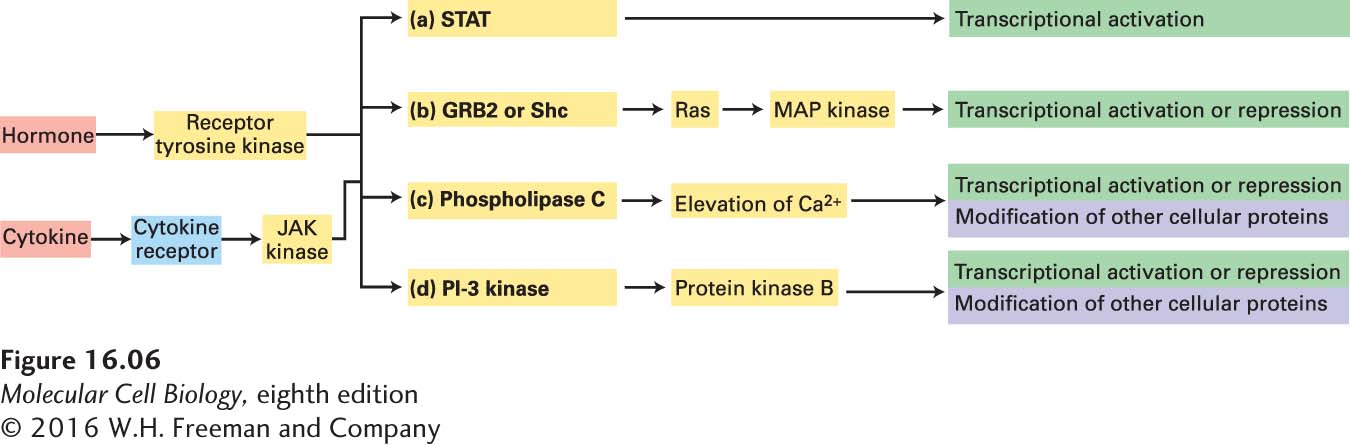
FIGURE 16- 6 Overview of signal transduction pathways triggered by receptors that activate protein tyrosine kinases. Both receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and cytokine receptors activate multiple signal transduction pathways that ultimately regulate transcription of genes. (a) In the most direct pathway, mainly employed by cytokine receptors, a STAT transcription factor binds to the activated receptor, becomes phosphorylated, moves to the nucleus, and directly activates transcription. (b) Binding of one type of adapter protein (GRB2 or Shc) to an activated receptor leads to activation of the Ras/MAP kinase pathway (see Section 16.4). (c, d) Two phosphoinositide pathways are triggered by recruitment of phospholipase Cγ and PI- 3 kinase to the membrane (see Section 16.4). Elevated levels of Ca2+ and activated protein kinase B modulate the activity of transcription factors as well as of cytosolic proteins that are involved in metabolic pathways or cell movement or shape.
[Leave] [Close]