively. The key regulatory enzyme glycogen phosphorylase kinase (GPK) is activated by binding Ca2+ ions and by phosphorylation by cAMP- dependent PKA. (b) In liver cells, hormonal stimulation of two β-adrenergic receptors leads to increased cytosolic concentrations of cAMP and two other second messengers, diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5- trisphosphate (IP3). Enzymes are marked by white boxes. (+) = activation of enzyme activity; (−) = inhibition.
[Leave] [Close]